Abstract
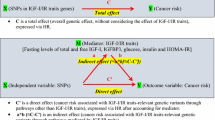
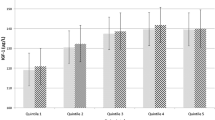
Circulating concentrations of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 are associated with risk of pre-menopausal breast cancer. Racial differences in levels of these factors have been reported, and determinants of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 levels within racial and ethnic groups are unclear. In this study we examine genetic, anthropometric, diet, and lifestyle factors that may predict serum levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 among Hispanic and non-Hispanic white women. A sample of healthy controls participating in the SHINE (Southwest Hormone, Insulin, Nutrition, and Exercise Study) case-control breast cancer in Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah were included in these analyses. Subjects included 210 Hispanic and 284 non-Hispanic white women. Hispanic women had significantly lower levels of IGFBP-3 (mean=3764.3 mcg/ml) after adjusting for age, body size, physical activity, menopausal status, and dietary factors than non-Hispanic white women (mean = 4058.0 mcg/ml; p<0.01). The CC genotype of the −202 A>C polymorphism of the IGFBP3 gene was associated with lower IGFBP-3 levels in both ethnic groups. The frequency of the IGFBP3 C allele differed between Hispanic (0.65) and non-Hispanic white women (0.53), but serum levels of IGFBP-3 were lower for Hispanic women than non-Hispanic after accounting for IGFBP3 genotype. Body size indicators, vigorous physical activity, and dietary factors appeared to influence serum levels of IGF-1 and the ratio of IGF-1 to IGFBP-3 in pre-menopausal women more than in post-menopausal women. On the other hand, using aspirin/NSAIDs appeared to increase IGFBP-3 levels significantly among pre-menopausal Hispanic women. Results from this study suggest that differences in IGFBP-3 levels exist in Hispanic and non-Hispanic white women. These differences could be due to the combined effects of genetic and behavioral factors which could account for ethnic differences in the risk of breast cancer and other chronic diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KB Baumgartner WC Hunt RN Baumgartner et al. (2004) ArticleTitleAssociation of body composition and weight history with breast cancer prognostic markers: divergent pattern for Hispanic and non-Hispanic White women Am J Epidemiol 160 1087–1097 Occurrence Handle10.1093/aje/kwh313 Occurrence Handle15561988
D Batty I Thune (2000) ArticleTitleDoes physical activity prevent cancer? Evidence suggests protection against colon cancer and probably breast cancer BMJ 321 1424–1425 Occurrence Handle10.1136/bmj.321.7274.1424 Occurrence Handle11110720
CM Friedenreich (2001) ArticleTitleReview of anthropometric factors and breast cancer risk Eur J Cancer Prev 10 15–32 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00008469-200102000-00003 Occurrence Handle11263588
PA Brandt Particlevan den D Spiegelman SS Yaun et al. (2000) ArticleTitlePooled analysis of prospective cohort studies on height, weight, and breast cancer risk Am J Epidemiol 152 514–527 Occurrence Handle10.1093/aje/152.6.514 Occurrence Handle10997541
LM Morimoto E White Z Chen et al. (2002) ArticleTitleObesity, body size, and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer: the women’s health initiative (United States) Cancer Cause Control 13 741–751 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020239211145
PH Lahmann K Hoffmann N Allen et al. (2004) ArticleTitleBody size and breast cancer risk: findings from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer And Nutrition (EPIC) Int J Cancer 111 762–771 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.20315 Occurrence Handle15252848
A McTiernan C Kooperberg E White et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRecreational physical activity and the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women: the Women’s Health Initiative Cohort Study Jama 290 1331–1336 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.290.10.1331 Occurrence Handle12966124
Chlebowski RT (2005) Obesity and early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
E Weiderpass T Braaten C Magnusson et al. (2004) ArticleTitleA prospective study of body size in different periods of life and risk of premenopausal breast cancer Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13 1121–1127 Occurrence Handle15247122
Lethbridge-Cejku M, Schiller JS, Bernadel L (2004) Summary Health Statistics for U.S. Adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2002. National Center for Health Statistics.
RM Elledge GM Clark GC Chamness CK Osborne (1994) ArticleTitleTumor biologic factors and breast cancer prognosis among white, Hispanic, and black women in the United States J Natl Cancer Inst 86 705–712 Occurrence Handle7908990
CI Li KE Malone JR Daling (2002) ArticleTitleDifferences in breast cancer hormone receptor status and histology by race and ethnicity among women 50 years of age and older Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11 601–607 Occurrence Handle12101106
LAG Ries MP Eisner CL Kosary (Eds) et al. (2004) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2001. National Cancer Institute Bethesda, MD
CI Li KE Malone JR Daling (2003) ArticleTitleDifferences in breast cancer stage, treatment, and survival by race and ethnicity Arch Intern Med 163 49–56 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archinte.163.1.49 Occurrence Handle12523916
FD Gilliland WC Hunt KB Baumgartner et al. (1998) ArticleTitleReproductive risk factors for breast cancer in Hispanic and non-Hispanic white women: the New Mexico Women’s Health Study Am J Epidemiol 148 683–692 Occurrence Handle9778175
H Yu T Rohan (2000) ArticleTitleRole of the insulin-like growth factor family in cancer development and progression J Natl Cancer Inst 92 1472–1489 Occurrence Handle10.1093/jnci/92.18.1472 Occurrence Handle10995803
AG Renehan M Zwahlen PC Minder ST O’Dwyer PSM Shalet PM Egger (2004) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein−3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis The Lancet 363 1346–1353 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16044-3
H Jernstrom W Chu D Vesprini et al. (2001) ArticleTitleGenetic factors related to racial variation in plasma levels of insulin- like growth factor−1: implications for premenopausal breast cancer risk Mol Genet Metab 72 144–154 Occurrence Handle10.1006/mgme.2000.3130 Occurrence Handle11161840
K DeLellis S Rinaldi RJ Kaaks LN Kolonel B Henderson L Le Marchand (2004) ArticleTitleDietary and lifestyle correlates of plasma insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3): The Multiethnic Cohort Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13 1444–1451 Occurrence Handle15342444
MH Polymeropoulos DS Rath H Xiao CR Merril (1991) ArticleTitleDinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human gene for insulin-like growth factor I (IGFI) Nucleic Acids Res 19 5797
CJ Rosen ES Kurland D Vereault et al. (1998) ArticleTitleAssociation between serum insulin growth factor-I (IGF-I) and a simple sequence repeat in IGF-I gene: implications for genetic studies of bone mineral density J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83 2286–2290 Occurrence Handle10.1210/jc.83.7.2286 Occurrence Handle9661596
N Vaessen P Heutink JA Janssen et al. (2001) ArticleTitleA polymorphism in the gene for IGF-I: functional properties and risk for type 2 diabetes and myocardial infarction Diabetes 50 637–642 Occurrence Handle11246885
SA Missmer CA Haiman DJ Hunter et al. (2002) ArticleTitleA sequence repeat in the insulin-like growth factor-1 gene and risk of breast cancer Int J Cancer 100 332–336 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.10473 Occurrence Handle12115549
C Deal J Ma F Wilkin et al. (2001) ArticleTitleNovel promoter polymorphism in insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3: correlation with serum levels and interaction with known regulators J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86 1274–1280 Occurrence Handle10.1210/jc.86.3.1274 Occurrence Handle11238520
ES Schernhammer SE Hankinson DJ Hunter MJ Blouin MN Pollak (2003) ArticleTitlePolymorphic variation at the −202 locus in IGFBP3: influence on serum levels of insulin-like growth factors, interaction with plasma retinol and vitamin D and breast cancer risk Int J Cancer 107 60–64 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.11358 Occurrence Handle12925957
Z Ren Q Cai XO Shu et al. (2004) ArticleTitleGenetic polymorphisms in the IGFBP3 gene: association with breast cancer risk and blood IGFBP-3 protein levels among Chinese women Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13 1290–1295 Occurrence Handle15298948
ML Slattery BJ Caan D Duncan TD Berry A Coates R Kerber (1994) ArticleTitleA computerized diet history questionnaire for epidemiologic studies J Am Diet Assoc 94 761–766 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0002-8223(94)91944-5 Occurrence Handle8021418
ML Irwin EJ Mayer-Davis CL Addy et al. (2000) ArticleTitleModerate-intensity physical activity and fasting insulin levels in women: the cross-cultural activity participation study Diabetes Care 23 449–454 Occurrence Handle10857933
SJ Moschos CS Mantzoros (2002) ArticleTitleThe role of the IGF system in cancer: from basic to clinical studies and clinical applications Oncology 63 317–332 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000066230 Occurrence Handle12417786
S Oesterreich P Zhang RL Guler et al. (2001) ArticleTitleRe-expression of estrogen receptor alpha in estrogen receptor alpha-negative MCF−7 cells restores both estrogen and insulin-like growth factor-mediated signaling and growth Cancer Res 61 5771–5777 Occurrence Handle11479214
Lee AV, Cui X, Oesterreich S (2001) Cross-talk among estrogen receptor, epidermal growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7: 4429s–4435s; discussion 4411s–4412s.
L Sepp-Lorenzino N Rosen DE Lebwohl (1994) ArticleTitleInsulin and insulin-like growth factor signaling are defective in the MDA MB−468 human breast cancer cell line Cell Growth Differ 5 1077–1083 Occurrence Handle7848909
PF Bruning JMG Bonfrèr PAH Noord Particlevan AAM Hart M Jong-Bakker Particlede WJ. Nooijen (1992) ArticleTitleInsulin resistance and breast-cancer risk Int J Cancer 52 511–516 Occurrence Handle1399128
D Yam A Fink A Mashiah E Ben-Hur (1996) ArticleTitleHyperinsulinemia in colon, stomach and breast cancer patients Cancer Lett 104 129–132 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3835(96)04211-5 Occurrence Handle8665479
JM Chan MJ Stampfer E Giovannucci et al. (1998) ArticleTitlePlasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study Science 279 563–566 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.279.5350.563 Occurrence Handle9438850
ME Del Giudice IG Fantus S Ezzat G McKeown-Eyssen D Page PJ Goodwin (1998) ArticleTitleInsulin and related factors in premenopausal breast cancer risk Breast Cancer Res Treat 47 111–120 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005831013718 Occurrence Handle9497099
SE Hankinson WC Willett GA Colditz et al. (1998) ArticleTitleCirculating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer Lancet 351 1393–1396 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(97)10384-1 Occurrence Handle9593409
K Bohlke DW Cramer D Trichopoulos CS Mantzoros (1998) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor-I in relation to premenopausal ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast Epidemiology 9 570–573 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00001648-199809000-00016 Occurrence Handle9730040
P Muti T Quattrin BJ Grant et al. (2002) ArticleTitleFasting glucose is a risk factor for breast cancer: a prospective study Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11 1361–1368 Occurrence Handle12433712
RA Krajcik ND Borofsky S Massardo N Orentreich (2002) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-binding proteins, and breast cancer Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11 1566–1573 Occurrence Handle12496045
L Keinan-Boker HB Bueno Mesquita ParticleDe R Kaaks et al. (2003) ArticleTitleCirculating levels of insulin-like growth factor I, its binding proteins -1, -2, -3, C-peptide and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer Int J Cancer 106 90–95 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.11193 Occurrence Handle12794762
BD Li MJ Khosravi HJ Berkel et al. (2001) ArticleTitleFree insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer risk Int J Cancer 91 736–739 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1097-0215(200002)9999:9999<::AID-IJC1111>3.0.CO;2-# Occurrence Handle11267989
A Malin Q Dai H Yu et al. (2004) ArticleTitleEvaluation of the synergistic effect of insulin resistance and insulin-like growth factors on the risk of breast carcinoma Cancer 100 694–700 Occurrence Handle10.1002/cncr.20023 Occurrence Handle14770423
K DeLellis S Ingles L Kolonel et al. (2003) ArticleTitleIGF1 genotype, mean plasma level and breast cancer risk in the Hawaii/Los Angeles multiethnic cohort Br J Cancer 88 277–282 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.bjc.6600728 Occurrence Handle12610514
H Jernstrom E Barrett-Connor (1999) ArticleTitleObesity, weight change, fasting insulin, proinsulin, C-peptide, and insulin-like growth factor-1 levels in women with and without breast cancer: the Rancho Bernardo Study J Womens Health Gend Based Med 8 1265–1272 Occurrence Handle10643834
H Jernstrom H Olsson (1998) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor-1 in relation to adult weight and birth weight in healthy nulliparous women Int J Gynaecol Obstet 62 11–18 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0020-7292(98)00060-5 Occurrence Handle9722119
S Teramukai T Rohan H Eguchi T Oda K Shinchi S Kono (2002) ArticleTitleAnthropometric and behavioral correlates of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in middle-aged Japanese men Am J Epidemiol 156 344–348 Occurrence Handle10.1093/aje/kwf069 Occurrence Handle12181104
DW Voskuil HB Bueno Mesquita Particlede R Kaaks et al. (2001) ArticleTitleDeterminants of circulating insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding proteins 1–3 in premenopausal women: physical activity and anthropometry (Netherlands) Cancer Cause Control 12 951–958 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1013708627664
NE Allen PN Appleby GK Davey R Kaaks S Rinaldi TJ Key (2002) ArticleTitleThe associations of diet with serum insulin-like growth factor I and its main binding proteins in 292 women meat-eaters, vegetarians, and vegans Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 11 1441–1448 Occurrence Handle12433724
E Giovannucci M Pollak Y Liu et al. (2003) ArticleTitleNutritional predictors of insulin-like growth factor I and their relationships to cancer in men Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12 84–89 Occurrence Handle12582016
MR Daws BR Westley FE May (1996) ArticleTitleParadoxical effects of overexpression of the type I insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor on the responsiveness of human breast cancer cells to IGFs and estradiol Endocrinology 137 1177–1186 Occurrence Handle10.1210/en.137.4.1177 Occurrence Handle8625887
M Sanderson XO Shu H Yu et al. (2004) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor-I, soy protein intake, and breast cancer risk Nutr Cancer 50 8–15 Occurrence Handle10.1207/s15327914nc5001_2 Occurrence Handle15572292
A Sugumar YC Liu Q Xia YS Koh K Matsuo (2004) ArticleTitleInsulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein 3 and the risk of premenopausal breast cancer: a meta-analysis of literature Int J Cancer 111 293–297 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.20253 Occurrence Handle15197785
LB Johnston J Dahlgren J Leger et al. (2003) ArticleTitleAssociation between insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) polymorphisms, circulating IGF-I, and pre- and postnatal growth in two European small for gestational age populations J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88 4805–4810 Occurrence Handle10.1210/jc.2003-030563 Occurrence Handle14557458
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slattery, M.L., Baumgartner, K.B., Byers, T. et al. Genetic, Anthropometric, and Lifestyle Factors Associated with IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 Levels in Hispanic and Non-Hispanic White Women. Cancer Causes Control 16, 1147–1157 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-005-0318-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-005-0318-2