Abstract
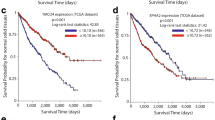
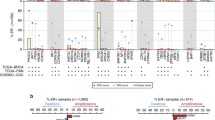
The aim of this study is to identify and validate copy number aberrations in early-stage primary breast tumors associated with bone or non-bone metastasis. Whole-genome molecular inversion probe arrays were used to evaluate copy number imbalances (CNIs) in breast tumors from 960 early-stage patients with information about site of metastasis. The CoxBoost algorithm was used to select metastasis site-related CNIs and to fit a Cox proportional hazards model. Gains at 1q41 and 1q42.12 and losses at 1p13.3, 8p22, and Xp11.3 were significantly associated with bone metastasis. Gains at 2p11.2, 3q21.3–22.2, 3q27.1, 10q23.1, and 14q13.2–3 and loss at 7q21.11 were associated with non-bone metastasis. To examine the joint effect of CNIs and clinical predictors, patients were stratified into three risk groups (low, intermediate, and high) based on the sum of predicted linear hazard ratios. For bone metastasis, the hazard (95 % confidence interval) for the low-risk group was 0.32 (0.11–0.92) compared to the intermediate-risk group and 2.99 (1.74–5.11) for the high-risk group. For non-bone metastasis, the hazard for the low-risk group was 0.34 (0.17–0.66) and 2.33 (1.59–3.43) for the high-risk group. The prognostic value of loss at 8p22 for bone metastasis and gains at 10q23.1 for non-bone metastasis, and gain at 11q13.5 for both bone and non-bone metastases were externally validated in 335 breast tumors pooled from four independent cohorts. Distinct CNIs are independently associated with bone and non-bone metastasis for early-stage breast cancer patients across cohorts. These data warrant consideration for tailoring surveillance and management of metastasis risk.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Cancer Society (2010). Breast cancer facts and figures 2009–2010. http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@nho/documents/document/f861009final90809pdf.pdf)
Coleman RE (2006) Clinical features of metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clin Cancer Res 12(20 Pt 2):6243s–6249s. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0931
Paget S (1989) The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast (1889). Cancer Metastasis Rev 8(2):98–101
Kang Y, Siegel PM, Shu W, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordon-Cardo C, Guise TA, Massague J (2003) A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell 3(6):537–549. doi:S1535610803001326
Ramaswamy S, Ross KN, Lander ES, Golub TR (2003) A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumors. Nat Genet 33(1):49–54. doi:10.1038/ng1060ng1060
Evans AJ, James JJ, Cornford EJ, Chan SY, Burrell HC, Pinder SE, Gutteridge E, Robertson JF, Hornbuckle J, Cheung KL (2004) Brain metastases from breast cancer: identification of a high-risk group. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 16(5):345–349
Duchnowska R, Szczylik C (2005) Central nervous system metastases in breast cancer patients administered trastuzumab. Cancer Treat Rev 31(4):312–318. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2005.04.008
Hicks DG, Short SM, Prescott NL, Tarr SM, Coleman KA, Yoder BJ, Crowe JP, Choueiri TK, Dawson AE, Budd GT, Tubbs RR, Casey G, Weil RJ (2006) Breast cancers with brain metastases are more likely to be estrogen receptor negative, express the basal cytokeratin CK5/6, and overexpress HER2 or EGFR. Am J Surg Pathol 30(9):1097–1104. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000213306.05811.b900000478-200609000-00005
Nam BH, Kim SY, Han HS, Kwon Y, Lee KS, Kim TH, Ro J (2008) Breast cancer subtypes and survival in patients with brain metastases. Breast Cancer Res 10(1):R20. doi:10.1186/bcr1870
Bos PD, Zhang XH, Nadal C, Shu W, Gomis RR, Nguyen DX, Minn AJ, van de Vijver MJ, Gerald WL, Foekens JA, Massague J (2009) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature 459(7249):1005–1009. doi:10.1038/nature08021
Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL, Massague J (2005) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436(7050):518–524. doi:10.1038/nature03799
Singletary SE, Walsh G, Vauthey JN, Curley S, Sawaya R, Weber KL, Meric F, Hortobagyi GN (2003) A role for curative surgery in the treatment of selected patients with metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist 8(3):241–251
Brewster AM, Do KA, Thompson PA, Hahn KM, Sahin AA, Cao Y, Stewart MM, Murray JL, Hortobagyi GN, Bondy ML (2007) Relationship between epidemiologic risk factors and breast cancer recurrence. J Clin Oncol 25(28):4438–4444. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.10.6815
Thompson PA, Brewster AM, Kim-Anh D, Baladandayuthapani V, Broom BM, Edgerton ME, Hahn KM, Murray JL, Sahin A, Tsavachidis S, Wang Y, Zhang L, Hortobagyi GN, Mills GB, Bondy ML (2011) Selective genomic copy number imbalances and probability of recurrence in early-stage breast cancer. PLoS One 6(8):e23543. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023543
Binder H, Schumacher M (2008) Allowing for mandatory covariates in boosting estimation of sparse high-dimensional survival models. BMC Bioinformatics 9:14. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-14
Hoeting J, Madigan D, Raftery AE, Volinsky C (1999) Bayesian model averaging: a tutorial. Stat Sci 14:382–417
Volinsky C, Madigan D, Raftery A, Kronmal R (1997) Bayesian model averaging in proportional hazard models: assessing the risk of a stroke. Appl Stat 46:433–448
Rodriguez C, Hughes-Davies L, Valles H, Orsetti B, Cuny M, Ursule L, Kouzarides T, Theillet C (2004) Amplification of the BRCA2 pathway gene EMSY in sporadic breast cancer is related to negative outcome. Clin Cancer Res 10(17):5785–5791. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-04100/17/5785
Szepetowski P, Ollendorff V, Grosgeorge J, Courseaux A, Birnbaum D, Theillet C, Gaudray P (1992) DNA amplification at 11q13.5–q14 in human breast cancer. Oncogene 7(12):2513–2517
Bekri S, Adelaide J, Merscher S, Grosgeorge J, Caroli-Bosc F, Perucca-Lostanlen D, Kelley PM, Pebusque MJ, Theillet C, Birnbaum D, Gaudray P (1997) Detailed map of a region commonly amplified at 11q13– >q14 in human breast carcinoma. Cytogenet Cell Genet 79(1–2):125–131
Hirano A, Emi M, Tsuneizumi M, Utada Y, Yoshimoto M, Kasumi F, Akiyama F, Sakamoto G, Haga S, Kajiwara T, Nakamura Y (2001) Allelic losses of loci at 3p25.1, 8p22, 13q12, 17p13.3, and 22q13 correlate with postoperative recurrence in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7(4):876–882
Utada Y, Haga S, Kajiwara T, Kasumi F, Sakamoto G, Nakamura Y, Emi M (2000) Allelic loss at the 8p22 region as a prognostic factor in large and estrogen receptor negative breast carcinomas. Cancer 88(6):1410–1416. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(20000315)
Dahmane N, Sanchez P, Gitton Y, Palma V, Sun T, Beyna M, Weiner H, Ruiz i, Altaba A (2001) The sonic Hedgehog-Gli pathway regulates dorsal brain growth and tumorigenesis. Development 128(24):5201–5212
Liu CJ, Lin SC, Chen YJ, Chang KM, Chang KW (2006) Array-comparative genomic hybridization to detect genomewide changes in microdissected primary and metastatic oral squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Carcinog 45(10):721–731. doi:10.1002/mc.20213
Martinez-Cardus A, Martinez-Balibrea E, Bandres E, Malumbres R, Gines A, Manzano JL, Taron M, Garcia-Foncillas J, Abad A (2009) Pharmacogenomic approach for the identification of novel determinants of acquired resistance to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 8(1):194–202. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0659
Lassmann S, Weis R, Makowiec F, Roth J, Danciu M, Hopt U, Werner M (2007) Array CGH identifies distinct DNA copy number profiles of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in chromosomal- and microsatellite-unstable sporadic colorectal carcinomas. J Mol Med (Berl) 85(3):293–304. doi:10.1007/s00109-006-0126-5
Maire G, Forus A, Foa C, Bjerkehagen B, Mainguene C, Kresse SH, Myklebost O, Pedeutour F (2003) 11q13 alterations in two cases of hibernoma: large heterozygous deletions and rearrangement breakpoints near GARP in 11q13.5. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 37(4):389–395. doi:10.1002/gcc.10223
Hughes-Davies L, Huntsman D, Ruas M, Fuks F, Bye J, Chin SF, Milner J, Brown LA, Hsu F, Gilks B, Nielsen T, Schulzer M, Chia S, Ragaz J, Cahn A, Linger L, Ozdag H, Cattaneo E, Jordanova ES, Schuuring E, Yu DS, Venkitaraman A, Ponder B, Doherty A, Aparicio S, Bentley D, Theillet C, Ponting CP, Caldas C, Kouzarides T (2003) EMSY links the BRCA2 pathway to sporadic breast and ovarian cancer. Cell 115(5):523–535. doi:S0092867403009309
Surawska H, Ma PC, Salgia R (2004) The role of Ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15(6):419–433. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.09.002
Liu J, Ghanim M, Xue L, Brown CD, Iossifov I, Angeletti C, Hua S, Negre N, Ludwig M, Stricker T, Al-Ahmadie HA, Tretiakova M, Camp RL, Perera-Alberto M, Rimm DL, Xu T, Rzhetsky A, White KP (2009) Analysis of Drosophila segmentation network identifies a JNK pathway factor overexpressed in kidney cancer. Science 323(5918):1218–1222. doi:10.1126/science.1157669
Lee J, Sayegh J, Daniel J, Clarke S, Bedford MT (2005) PRMT8, a new membrane-bound tissue-specific member of the protein arginine methyltransferase family. J Biol Chem 280(38):32890–32896. doi:10.1074/jbc.M506944200
Goodison S, Yuan J, Sloan D, Kim R, Li C, Popescu NC, Urquidi V (2005) The RhoGAP protein DLC-1 functions as a metastasis suppressor in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 65(14):6042–6053. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3043
Wang Z, Shen D, Parsons DW, Bardelli A, Sager J, Szabo S, Ptak J, Silliman N, Peters BA, van der Heijden MS, Parmigiani G, Yan H, Wang TL, Riggins G, Powell SM, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Velculescu VE (2004) Mutational analysis of the tyrosine phosphatome in colorectal cancers. Science 304(5674):1164–1166. doi:10.1126/science.1096096
Niedergethmann M, Alves F, Neff JK, Heidrich B, Aramin N, Li L, Pilarsky C, Grutzmann R, Allgayer H, Post S, Gretz N (2007) Gene expression profiling of liver metastases and tumour invasion in pancreatic cancer using an orthotopic SCID mouse model. Br J Cancer 97(10):1432–1440. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604031
Batlle E, Bacani J, Begthel H, Jonkheer S, Gregorieff A, van de Born M, Malats N, Sancho E, Boon E, Pawson T, Gallinger S, Pals S, Clevers H (2005) EphB receptor activity suppresses colorectal cancer progression. Nature 435(7045):1126–1130. doi:10.1038/nature03626
Sheng Z, Wang J, Dong Y, Ma H, Zhou H, Sugimura H, Lu G, Zhou X (2008) EphB1 is underexpressed in poorly differentiated colorectal cancers. Pathobiology 75(5):274–280. doi:10.1159/000151707
Nakamoto M, Bergemann AD (2002) Diverse roles for the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases in carcinogenesis. Microsc Res Tech 59(1):58–67. doi:10.1002/jemt.10177
Acknowledgments
We thank Melissa May, Dr. Jeong Yun Shim, and Dr. Agbe Samuel for retrieving and processing all the tumor specimens used in the study; Wanda Williams, who supervised the medical record abstraction; Phyllis Adatto, who supervised the study staff; and Betsy C. Wertheim for careful review and editing of the manuscript. For providing tumor specimens and clinical data, the authors gratefully acknowledge for the MicMa cohort, Dr. Bjørn Naume, and Dr. Marit Synnestvedt; for the ULL cohort, Dr. Anita Langerød; for the MDG cohort, Dr. Vilde D. Haakensen and Dr. Åslaug Helland, all Oslo University Hospital, Norway. For the Uppsala cohort we wish to thank Dr. Johan Botling, Department of Surgery, Uppsala University, Sweden. For technical support performing the aCGH experiments we wish to thank Dr. Hans Kristian M. Vollan, Ida J. Schneider, and Eldri U. Due, Oslo University Hospital, Norway. This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through grant R01CA089608. Additional support was provided by Susan G. Komen for the Cure, by the National Breast Cancer Foundation, and by NIH through SPORE P50CA116199, MD Anderson’s Cancer Center Support Grant (CCSG) CA016672, and the Arizona Cancer Center’s CCSG CA023074. Grants to ALBD lab supporting this study: Norwegian Research Council grants 175240/S10, 159188/S10, and 193387/V50, Norwegian Cancer Society grant 138296-PR-2008-0108.
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y. Liu and R. Zhou have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhou, R., Baumbusch, L.O. et al. Genomic copy number imbalances associated with bone and non-bone metastasis of early-stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 143, 189–201 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2796-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2796-3