Abstract
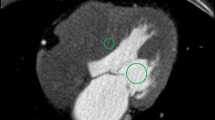
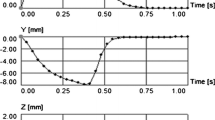
The aim of this study was to compare the radiation dose and image quality of different adenosine-stress dynamic myocardial perfusion CT protocols using a 128-slice dual-source computed tomography (DSCT) scanner. We included 330 consecutive patients with suspected coronary artery disease. Protocols employed the following dynamic scan parameters: protocol I, a 30-s scan with a fixed tube current (FTC, n = 172); protocol II, a 30-s scan using an automatic tube current modulation (ATCM) technique (n = 108); protocol III, a 14-s scan using an ATCM (n = 50). To determine the scan interval for protocol III, we analyzed time-attenuation curves of 26 patients with myocardial perfusion who had been scanned using protocol I or II. The maximum attenuation difference between normal and abnormal myocardium occurred at 18.0 s to 30.3 s after initiation of contrast injection. Myocardial perfusion images of FTC and ATCM were of diagnostic image quality based on visual analysis. The mean radiation dose associated with protocols I, II, and III was 12.1 ± 1.6 mSv, 7.7 ± 2.5 mSv, and 3.8 ± 1.3 mSv, respectively (p < 0.01). Use of a dose-modulation technique and a 14-s scan duration for adenosine-stress CT enables significant dose reduction while maintaining diagnostic image quality.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSCT:
-
Dual-source computed tomography
- FTC:
-
Fixed tube current
- ATCM:
-
Automatic tube current modulation
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- MDCT:
-
Multidetector computed tomography
- CCTA:
-
Coronary CT angiography
- MBF:
-
Myocardial blood flow
References
Kurata A, Mochizuki T, Koyama Y et al (2005) Myocardial perfusion imaging using adenosine triphosphate stress multi-slice spiral computed tomography: alternative to stress myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Circ J 69(5):550–557
George RT, Silva C, Cordeiro MA et al (2006) Multidetector computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging during adenosine stress. J Am Coll Cardiol 48(1):153–160
Rocha-Filho JA, Blankstein R, Shturman LD et al (2010) Incremental value of adenosine-indeced stress myocardial perfusion imaging with dual-source CT at cardiac CT angiography. Radiology 254(2):410–419
Blankstein R, Shturman LD, Rogers IS et al (2009) Adenosine-induced stress myocardial perfusion imaging using dual-source cardiac computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 54(12):1072–1084
Bastarrika G, Ramos-Duran L, Rosenblum MA et al (2010) Adenosine-stress dynamic myocardial CT perfusion imaging: initial clinical experience. Invest Radiol 45(6):306–313
Bamberg F, Becker A, Schwarz F et al (2011) Detection of hemodynamically significant coronary artery stenosis: incremental diagnostic value of dynamic CT-based myocardial perfusion imaging. Radiology 260(3):689–698
Ho KT, Chua KC, Klotz E, Panknin C (2010) Stress and rest dynamic myocardial perfusion imaging by evaluation of complete time-attenuation curves with dual-source CT. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 3(8):811–820
Bruder H, Raupach R, Klotz E, Stierstorfer K, Flohr T (2009) Spatio-temporal filtration of dynamic CT data using diffusion filters. In: Samei E, Hsieh J (eds) Medical imaging 2009: physics of medical imaging, proceedings of the SPIE. Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, pp 725810–725857
Einstein AJ, Moser KW, Thompson RC et al (2007) Radiation dose to patients from cardiac diagnostic imaging. Circulation 116(11):1290–1305
Kalra MK, Maher MM, Toth TL et al (2004) Techniques and applications of automatic tube current modulation for CT. Radiology 233(3):649–657
Rizzo S, Kalra M, Schmidt B et al (2006) Comparison of angular and combined automatic tube current modulation techniques with constant tube current CT of the abdomen and pelvis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(3):673–679
Graser A, Wintersperger BJ, Suess C et al (2006) Dose reduction and image quality in MDCT colonography using tube current modulation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187(3):695–701
Smith AB, Dillon WP, Lau BC et al (2008) Radiation dose reduction strategy for CT protocols: successful implementation in neuroradiology section. Radiology 247(2):499–506
Kalra MK, Rizzo S, Maher MM et al (2005) Chest CT performed with z-axis modulation: scanning protocol and radiation dose. Radiology 237(1):303–308
Goo HW, Suh DS (2006) Tube current reduction in pediatric non-ECG-gated heart CT by combined tube current modulation. Pediatr Radiol 36(8):344–351
Herzog C, Mulvihill DM, Nquyen SA et al (2008) Pediatric cardiovascular CT angiography: radiation dose reduction using automatic anatomic tube current modulation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190(5):1232–1240
Nakauchi Y, Iwanaga Y, Ikuta S et al (2012) Quantitative myocardial perfusion analysis using multi-row detector CT in acute myocardial infarction. Heart 98(7):566–572
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.M., Kim, Y.N. & Choe, Y.H. Adenosine-stress dynamic myocardial perfusion imaging using 128-slice dual-source CT: optimization of the CT protocol to reduce the radiation dose. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29, 875–884 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-012-0138-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-012-0138-x