Abstract
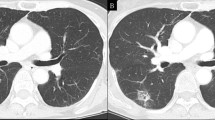
Pulmonary artery compression in adults resulting from tumors is an uncommon condition often associated with poor prognosis. Among the imaging modalities used for diagnosis, the role of trans thoracic echocardiography in identifying secondary pulmonic stenosis due to extrinsic or intrinsic compression and more importantly the physiologic significance has been increasingly recognized. We describe here a case of isolated left pulmonary artery stenosis which was initially suspected based on classic echocardiographic features of obstruction of pulmonary artery and subsequently confirmed by CT imaging. This case illustrates the versatility of trans thoracic echocardiography in diagnosing incidental abnormalities with potential significant consequences.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dumont P, Diot P, Aupart MR et al (1998) Leiomyosarcoma of the pulmonary artery. Ann Thorac Surg 66:2089–2091
Rafal RB, Nichols JN, Markisz JA (1995) Pulmonary artery sarcoma: diagnosis and postoperative follow-up with gadolinium-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Mayo Clin Proc 70:173–176
Meckel S, Buitrago-Tellez C, Herrmann R et al (2003) Stenting for pulmonary artery stenosis due to a recurrent primary leiomyosarcoma. J Endovasc Ther 10:141–146
Takeda S, Miyoshi S, Omori K et al (1999) Surgical rescue for life-threatening hypoxemia caused by a mediastinal tumor. Ann Thorac Surg 68:2324–2326
Valsangiacomo Buchel ER, DiBernardo S, Bauersfeld U et al (2005) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography of the great arteries in patients with congenital heart disease: an accurate tool for planning catheter-guided interventions. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 21:313–322
Katz ES, Shah A, Rosenzweig BP et al (2003) Bilateral pulmonary artery compression and obstruction by tumor: diagnosis by unusual Doppler flow patterns. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 16:185–187
Tunick PA, Slater W, Kronzon I (1989) The hemodynamics of left ventricular pseudoaneurysm: color Doppler echocardiographic study. Am Heart J 117:1161–1165
Kronzon I (1997) Diagnosis and treatment of iatrogenic femoral artery pseudoaneurysm: a review. J Am Soc Echocardiog 10:236–245
Katz ES, Tsiamtsiouris T, Applebaum RM et al (2000) Surgical left atrial appendage ligation is frequently incomplete: a transesophageal echocardiograhic study. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:468–471
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaffery, Z., Ananthasubramaniam, K. Isolated left pulmonary artery stenosis due to extrinsic compression by intra thoracic tumor: recognition of unusual Doppler flow pattern and correlation with computed tomography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 23, 507–510 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-006-9167-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-006-9167-7