Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to investigate the association between the content of marine n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in adipose tissue, a biomarker for the long-term intake of seafood, and the subsequent development of breast cancer (BC).
Design
We designed a case–cohort study based on a cohort of healthy Danish women, who in the 1990s donated adipose tissue biopsies to a biobank in order to investigate the role of diet for the development of cancer and chronic disease. During follow-up, incident cases of BC were identified through national registries, and the content of n-3 PUFA in adipose tissue was compared between cases and the cohort sample.
Results
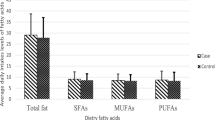
During follow-up, 463 new cases of BC were identified. After adjusting for potential confounders, no significant association between the content of marine n-3 PUFA and BC was found. When comparing the highest with the lowest quintile, the hazard ratio (HR) was 0.96 (95% CI 0.64–1.43) for total marine n-3 PUFA, 0.84 (95% CI 0.58–1.23) for eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and 1.08 (95% CI 0.73–1.58) for docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Conclusion
This study does not indicate any association between the content of total or individual marine n-3 PUFA in adipose tissue and development of BC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research (2007) Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective. AICR, Washington, DC
Boyd NF, Stone J, Vogt KN, Connelly BS, Martin LJ, Minkin S (2003) Dietary fat and breast cancer risk revisited: a meta-analysis of the published literature. Br J Cancer 89:1672–1685
Bakker N, van’t VP, Zock PL (1997) Adipose fatty acids and cancers of the breast, prostate and colon: an ecological study. EURAMIC Study Group. Int J Cancer 72:587–591
Curado MP, Edwards B, Shin HR, Storm H, Ferlay J, Heanue M (2007) Cancer incidence in five continents. IARC scientific publications no. 160, IARC, Lyon
Deapen D, Liu L, Perkins C, Bernstein L, Ross RK (2002) Rapidly rising breast cancer incidence rates among Asian-American women. Int J Cancer 99:747–750
Ziegler RG, Hoover RN, Pike MC et al (1993) Migration patterns and breast cancer risk in Asian-American women. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:1819–1827
Calder PC (2004) n-3 Fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: evidence explained and mechanisms explored. Clin Sci (Lond) 107:1–11
Cave WT Jr (1997) Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in rodent models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 46:239–246
Chen J, Power KA, Mann J, Cheng A, Thompson LU (2007) Flaxseed alone or in combination with tamoxifen inhibits MCF-7 breast tumor growth in ovariectomized athymic mice with high circulating levels of estrogen. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 232:1071–1080
Hardman WE (2007) Dietary canola oil suppressed growth of implanted MDA-MB 231 human breast tumors in nude mice. Nutr Cancer 57:177–183
Karmali RA, Adams L, Trout JR (1993) Plant and marine n-3 fatty acids inhibit experimental metastasis of rat mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 48:309–314
Rose DP, Connolly JM (1999) Antiangiogenicity of docosahexaenoic acid and its role in the suppression of breast cancer cell growth in nude mice. Int J Oncol 15:1011–1015
Rose DP, Connolly JM (2000) Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by dietary fatty acids and eicosanoids. Nutr Cancer 37:119–127
Sauer LA, Blask DE, Dauchy RT (2007) Dietary factors and growth and metabolism in experimental tumors. J Nutr Biochem 18:637–649
Schley PD, Jijon HB, Robinson LE, Field CJ (2005) Mechanisms of omega-3 fatty acid-induced growth inhibition in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 92:187–195
Stillwell W, Shaikh SR, Zerouga M, Siddiqui R, Wassall SR (2005) Docosahexaenoic acid affects cell signaling by altering lipid rafts. Reprod Nutr Dev 45:559–579
MacLean CH, Newberry SJ, Mojica WA et al (2006) Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on cancer risk: a systematic review. JAMA 295:403–415
Terry PD, Rohan TE, Wolk A (2003) Intakes of fish and marine fatty acids and the risks of cancers of the breast and prostate and of other hormone-related cancers: a review of the epidemiologic evidence. Am J Clin Nutr 77:532–543
Thiebaut AC, Kipnis V, Schatzkin A, Freedman LS (2008) The role of dietary measurement error in investigating the hypothesized link between dietary fat intake and breast cancer–a story with twists and turns. Cancer Invest 26:68–73
Astorg P, Bertrais S, Laporte F et al (2008) Plasma n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids as biomarkers of their dietary intakes: a cross-sectional study within a cohort of middle-aged French men and women. Eur J Clin Nutr 62:1155–1161
Cao J, Schwichtenberg KA, Hanson NQ, Tsai MY (2006) Incorporation and clearance of omega-3 fatty acids in erythrocyte membranes and plasma phospholipids. Clin Chem 52:2265–2272
Katan MB, Deslypere JP, van Birgelen AP, Penders M, Zegwaard M (1997) Kinetics of the incorporation of dietary fatty acids into serum cholesteryl esters, erythrocyte membranes, and adipose tissue: an 18-month controlled study. J Lipid Res 38:2012–2022
Tjonneland A, Overvad K, Thorling E, Ewertz M (1993) Adipose tissue fatty acids as biomarkers of dietary exposure in Danish men and women. Am J Clin Nutr 57:629–633
Tjonneland A, Olsen A, Boll K et al (2007) Study design, exposure variables, and socioeconomic determinants of participation in Diet, Cancer and Health: a population-based prospective cohort study of 57, 053 men and women in Denmark. Scand J Public Health 35:432–441
Raaschou-Nielsen O, Pavuk M, Leblanc A et al (2005) Adipose organochlorine concentrations and risk of breast cancer among postmenopausal Danish women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:67–74
Beynen AC, Katan MB (1985) Rapid sampling and long-term storage of subcutaneous adipose-tissue biopsies for determination of fatty acid composition. Am J Clin Nutr 42:317–322
IUPAC Method 2.301 (1987) IUPAC standard methods of oils, fats, and derivatives, report of IUPAC working group WG 2/87, 7th edn. Blackwell Scientific Publications
Kalbfleisch JD, Lawless JF (1988) Likelihood analysis of multi-state models for disease incidence and mortality. Stat Med 7:149–160
Jude S, Roger S, Martel E et al (2006) Dietary long-chain omega-3 fatty acids of marine origin: a comparison of their protective effects on coronary heart disease and breast cancers. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 90:299–325
Larsson SC, Kumlin M, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Wolk A (2004) Dietary long-chain n-3 fatty acids for the prevention of cancer: a review of potential mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr 79:935–945
Noguchi M, Rose DP, Miyazaki I (1996) Breast cancer chemoprevention: clinical trials and research. Oncology 53:175–181
Stripp C, Overvad K, Christensen J et al (2003) Fish intake is positively associated with breast cancer incidence rate. J Nutr 133:3664–3669
Saadatian-Elahi M, Norat T, Goudable J, Riboli E (2004) Biomarkers of dietary fatty acid intake and the risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer 111:584–591
Kuriki K, Hirose K, Wakai K et al (2007) Breast cancer risk and erythrocyte compositions of n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids in Japanese. Int J Cancer 121:377–385
Shannon J, King IB, Moshofsky R et al (2007) Erythrocyte fatty acids and breast cancer risk: a case–control study in Shanghai, China. Am J Clin Nutr 85:1090–1097
Bagga D, Capone S, Wang HJ et al (1997) Dietary modulation of omega-3/omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid ratios in patients with breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 89:1123–1131
Lof M, Sandin S, Lagiou P et al (2007) Dietary fat and breast cancer risk in the Swedish women’s lifestyle and health cohort. Br J Cancer 97:1570–1576
Trichopoulos D, Adami HO, Ekbom A, Hsieh CC, Lagiou P (2008) Early life events and conditions and breast cancer risk: from epidemiology to etiology. Int J Cancer 122:481–485
Bougnoux P, Giraudeau B, Couet C (2006) Diet, cancer, and the lipidome. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15:416–421
Althuis MD, Fergenbaum JH, Garcia-Closas M, Brinton LA, Madigan MP, Sherman ME (2004) Etiology of hormone receptor-defined breast cancer: a systematic review of the literature. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:1558–1568
Hedelin M, Chang ET, Wiklund F et al (2007) Association of frequent consumption of fatty fish with prostate cancer risk is modified by COX-2 polymorphism. Int J Cancer 120:398–405
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from The Danish Cancer Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Witt, P.M., Christensen, J.H., Schmidt, E.B. et al. Marine n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in adipose tissue and breast cancer risk: a case–cohort study from Denmark. Cancer Causes Control 20, 1715–1721 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-009-9423-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-009-9423-y