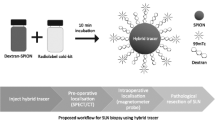
Abstract
The standard for the treatment of early non-palpable breast cancers is wide local excision directed by wire-guided localization and sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB). This has drawbacks technically and due to reliance upon radioisotopes. We evaluated the use of a magnetic tracer for its localization capabilities and concurrent performance of SLNB using a handheld magnetometer in a porcine model as a novel alternative to the current standard. Ethical approval by the IRCAD Ethics Review Board, Strasbourg (France) was received. A magnetic tracer was injected in varying volumes (0.1–5 mL) subcutaneously into the areolar of the left and right 3rd inguinal mammary glands in 16 mini-pigs. After 4 h magnetometer counts were taken at the injection sites and in the groins. The magnetometer was used to localize any in vivo signal from the draining inguinal lymph nodes. Magnetic SLNB followed by excision of the injection site was performed. The iron content of sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) were graded and quantified. All excised specimens were weighed and volumes were calculated. Univariate analyses were performed to evaluate correlation. Magnetic SLNB was successful in all mini-pigs. There was a significant correlation (r = 0.86; p < 0.01) between magnetometer counts and iron content of SLNs. Grading of SLNs on both H&E and Perl’s staining correlated significantly with the iron content (p = 0.001; p = 0.003) and magnetometer counts (p < 0.001; p = 0.004). The peak counts corresponded to the original magnetic tracer injection sites 4 h after injection in all cases. The mean volume and weight of excised injection site specimens was 2.9 cm3 (SD 0.81) and 3.1 g (SD 0.85), respectively. Injection of ≥0.5 mL magnetic tracer was associated with significantly greater volume (p = 0.05) and weight of excision specimens (p = 0.01). SLNB and localization can be performed in vivo using a magnetic tracer. This could provide a viable alternative for lesion localization and concurrent SLNB in the treatment of non-palpable breast cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lovrics PJ, Cornacchi SD, Farrokhyar F, Garnett A, Chen V, Franic S, Simunovic M (2009) The relationship between surgical factors and margin status after breast-conservation surgery for early stage breast cancer. Am J Surg 197(6):740–746
Frank HA, Hall FM, Steer ML (1976) Preoperative localization of nonpalpable breast lesions demonstrated by mammography. N Engl J Med 295(5):259–260
Gill G (2009) Surgeons STGotRACo, Centre NCT: sentinel-lymph-node-based management or routine axillary clearance? One-year outcomes of sentinel node biopsy versus axillary clearance (SNAC): a randomized controlled surgical trial. Ann Surg Oncol 16(2):266–275
Kim T, Giuliano AE, Lyman GH (2006) Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast carcinoma: a metaanalysis. Cancer 106(1):4–16
Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM, Harlow SP, Ashikaga T, Weaver DL, Miller BJ, Jalovec LM, Frazier TG et al. (2007) Technical outcomes of sentinel-lymph-node resection and conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer: results from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 8(10):881–888
Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, Goyal A, Newcombe RG, Dixon JM, Yiangou C, Horgan K, Bundred N, Monypenny I et al (2006) Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: the ALMANAC Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(9):599–609
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Viale G, Luini A, Zurrida S, Galimberti V, Intra M, Veronesi P, Robertson C, Maisonneuve P et al (2003) A randomized comparison of sentinel-node biopsy with routine axillary dissection in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 349(6):546–553
Zavagno G, De Salvo GL, Scalco G, Bozza F, Barutta L, Del Bianco P, Renier M, Racano C, Carraro P, Nitti D et al (2008) A randomized clinical trial on sentinel lymph node biopsy versus axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer: results of the Sentinella/GIVOM trial. Ann Surg 247(2):207–213
Rescigno J, Zampell JC, Axelrod D (2009) Patterns of axillary surgical care for breast cancer in the era of sentinel lymph node biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol 16(3):687–696
Leong SP, Shen ZZ, Liu TJ, Agarwal G, Tajima T, Paik NS, Sandelin K, Derossis A, Cody H, Foulkes WD (2010) Is breast cancer the same disease in Asian and Western countries? World J Surg 34(10):2308–2324
Ahmed M, Douek M (2013) Radioactive seed localisation in the treatment of non-palpable breast cancers: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast (In press)
Ahmed M, Douek M (2013) Systematic review of radioguided versus wire-guided localization in the treatment of non-palpable breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat (In press)
Lovrics PJ, Cornacchi SD, Vora R, Goldsmith CH, Kahnamoui K (2011) Systematic review of radioguided surgery for non-palpable breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 37(5):388–397
Sajid MS, Parampalli U, Haider Z, Bonomi R (2012) Comparison of radioguided occult lesion localization (ROLL) and wire localization for non-palpable breast cancers: a meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol 105(8):852–858
Harnan SE, Cooper KL, Meng Y, Ward SE, Fitzgerald P, Papaioannou D, Ingram C, Lorenz E, Wilkinson ID, Wyld L (2011) Magnetic resonance for assessment of axillary lymph node status in early breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol 37(11):928–936
Houssami N, Ciatto S, Turner RM, Cody HS III, Macaskill P (2011) Preoperative ultrasound-guided needle biopsy of axillary nodes in invasive breast cancer: meta-analysis of its accuracy and utility in staging the axilla. Ann Surg 254(2):243–251
Meng Y, Ward S, Cooper K, Harnan S, Wyld L (2011) Cost-effectiveness of MRI and PET imaging for the evaluation of axillary lymph node metastases in early stage breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 37(1):40–46
Alexiou C, Jurgons R, Seliger C, Iro H (2006) Medical applications of magnetic nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 6(9–10):2762–2768
Joshi T, Pankhurst QA, Hattersley S, Brazdeikis A, Hall-Craggs M, De Vita E, Bainbridge A, Sainsbury R, Sharma A, Douek M (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles for detecting sentinel lymph nodes. Eur J Surg Oncol 33(9):1135
Johnson L, Pinder SE, Douek M (2013) Deposition of superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles in axillary sentinel lymph nodes following subcutaneous injection. Histopathology 62(3):481–486
Harada T, Tanigawa N, Matsuki M, Nohara T, Narabayashi I (2007) Evaluation of lymph node metastases of breast cancer using ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol 63(3):401–407
Douek M (2010) SentiMag Multicentre Trial (NIHR) UKCRN ID12178
Douek M (2013) MELAMAG Multicentre Trial (NIHR) UKCRN ID14011
Barthelmes L, Goyal A, Newcombe RG, McNeill F, Mansel RE, New S (2010) Adverse reactions to patent blue V dye—The NEW START and ALMANAC experience. Eur J Surg Oncol 36(4):399–403
Goyal A, Newcombe RG, Mansel RE (2005) Axillary lymphatic mapping against nodal axillary clearance trialists G: clinical relevance of multiple sentinel nodes in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg 92(4):438–442
Visscher M, Pouw JJ, Baarlen J, Klaase J, Haken B (2013) Quantitative analysis of superparamagnetic contrast agent in sentinel lymph nodes using ex vivo vibrating sample magnetometry. IEEE Trans Bio-med Eng
Ahmed M, Douek M (2013) Pre-clinical studies of the role of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles for non-palpable lesion localization in breast cancer. J Surg Res (In press)
Medina-Franco H, Abarca-Perez L, Garcia-Alvarez MN, Ulloa-Gomez JL, Romero-Trejo C, Sepulveda-Mendez J (2008) Radioguided occult lesion localization (ROLL) versus wire-guided lumpectomy for non-palpable breast lesions: a randomized prospective evaluation. J Surg Oncol 97(2):108–111
Moreno M, Wiltgen JE, Bodanese B, Schmitt RL, Gutfilen B, da Fonseca LM (2008) Radioguided breast surgery for occult lesion localization - correlation between two methods. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27:29
Ocal K, Dag A, Turkmenoglu O, Gunay EC, Yucel E, Duce MN (2011) Radioguided occult lesion localization versus wire-guided localization for non-palpable breast lesions: randomized controlled trial. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 66(6):1003–1007
Mariscal Martinez A, Sola M, de Tudela AP, Julian JF, Fraile M, Vizcaya S, Fernandez J (2009) Radioguided localization of nonpalpable breast cancer lesions: randomized comparison with wire localization in patients undergoing conservative surgery and sentinel node biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193(4):1001–1009
Postma EL, Verkooijen HM, van Esser S, Hobbelink MG, van der Schelling GP, Koelemij R, Witkamp AJ, Contant C, van Diest PJ, Willems SM et al (2012) Efficacy of ‘radioguided occult lesion localisation’ (ROLL) versus ‘wire-guided localisation’ (WGL) in breast conserving surgery for non-palpable breast cancer: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136(2):469–478
Rampaul RS, Bagnall M, Burrell H, Pinder SE, Evans AJ, Macmillan RD (2004) Randomized clinical trial comparing radioisotope occult lesion localization and wire-guided excision for biopsy of occult breast lesions. Br J Surg 91(12):1575–1577
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Marescaux and his team at the IRCAD Institute, Strasbourg (France) for their kind assistance in allowing us to perform this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no disclosures to make concerning financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence their work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bauke Anninga and Muneer Ahmed are joint first authors and contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anninga, B., Ahmed, M., Van Hemelrijck, M. et al. Magnetic sentinel lymph node biopsy and localization properties of a magnetic tracer in an in vivo porcine model. Breast Cancer Res Treat 141, 33–42 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2657-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2657-0