Abstract
Summary
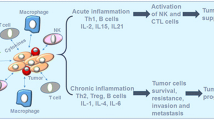
Interleukin-18 (IL-18, interferon [IFN]-gamma-inducing factor) is a proinflammatory cytokine converted to a biologically active molecule by interleukin (IL)-1beta converting enzyme (caspase-1). A wide range of normal and cancer cell types can produce and respond to IL-18 through a specific receptor (IL-18R) belonging to the toll-like receptor family. The activity of IL-18 is regulated by IL-18-binding protein (IL-18bp), a secreted protein possessing the ability to neutralize IL-18 and whose blood level is affected by renal function and is induced by IFNgamma. IL-18 plays a central role in inflammation and immune response, contributing to the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of infectious and inflammatory diseases. Because immune-stimulating effects of IL-18 have antineoplastic properties, IL-18 has been proposed as a novel adjuvant therapy against cancer. However, IL-18 increases in the blood of the majority of cancer patients and has been associated with disease progression and, in some cancer types, with metastatic recurrence risk and poor clinical outcome and survival. Under experimental conditions, cancer cells can also escape immune recognition, increase their adherence to the microvascular wall and even induce production of angiogenic and tumor growth-stimulating factors via IL-18-dependent mechanism. This is particularly visible in melanoma cells. Thus, the role of IL-18 in cancer progression and metastasis remains controversial. This review examines the clinical correlations and biological effects of IL-18 during cancer development and highlights recent experimental insights into prometastatic and proangiogenic effects of IL-18 and the use of IL-18bp against cancer progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dinarello, C. A. (1999). Interleukin-18. Methods, 19, 121–132.
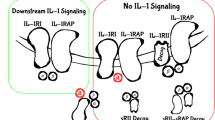
Sims J. E. (2002). IL-1 and IL-18 receptors, and their extended family. Current Opinion in Immunology, 14, 117–122.
Torigoe, K., Ushio, S., Okura, T., Kobayashi, S., Taniai, M., & Kunikata, T., et al. (1997). Purification and characterization of the human interleukin-18 receptor. Journal Of Biological Chemistry, 272, 25737–25742.
Born, T. L., Thomassen, E., Bird, T. A., & Sims, J. E. (1998). Cloning of a novel receptor subunit, AcPL, required for interleukin-18 signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 29445–29450.
Dinarello, C. A., Novick, D., Puren, A. J., Fantuzzi, G., Shapiro, L., & Mu¨hl, H., et al. (1998). Overview of interleukin-18: more than an interferon-gamma inducing factor. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 63, 658–666.
Takeuchi, M., Okura, T., Mori, T., Akita, K., Ohta, T., & Ikeda, M., et al. (1999). Intracellular production of interleukin-18 in human epithelial- like cell lines is enhanced by hyperosmotic stress in vitro. Cell & Tissue Research, 297, 467–473.
Puren, A. J., Fantuzzi, G., Gu, Y., Su, M. S., & Dinarello, C. A. (1998). Interleukin-18 (IFNgamma-inducing factor) induces IL-8 and IL-1beta via TNFalpha production from non-CD14+ human blood mononuclear cells. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 101, 711–719.
Nakanishi, K., Yoshimoto, T., Tsutsui, H., & Okamura, H. (2001). Interleukin-18 is a unique cytokine that stimulates both Th1 and Th2 responses depending on its cytokine milieu. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews, 12, 53–72.
Dinarello, C. A. (2000). Targeting interleukin 18 with interleukin 18 binding protein. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 59(Suppl. 1), i17.
Moller, B., Paulukat, J., Nold, M., Behrens, M., Kukoc-Zivojnov, N., & Kaltwasser, J. P., et al. (2003). Interferon-gamma induces expression of interleukin-18 binding protein in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford), 42, 442–445.
Neumayr, G., Ludwiczek, O., Hoertnagl, H., Pfister, R., Mitterbauer, G., & Moschen, A., et al. (2005). The impact of prolonged strenuous endurance exercise on interleukin 18 and interleukin 18 binding protein in recreational cyclists. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 26, 836–840.
Stuyt, R. J., Netea, M. G., van Krieken, J. H., van der Meer, J. W., & Kullberg, B. J. (2004). Recombinant interleukin-18 protects against disseminated Candida albicans infection in mice. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 189, 1524–1527.
Pizarro, T. T., Michie, M. H., Bentz, M., Woraratanadharm, J., Smith, M. F. Jr., & Foley, E., et al. (1999). IL-18, a novel immunoregulatory cytokine, is up-regulated in Crohn's disease: expression and localization in intestinal mucosal cells. Journal of Immunology, 162, 6829–6835.
Menge, T., Jander, S., & Stoll, G. (2001). Induction of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-18 by axonal injury. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 65, 332–339.
Marino, E., & Cardier, J. E. (2003). Differential effect of IL-18 on endothelial cell apoptosis mediated by TNF-alpha and Fas (CD95). Cytokine, 22, 142–148.
Kaser, A., Novick, D., Rubinstein, M., Siegmund, B., Enrich, B., & Koch, R. O., et al. (2002). Interferon-alpha induces interleukin-18 binding protein in chronic hepatitis C patients. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 129, 332–338.
Ludwiczek, O., Kaser, A., Novick, D., Dinarello, C. A., Rubinstein, M., & Vogel W, et al. (2002). Plasma levels of interleukin-18 and interleukin-18 binding protein are elevated in patients with chronic liver disease. Journal of Clinical Immunology, 22, 331–337.
Ueno, N., Kashiwamura, S., Ueda, H., Okamura, H., Tsuji, N. M., & Hosohara, K., et al. (2005). Role of interleukin 18 in nitric oxide production and pancreatic damage during acute pancreatitis. Shock, 24, 564–570.
Lissoni, P., Brivio, F., Rovelli, F., Fumagalli, G., Malugani, F., & Vaghi, M., et al. (2000). Serum concentrations of interleukin-18 in early and advanced cancer patients: enhanced secretion in metastatic disease. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents, 14, 275–277.
Tsuboi, K., Miyazaki, T., Nakajima, M., Fukai, Y., Masuda, N., & Manda, R., et al. (2004). Serum interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 levels as a tumor marker in patients with esophageal carcinoma. Cancer Letter, 205, 207–214.
Kawabata, T., Ichikura, T., Majima, T., Seki, S., Chochi, K., & Takayama, E., et al. (2001). Preoperative serum interleukin-18 level as a postoperative prognostic marker in patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer, 92, 2050–2055.
Majima, T., Ichikura, T., Seki, S., Takayama, E., Matsumoto, A., & Kawabata, T., et al. (2002). The influence of interleukin-10 and interleukin-18 on interferon-gamma production by peritoneal exudate cells in patients with gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Research, 22, 1193–1199.
Bellone, G., Smirne, C., Mauri, F. A., Tonel, E., Carbone, A., & Buffolino, A., et al. (2006). Cytokine expression profile in human pancreatic carcinoma cells and in surgical specimens: implications for survival. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 55, 684–698.
Carrascal, T., Mendoza, L., Valcarcel, M., Salado, C., Egilegor, E., & Tellerýa, N., et al. (2003). Interleukin-18 binding protein reduces B16 melanoma hepatic metastasis by neutralizing adhesiveness and growth factors of sinusoidal endothelium. Cancer Research, 63, 491–497.
Mendoza, L., Valcarcel, M., Carrascal, T., Egilegor, E., Salado, C., & Sim, B. K., et al. (2004). Inhibition of cytokine-induced microvascular arrest of tumor cells by recombinant endostatin prevents experimental hepatic melanoma metastasis. Cancer Research, 64, 304–310.
Pages, F., Berger, A., Henglein, B., Piqueras, B., Danel, C., & Zinzindohoue, F., et al. (1999). Modulation of interleukin-18 expression in human colon carcinoma: consequences for tumor immune surveillance. International Journal of Cancer, 84, 326–330.
Wen, Z., Ouyang, Q., Chen, D., & Su, X. (2003). Interleukin 18 expression in colon cancer and adenoma. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 34, 262–264.
Asakawa M., Kono H., Amemiya H., Matsuda M., Suzuki T., & Maki A., et al. (2006). Role of interleukin-18 and its receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis C virus infection. International Journal of Cancer, 118, 564–570.
Riedel, F., Adam, S., Feick, P., Haas, S., Gotte, K., & Hormann, K. (2004). Mannheim Alcohol Study Group. Expression of IL-18 in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 13, 267–272.
Cortesina, G. (2004). Constitutive expression of interleukin-18 in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Head Neck, 26, 494–503.
Park, H., Byun, D., Kim, T. S., Kim, Y. I., Kang, J. S., & Hahm, E. S., et al. (2001). Enhanced IL-18 expression in common skin tumors. Immunology Letters, 79, 215–219.
Jablonska, E., Puzewska, W., Grabowska, Z., Jablonski, J., & Talarek, L. (2005). VEGF, IL-18 and NO production by neutrophils and their serum levels in patients with oral cavity cancer. Cytokine, 30, 93–99.
Pratesi, C., Bortolin, M. T., Bidoli, E., Tedeschi, R., Vaccher, E., & Dolcetti, R., et al. (2006). Interleukin-10 and interleukin-18 promoter polymorphisms in an Italian cohort of patients with undifferentiated carcinoma of nasopharyngeal type. Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy, 55, 23–30.
Naumnik, W., Chyczewska, E., Kovalchuk, O., Talalaj, J., Izycki, T., & Panek, B. (2004). Serum levels of interleukin-18 (IL-18) and soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) in lung cancer. Roczniki Akademii Medycznej w Biaøymstoku, 49, 246–251.
Takahata, Y., Takada, H., Nomura, A., Ohshima, K., Nakayama, H., & Tsuda, T., et al. (2001). Interleukin-18 in human milk. Pediatric Research, 50, 268–272.
Merendino, R. A., Gangemi, S., Ruello, A., Bene, A., Losi, E., & Lonbardo, G., et al. (2001). Serum levels of interleukin-18 and sICAM-1 in patients affected by breast cancer: preliminary considerations. International Journal of Biological Markers, 16, 126–129.
Gunel, N., Coskun, U., Sancak, B., Gunel, U., Hasdemir, O., & Bozkurt, S. (2002). Clinical importance of serum interleukin-18 and nitric oxide activities in breast carcinoma patients. Cancer, 95, 663–667.
Nouh, M. A., Eissa, S. A., Zaki, S. A., El-Maghraby, S. M., & Kadry, D. Y. (2005). Importance of Serum IL-18 and RANTES as Markers for Breast Carcinoma Progression. Journal of Egyptian National Cancer Institute, 17, 51–55.
Gunel, N., Coskun, U., Sancak, B., Hasdemir, O., Sare, M., & Bayram, O., et al. (2003). Prognostic value of serum IL-18 and nitric oxide activity in breast cancer patients at operable stage. American Journal of Clinical Oncology, 26, 416–421.
Akahiro, J., Konno, R., Ito, K., Okamura, K., & Yaegashi, N. (2004). Impact of serum interleukin-18 level as a prognostic indicator in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma. International Journal of Clinical Oncology, 9, 42–46.
Bushley, A. W., Ferrell, R., McDuffie, K., Terada, K. Y., Carney, M. E., & Thompson P. J., et al. (2004). Polymorphisms of interleukin (IL)-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-18 and the risk of ovarian cancer. Gynecologic Oncology, 95, 672–679.
Wang, Z. Y., Gaggero. A., Rubartelli, A., Rosso, O., Miotti, S., & Mezzanzanica, D., et al. (2002). Expression of interleukin-18 in human ovarian carcinoma and normal ovarian epithelium: evidence for defective processing in tumor cells. International Journal of Cancer, 98, 873–878.
Le Page, C., Ouellet, V., Madore, J., Hudson, T. J., Tonin, P. N., & Provencher, D. M., et al. (2006). From gene profiling to diagnostic markers: IL-18 and FGF-2 complement CA125 as serum-based markers in epithelial ovarian cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 118, 1750–1758.
Thalmann, G. N., Sermier, A., Rentsch, C., Mohrle, K., Cecchini, M. G., & Studer, U. E. (2000). Urinary Interleukin-8 and 18 predict the response of superficial bladder cancer to intravesical therapy with bacillus Calmette–Guerin. Journal of Urology, 164, 2129–2133.
Bukan, N., Sozen, S., Coskun, U., Sancak, B., Gunel, N., & Bozkirli, I., et al. (2003). Serum interleukin-18 and nitric oxide activity in bladder carcinoma. European Cytokine Network, 14, 163–167.
Eto, M., Koga, H., Noma, H., Yamaguchi, A., Yoshikai, Y., & Naito, S. (2005). Importance of urinary interleukin-18 in intravesical immunotherapy with bacillus Calmette–Guerin for superficial bladder tumors. Urologia Internationalis, 75, 114–118.
Luo, Y., Yamada, H., Chen, X., Ryan, A. A., Evanoff, D. P., & Triccas, J. A., et al. (2004). Recombinant Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette–Guerin (BCG) expressing mouse IL-18 augments Th1 immunity and macrophage cytotoxicity. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 137, 24–34.
Sozen, S., Coskun, U., Sancak, B., Bukan, N., Gunel, N., & Tunc, L., et al. (2004). Serum levels of interleukin-18 and nitrite+nitrate in renal cell carcinoma patients with different tumor stage and grade. Neoplasma, 51, 25–29.
Lebel-Binay, S., Thiounn, N., De Pinieux, G., Vieillefond, A., Debre, B., & Bonnefoy, J. Y. et al. (2003). IL-18 is produced by prostate cancer cells and secreted in response to interferons. International Journal of Cancer, 106, 827–835.
Zhang, B., Wang, Y., Zheng, G. G., Ma, X. T., Li, G., & Zhang, F. K., et al. (2002). Clinical significance of IL-18 gene over-expression in AML. Leukemia Research, 26, 887–892.
Zhang, B., Wu, K. F., Cao, Z. Y., Rao, Q., Ma, X. T., & Zheng, G. G., et al. (2004). IL-18 increases invasiveness of HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells: up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9) expression. Leukemia Research, 28, 91–95.
Alexandrakis, M. G., Passam, F. H., Sfiridaki, K., Moschandrea, J., Pappa, C., & Liapi, D., et al. (2004). Interleukin-18 in multiple myeloma patients: serum levels in relation to response to treatment and survival. Leukemia Research, 28, 259–266.
Airoldi, I., Raffaghello, L., Cocco, C., Guglielmino, R., Roncella, S., & Fedeli, F., et al. (2004). Heterogeneous expression of interleukin-18 and its receptor in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders deriving from naive, germinal center, and memory B lymphocytes. Clinical Cancer Research, 10(1 Pt 1), 144–154.
Mazodier, K., Marin, V., Novick, D., Farnarier, C., Robitail, S., & Schleinitz, N., et al. (2005). Severe imbalance of IL-18/IL-18bp in patients with secondary hemophagocytic syndrome. Blood, 106, 3483–3489.
Kobashi, K., Iwagaki, H., Yoshino, T., Morimoto, Y., Kohka, H., & Kodama, M., et al. (2001). Down-regulation of IL-18 receptor in cancer patients: its clinical significance. Anticancer Research, 21, 3285–3293.
Smith, V. P., Bryant, N. A., & Alcami, A. (2000). Ectromelia, vaccinia and cowpox viruses encode secreted interleukin-18-binding proteins. Journal of General Virology, 81, 1223–1231.
Xiang, Y., Moss, B. (1999). IL-18 binding and inhibition of interferon induction by human poxvirus-encoded proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96, 11537.
Lee, S. J., Cho, Y. S., Cho, M. C., Shim, J. H., Lee, K. A., & Ko, K. K., et al. (2001). Both E6 and E7 oncoproteins of human papillomavirus 16 inhibit IL-18-induced IFN-gamma production in human peripheral blood mononuclear and NK cells. Journal of Immunology, 167, 497–504.
Lee, K. A., Cho, K. J., Kim, S. H., Shim, J. H., Lim, J. S., & Cho, D. H., et al. (2005). IL-18 E42A mutant is resistant to the inhibitory effects of HPV-16 E6 and E7 oncogenes on the IL-18-mediated immune response. Cancer Letter, 229, 261–270.
Jonak, Z. L., Trulli, S., Maier, C., McCabe, F. L., Kirkpatrick, R., & Johanson, K., et al. (2002). High-dose recombinant interleukin-18 induces an effective Th1 immune response to murine MOPC-315 plasmacytoma. Journal of Immunotherapy, 25(Suppl 1), S20–S27.
Yamashita, K., Iwasaki, T., Tsujimura, T., Sugihara, A., Yamada, N., & Ueda, H., et al. (2002). Interleukin-18 inhibits lodging and subsequent growth of human multiple myeloma cells in the bone marrow. Oncology Reports, 9, 1237–1244.
Okamoto, T., Yamada, N., Tsujimura, T., Sugihara, A., Nishizawa, Y., & Ueda, H., et al. (2004). Inhibition by interleukin-18 of the growth of Dunn osteosarcoma cells. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research, 24, 161–167.
Arai, N., Akamatsu, S., Arai, S., Toshimori, Y., Hanaya, T., & Tanimoto, T., et al. (2000). Interleukin-18 in combination with IL-2 enhances natural killer cell activity without inducing large amounts of IFN-gamma in vivo. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research, 20, 217–224.
Son, Y. I., Dallal, R. M., & Lotze, M. T. (2003). Combined treatment with interleukin-18 and low-dose interleukin-2 induced regression of a murine sarcoma and memory response. Journal of Immunotherapy, 26, 234–240.
Redlinger, R. E. Jr, Mailliard, R. B., Lotze, M. T., & Barksdale, E. M. Jr (2003). Synergistic interleukin-18 and low-dose interleukin-2 promote regression of established murine neuroblastoma in vivo. Journal of Pediatric Surgery, 38, 301–307.
Osaki, T., Peron, J. M., Cai, Q., Okamura, H., Robbins, P. D., & Kurimoto, M., et al. (1998). IFNgamma-inducing factor/IL-18 administration mediates IFNgamma-and IL-12-independent antitumor effects. Journal of Immunology, 160, 1742–1749.
Yao, N. S., Chen, Y. M., Perng, R. P., & Whang-Peng, J. (2002). Additive effect of Interleukin-12 and Interleukin-18 on the T-helper cell pathway of malignant pleural effusion. Lung, 180, 15–24.
Li, Q., Carr, A. L., Donald, E. J., Skitzki, J. J., Okuyama, R., & Stoolman L. M., et al. (2005). Synergistic effects of IL-12 and IL-18 in skewing tumor-reactive T-cell responses towards a type 1 pattern. Cancer Research, 65, 1063–1070.
Osaki, T., Hashimoto, W., Gambotto, A., Okamura, H., Robbins, P. D., & Kurimoto, M., et al. (1999). Potent antitumor effects mediated by local expression of the mature form of the interferon-gamma inducing factor, interleukin-18 (IL-18). Gene Theraphy, 6, 808–815.
Tatsumi, T., Gambotto, A., Robbins, P. D., & Storkus, W. J. (2002). Interleukin 18 gene transfer expands the repertoire of antitumor Th1-type immunity elicited by dendritic cell-based vaccines in association with enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Cancer Research, 62, 5853–5858.
Ju, D. W., Tao, Q., Lou, G., Bai, M., He, L., & Yang, Y., et al. (2001). Interleukin 18 transfection enhances antitumor immunity induced by dendritic cell–tumor cell conjugates. Cancer Research, 61, 3735–3740.
Tatsumi, T., Huang, J., Gooding, W. E., Gambotto, A., Robbinsm, P. D., & Vujanovic, N. L., et al. (2003). Intratumoral delivery of dendritic cells engineered to secrete both interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18 effectively treats local and distant disease in association with broadly reactive Tc1-type immunity. Cancer Research, 63, 6378–6386.
Hegardt, P., Widegren, B., Li, L., Sjogren, B., Kjellman, C., & Sur, I., et al. (2001). Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor and IL-18 enhance the anti-tumor immune response of rats carrying an intrahepatic colon carcinoma. Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy, 50, 491–501.
Iigo, M., Shimamura, M., Matsuda, E., Fujita, K., Nomoto, H., & Satoh, J., et al. (2004). Orally administered bovine lactoferrin induces caspase-1 and interleukin-18 in the mouse intestinal mucosa: a possible explanation for inhibition of carcinogenesis and metastasis. Cytokine, 25, 36–44.
Merendino, R. A., Ruello, A., Cascinu, S., Ferlazzo, B., Bene, A., & Bonanno, D., et al. (2002). Influence of 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid on interleukin-18 production in colorectal cancer patients. International Journal of Biological Markers, 17, 63–66.
Carbone, A., Rodeck, U., Mauri, F. A., Sozzi, M., Gaspari, F., & Smirne, C., et al. (2005). Human pancreatic carcinoma cells secrete bioactive interleukin-18 after treatment with 5-fluorouracil: implications for anti-tumor immune response. Cancer Biol Ther, 4, 31–241.
Coughlin, C. M., Salhany, K. E., Wysocka, M., Aruga, E., Kurzawa, H., & Chang A. E., et al. (1998). Interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 synergistically induce murine tumor regression which involves inhibition of angiogenesis. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 101, 1441–1452.
Cao, R., Farnebo, J., Kurimoto, M., & Cao, Y. (1999). Interleukin-18 acts as an angiogenesis and tumor suppressor. FASEB Journal, 13, 2195–2202.
Shimamura, M., Yamamoto, Y., Ashino, H., Oikawa, T., Hazato, T., & Tsuda, H., et al. (2004). Bovine lactoferrin inhibits tumor-induced angiogenesis. International Journal of Cancer, 111, 111–116.
Nakata, A., Tsujimura, T., Sugihara, A., Okamura, H., Iwasaki, T., & Shinkai, K., et al. (1999). Inhibition by interleukin 18 of osteolytic bone metastasis by human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Research 19, 4131–4138.
Iwasaki, T., Yamashita, K., Tsujimura, T., Kashiwamura, S., Tsutsui, H., & Kaisho, T., et al. (2002). Interleukin-18 inhibits osteolytic bone metastasis by human lung cancer cells possibly through suppression of osteoclastic bone-resorption in nude mice. Journal of Immunotherapy, 25 Suppl 1, S52–S60.
Nakamura, Y., Yamada, N., Ohyama, H., Nakasho, K., Nishizawa, Y., & Okamoto, T., et al. (2006). Effect of interleukin-18 on metastasis of mouse osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Immunology and immunotherapy, 12, 1–8, Jan.
Golab, J., & Stoklosa, T. (2005). Technology evaluation: SB-485232, GlaxoSmithKline. Current Opinion in Molecular Therapeutics, 7, 85–93.
Vidal-Vanaclocha, F., Amezaga, C., Asumendi, A., Kaplanski, G., & Dinarello, C. A. (1994). Interleukin-1 receptor blockade reduces the number and size of murine B16 melanoma hepatic metastases. Cancer Research, 54, 2667–2672.
Vidal-Vanaclocha, F., Fantuzzi, G., Mendoza, L., Fuentes, A. M., Anasagasti, M. J., & Martin, J., et al. (2000). IL-18 regulates IL-1beta-dependent hepatic melanoma metastasis via vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 734–739.
Mendoza, L., Carrascal, T., De Luca, M., Fuentes, A. M., Salado, C., & Blanco, J., et al. (2001). Hydrogen peroxide mediates vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression from interleukin-18-activated hepatic sinusoidal endothelium: implications for circulating cancer cell arrest in the murine liver. Hepatology, 34, 298–310.
Jiang, D., Ying, W., Lu, Y., Wan, J., Zhai, Y., & Liu, W. et al. (2003). Identification of metastasis-associated proteins by proteomic analysis and functional exploration of interleukin-18 in metastasis. Proteomics, 3, 724–737.
Cho, D., Song, H., Kim, Y. M., Houh, D., Hur, D. Y., & Park, H., et al. (2000). Endogenous interleukin-18 modulates immune escape of murine melanoma cells by regulating the expression of Fas ligand and reactive oxygen intermediates. Cancer Research, 60, 2703–2709.
Cho, D., Seung Kang, J., Hoon Park, J., Kim, Y. I., Hahm, E., & Lee, J., et al. (2002). The enhanced IL-18 production by UVB irradiation requires ROI and AP-1 signaling in human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 298, 289–295.
Hue, J., Kim, A., Song, H., Choi, I., Park, H., & Kim, T., et al. (2005). IL-18 enhances SCF production of melanoma cells by regulating ROI and p38 MAPK activity. Immunology Letters, 96, 211–217.
Telleria, N., Carrascal, T., Beaskoetxea, J., Salado, C., Egilegor, E., & Mendoza, L., et al. (2006). Interleukin-18 upregulates very late antigen-4 expression from melanoma cell variants of low intracellular glutathione content, via oxidative stress-induced autocrine tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cancer Research.
Majima, T., Ichikura, T., Chochi, K., Kawabata, T., Tsujimoto, H., & Sugasawa H., et al. (2006). Exploitation of interleukin-18 by gastric cancers for their growth and evasion of host immunity. International Journal of Cancer, 118, 388–395.
Park, C. C., Morel, J. C., Amin, M. A., Connors, M. A., Harlow, L. A., & Koch, A. E. (2001). Evidence of IL-18 as a novel angiogenic mediator. Journal of Immunology, 167, 1644–1653.
Gerdes, N., Sukhova, G. K., Libby, P., Reynolds, R. S., Young, J. L., & Schonbeck, U. (2002). Expression of interleukin (IL)-18 and functional IL-18 receptor on human vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and macrophages: implications for atherogenesis. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 195, 245–257.
Qiao, H., Sonoda, K. H., Sassa, Y., Hisatomi, T., Yoshikawa, H., & Ikeda, Y., et al. (2004). Abnormal retinal vascular development in IL-18 knockout mice. Laboratory Investigation, 84, 973–980.
Cho, M. L., Jung, Y. O., Moon, Y. M., Min, S. Y., Yoon, C. H., & Lee, S. H., et al. (2006). Interleukin-18 induces the production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via AP-1-dependent pathways. Immunology Letters, 103, 159–166.
Mendoza, L., Gutierrez, V., Carrascal, T., Valcárcel, M., Dinarello, C. A., & Vidal-Vanaclocha, F. (2006). Interleukin-18 mediates proangiogenic action of vascular endothelial growth factor on myofibroblast and endothelial cell recruitment into hepatic melanoma metastasis. Hepatology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vidal-Vanaclocha, F., Mendoza, L., Telleria, N. et al. Clinical and experimental approaches to the pathophysiology of interleukin-18 in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25, 417–434 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-006-9013-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-006-9013-3