Abstract
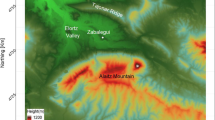
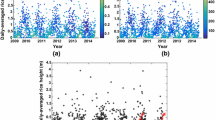
Ultrasonic wind measurements, sonic temperature and air temperature data at two heights in the advection experiment MORE II were used to establish a complete budget of sensible heat including vertical advection, horizontal advection and horizontal turbulent flux divergence. MORE II took place at the long-term Carbo-Europe IP site in Tharandt, Germany. During the growing period of 2003 three additional towers were established to measure all relevant parameters for an estimation of advective fluxes, primarily of CO2. Additionally, in relation to other advection experiments, a calculation of the horizontal turbulent flux divergence is proposed and the relation of this flux to atmospheric stability and friction velocity is discussed. In order to obtain a complete budget, different scaling heights for horizontal advection and horizontal turbulent flux divergence are tested. It is shown that neglecting advective fluxes may lead to incorrect results. If advective fluxes are taken into account, the sensible heat budget based upon vertical turbulent flux and storage change only, is reduced by approximately 30%. Additional consideration of horizontal turbulent flux divergence would in turn add 5–10% to this sum (i.e., the sum of vertical turbulent flux plus storage change plus horizontal and vertical advection). In comparison with available energy horizontal advection is important at night whilst horizontal turbulent flux divergence is rather insignificant. Obviously, advective fluxes typically improve poor nighttime energy budget closure and might change ecosystem respiration fluxes considerably.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubinet M, Grelle A, Ibrom A, Rannik Ü, Moncrieff J, Foken T, Kowalski AS, Martin PH, Berbgier P, Bernhofer C, Clement R, Elbers J, Granier A, Grünwald T, Morgenstern K, Pilegaard K, Rebmann C, Snijders W, Valentini R, Vesala T (2000) Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of forests: The EUROFLUX methodology. Adv Ecol Res 30:113–175
Aubinet M, Chermanne B, Vandenhaute M, Longdoz B, Yernaux M, Laitat E (2001) Long term carbon dioxide exchange above a mixed forest in the Belgian Ardennes. Agric For Meteorol 108:293–315
Aubinet M, Heinesch B, Yernaux M (2003) Horizontal and vertical CO2-advection in a sloping forest. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 108:397–417
Aubinet M, Berbigier P, Bernhofer C, Cescatti A, Feigenwinter C, Granier A, Grünwald T, Havrankova K, Heinesch B, Longdoz B, Marcolla B, Montagnani L, Sedlak P (2005) Comparing CO2 storage and advection conditions at night at different CARBOEUROFLUX sites. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 116:63–94
Baldocchi D, Finnigan J, Wilson K, Paw U, K. T., Falge E (2000) On measuring net ecosystem carbon exchange over tall vegetation on complex terrain. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 96:257–291
Bernhofer C, Aubinet M, Clement R, Grelle A, Grünwald T, Ibrom A, Jarvis P, Rebmann C, Schulze E-D, Tenhunen JD (2003) Spruce forests (Norway and Sitka Spruce, Including Douglas Fir): carbon and water fluxes and balances, ecological and ecophysiological determinants. In: Valentini R (ed) Fluxes of carbon, energy and water of European forests, ecological studies, vol 163. Springer, Berlin, pp 99–123
Bernhofer C, Feigenwinter C, Grünwald T, Vogt R (2003a) Spectral correction of water and carbon flux for EC measurements at the anchor station tharandt. In: Bernhofer C (ed) Tharandter Klimaprotokolle, vol 8. Dresden University of Technology, Dresden, pp 1–13
Bernhofer C, Köstner B (2003) Vertical transports of trace gases at anchor stations and their spatial/temporal extrapolation under complex natural conditions. AFO2000 Newslett 2:3–6
Bernhofer C, Vogt R (1999) Energy balance closure gaps – a methodical problem of Eddy covariance measurements? In: Dear RJ, Kalma JD, Oke TR, Auliciems A (eds) Biometeorology and urban climatology at the turn of the millennium: Selected papers from the conference ICB-ICUC’99 (Sydney, 8–12. November 1999), pp 199–203
Bernhofer C (1992) Applying a simple three-dimensional Eddy correlation system for latent and sensible heat flux to contrasting canopies. Theor Appl Climatol 46:163–172
Blanford JH, Bernhofer C, Gay LW (1991) Energy flux mechanism over a Pecan Orchard Oasis. In: Proceedings, 20th Agricultural and Forest Meteorology. Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, American Meteorological Society, 45 Beacon St., Boston, MA, pp 116–119
Eugster W, Senn W (1995) A cospectral correction model for measurement of turbulent NO2 flux. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 74:321–340
Feigenwinter C, Bernhofer C, Vogt R (2004) The influence of advection on short term CO2 budget in and above forest canopy. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 113:201–224
Finnigan JJ (1999) A comment on the paper by Lee (1998): “On micrometeorological observations of surface-air exchange over tall vegetation”. Agric For Meteorol 97:55–67
Goulden ML, Munger JW, Song-Miao F, Daube BC, Wofsy SC (1996) Measurements of carbon sequestration by long-term Eddy covariance: methods and a critical evaluation of accuracy. Global Change Biol 2:169–182
Grelle A, Lindroth Q (1996) Eddy-correlation system for long-term monitoring fluxes of heat, water vapour and CO2. Global Change Biol 2:297–307
Grünwald T (2002) Langfristige Beobachtungen von Kohlendioxidflüssen mittels Eddy-Kovarianz-Technik über einem Altfichtenbestand im Tharandter Wald. Ph.D. Dissertation, Dresden University of Technology, Dresden, Germany, 124 pp
Kaimal JC, Wyngaard JC, Coté OR (1972) Spectral characteristics of surface-layer turbulence. Quart J Roy Meteorol Soc 98:563–589
Lee X (1998) On micrometeorological observations of surface-air exchange over tall vegetation. Agric For Meteorol 91:39–49
Lee X, Hu X (2002) Forest-air fluxes of carbon, water and energy over non-flat terrain. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 103:277–301
Lee X (2004) Forest-air exchange in non-ideal conditions: the role of horizontal flux and its divergence. In: Mencuccini M, Grace J, Moncrieff J, McNaughton KG (eds) Forest at the land-atmosphere interface. CABI Publishing, Cambridge, pp 145–157
Marcolla B, Cescatti A, Montagnani L, Manca G, Kerschbaumer G, Minerbi S (2005) Importance of advection in the atmospheric CO2 exchanges of an alpine forest. Agric For Meteorol 130:193–206
Mellmann P (1998) Die Bedeutung der Speicherterme bei zeitlich hochauflösender Verdunstungsbestimmung am Beispiel des Tharandter Waldes. Diploma thesis, Dresden University of Technology, Dresden, Germany
Panin GN, Tetzlaff G, Raabe A (1998) Inhomogeneity of the land surface and problems in parameterisation of the surface fluxes in natural conditions. Theor Appl Climatol 60:163–178
Paw UKT, Baldocchi D, Meyers TP, Wilson KB (2000) Correction of Eddy-covariance measurements incorporation both advective effects and density fluxes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 97:487–511
Pilegaard K, Hummelshj P, Jensen NO, Chen Z (2001) Two years of continuous CO2 Eddy-flux measurements over a Danish beech forest. Agric For Meteorol 107:29–41
Queck R (2004) Fraktionierung und zeitliche Differenzierung von Depositionsraten in Waldbeständen. Ph.D. Dissertation, Dresden University of Technology, Dresden, Germany, 234 pp
Rebmann C, Göckede M, Foken T, Aubinet M, Aurela M, Berbigier P, Bernhofer C, Buchmann N, Carrara A, Cescatti A, Ceulemans R, Clement R, Elbers JA, Granier A, Grünwald T, Guyon D, Havrankova K, Heinesch B, Knohl A, Laurila T, Longdoz B, Marcolla B, Markkanen T, Miglietta F, Moncrieff J, Montagnani L, Moors E, Nardino M, Ourcival J-M, Rambal S, Rannik Ü, Rotenberg E, Sedlak P, Unterhuber G, Vesala T, Yakir D (2005) Quality analysis applied on Eddy covariance measurements at complex forest sites using footprint modelling. Theor Appl Climatol 80:121–141
Schotanus P, Nieuwstadt FTM, De Bruin HAR (1983) Temperature measurement with a sonic anemometer and its application to heat and moisture fluxes. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 26:81–93
Staebler RM, Fitzjarrald DR (2004) Observing subcanopy CO2 advection. Agric For Meteorol 122:139–156
Valentini R, De Angelis P, Matteucci G, Monaco R, Dore S, Scarascia Mucnozza GE (1996) Seasonal net carbon dioxide exchange of a beech forest with the atmosphere. Global Change Biol 2:199–207
Valentini R (ed) (2003) Fluxes of carbon, water and energy of European forests, ecological studies, vol 163. Springer, Berlin, 266 pp
Wilczak JM, Oncley SP, Stage SA (2001) Sonic anemometer tilt correction algorithms. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 99:127–150
Wilson K, Goldstein A, Falge E, Aubinet M, Baldocchi D, Berbigier P, Bernhofer C, Ceulemans R, Dolman H, Field C, Grelle A, Ibrom A, Law BE, Kowalski A, Meyers T, Moncrieff J, Monson R, Oechel W, Tenhunen J, Valentini R, Verma S (2002) Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites. Agric For Meteorol 113:223–243
Wyngaard JC, Rockwell L, Izumi Y (1971) Local free convection similarity and the budgets of shear stress and heat flux. J Atmos Sci 28:1171–1182
Yi C, Davis KJ, Bakwin PS, Berger BW, Marr LC (2000) Influence of advection on measurements of the net ecosystem-atmosphere exchange of CO2 from a very tall tower. J Geophys Res 105:9991–9999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moderow, U., Feigenwinter, C. & Bernhofer, C. Estimating the components of the sensible heat budget of a tall forest canopy in complex terrain. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 123, 99–120 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9136-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9136-7