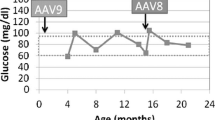
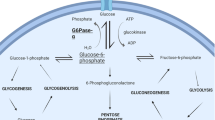
Abstract
Background
Glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD Ia) in dogs closely resembles human GSD Ia. Untreated patients with GSD Ia develop complications associated with glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) deficiency. Survival of human patients on intensive nutritional management has improved; however, long-term complications persist including renal failure, nephrolithiasis, hepatocellular adenomas (HCA), and a high risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Affected dogs fail to thrive with dietary therapy alone. Treatment with gene replacement therapy using adeno-associated viral vectors (AAV) expressing G6Pase has greatly prolonged life and prevented hypoglycemia in affected dogs. However, long-term complications have not been described to date.
Methods
Five GSD Ia-affected dogs treated with AAV-G6Pase were evaluated. Dogs were euthanized due to reaching humane endpoints related to liver and/or kidney involvement, at 4 to 8 years of life. Necropsies were performed and tissues were analyzed.
Results
Four dogs had liver tumors consistent with HCA and HCC. Three dogs developed renal failure, but all dogs exhibited progressive kidney disease histologically. Urolithiasis was detected in two dogs; uroliths were composed of calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate. One affected and one carrier dog had polycystic ovarian disease. Bone mineral density was not significantly affected.
Conclusions
Here, we show that the canine GSD Ia model demonstrates similar long-term complications as GSD Ia patients in spite of gene replacement therapy. Further development of gene therapy is needed to develop a more effective treatment to prevent long-term complications of GSD Ia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin SL, El-Gharbawy AH, Kasturi VG, James A, Kishnani PS (2013) Menorrhagia in patients with type I glycogen storage disease. Obstet Gynecol 122:1246–1254
Baheti AD, Yeh MM, O'Malley R, Lalwani N (2015) Malignant transformation of hepatic adenoma in glycogen storage disease type-1a: report of an exceptional case diagnosed on surveillance imaging. J Clin Imaging Sci 5:47
Bali DS, Chen YT, Austin S, Goldstein JL (1993) In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA et al (eds) Glycogen storage disease type I. GeneReviews((R)), Seattle
Brooks ED, Little D, Arumugam R et al (2013) Pathogenesis of growth failure and partial reversal with gene therapy in murine and canine Glycogen Storage Disease type Ia. Mol Genet Metab 109:161–170
Calderaro J, Labrune P, Morcrette G et al (2013) Molecular characterization of hepatocellular adenomas developed in patients with glycogen storage disease type I. J Hepatol 58:350–357
Carreiro G, Villela-Nogueira CA, Coelho H et al (2007) Orthotopic liver transplantation in glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency—Von Gierke disease—with multiple hepatic adenomas and concomitant focal nodular hyperplasia. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 20:545–549
Chang CY, Hernandez-Prera JC, Roayaie S, Schwartz M, Thung SN (2013) Changing epidemiology of hepatocellular adenoma in the United States: review of the literature. Int J Hepatol 2013:604860
Chen YT (2001) Glycogen storage diseases. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1521–1551
Clar J, Gri B, Calderaro J et al (2014) Targeted deletion of kidney glucose-6 phosphatase leads to nephropathy. Kidney Int 86:747–756
Crane B, Luo X, Demaster A et al (2012) Rescue administration of a helper-dependent adenovirus vector with long-term efficacy in dogs with glycogen storage disease type Ia. Gene Ther 19:443–452
Cunningham SC, Dane AP, Spinoulas A, Logan GJ, Alexander IE (2008) Gene delivery to the juvenile mouse liver using AAV2/8 vectors. Mol Ther 16:1081–1088
Demaster A, Luo X, Curtis S et al (2012) Long-term efficacy following readministration of an adeno-associated virus vector in dogs with glycogen storage disease type Ia. Hum Gene Ther 23:407–418
Denk H, Stumptner C, Zatloukal K (2000) Mallory bodies revisited. J Hepatol 32:689–702
Derks TG, van Rijn M (2015) Lipids in hepatic glycogen storage diseases: pathophysiology, monitoring of dietary management and future directions. J Inherit Metab Dis 38:537–543
Di Rocco M, Calevo MG, Taro M, Melis D, Allegri AE, Parenti G (2008) Hepatocellular adenoma and metabolic balance in patients with type Ia glycogen storage disease. Mol Genet Metab 93:398–402
Dingemanse W, Muller-Gerbl M, Jonkers I, Sloten JV, van Bree H, Gielen I (2017) A prospective follow up of age related changes in the subchondral bone density of the talus of healthy Labrador Retrievers. BMC Vet Res 13:57
Evans HE, Miller ME (2013) Miller’s anatomy of the dog. Elsevier, St. Louis
Fabry A, Benjamin SA, Angleton GM (1982) Nodular hyperplasia of the liver in the beagle dog. Vet Pathol 19:109–119
Farah BL, Landau DJ, Sinha RA et al (2016) Induction of autophagy improves hepatic lipid metabolism in glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency. J Hepatol 64:370–379
Franco LM, Krishnamurthy V, Bali D et al (2005) Hepatocellular carcinoma in glycogen storage disease type Ia: a case series. J Inherit Metab Dis 28:153–162
Gjorgjieva M, Raffin M, Duchampt A et al (2016) Progressive development of renal cysts in glycogen storage disease type I. Hum Mol Genet 25:3784–3797
Jonges GN, Van Noorden CJ, Gossrau R (1990) Quantitative histochemical analysis of glucose-6-phosphatase activity in rat liver using an optimized cerium-diaminobenzidine method. J Histochem Cytochem 38:1413–1419
Kelly PM, Poon FW (2001) Hepatic tumours in glycogen storage disease type 1 (von Gierke’s disease). Clin Radiol 56:505–508
Kishnani PS, Faulkner E, VanCamp S et al (2001) Canine model and genomic structural organization of glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD Ia). Vet Pathol 38:83–91
Kishnani PS, Chuang TP, Bali D et al (2009) Chromosomal and genetic alterations in human hepatocellular adenomas associated with type Ia glycogen storage disease. Hum Mol Genet 18:4781–4790
Kishnani PS, Austin SL, Abdenur JE et al (2014) Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage disease type I: a practice guideline of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med 16:e1
Koeberl DD, Sun BD, Damodaran TV et al (2006) Early, sustained efficacy of adeno-associated virus vector-mediated gene therapy in glycogen storage disease type Ia. Gene Ther 13:1281–1289
Koeberl DD, Kishnani PS, Chen YT (2007) Glycogen storage disease types I and II: treatment updates. J Inherit Metab Dis 30:159–164
Koeberl DD, Pinto C, Sun B et al (2008) AAV vector-mediated reversal of hypoglycemia in canine and murine glycogen storage disease type Ia. Mol Ther 16:665–672
Koeberl DD, Kishnani PS, Bali D, Chen YT (2009) Emerging therapies for glycogen storage disease type I. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20:252–258
Korljan Jelaska B, Ostojic SB, Berovic N, Kokic V (2013) Continuous glucose monitoring in the treatment of obesity in patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep 2013:130056
Labrune P, Trioche P, Duvaltier I, Chevalier P, Odievre M (1997) Hepatocellular adenomas in glycogen storage disease type I and III: a series of 43 patients and review of the literature. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 24:276–279
Landau DJ, Brooks ED, Perez-Pinera P et al (2016) In vivo zinc finger nuclease-mediated targeted integration of a glucose-6-phosphatase transgene promotes survival in mice with glycogen storage disease type IA. Mol Ther 24:697–706
Lawrence NT, Chengsupanimit T, Brown LM, Weinstein DA (2015) High incidence of serologic markers of inflammatory bowel disease in asymptomatic patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. JIMD Rep 24:123–128
Lee PJ, Patel A, Hindmarsh PC, Mowat AP, Leonard JV (1995) The prevalence of polycystic ovaries in the hepatic glycogen storage diseases: its association with hyperinsulinism. Clin Endocrinol 42:601–606
Lee YM, Jun HS, Pan CJ et al (2012) Prevention of hepatocellular adenoma and correction of metabolic abnormalities in murine glycogen storage disease type Ia by gene therapy. Hepatology 56:1719–1729
Lee YM, Pan CJ, Koeberl DD, Mansfield BC, Chou JY (2013) The upstream enhancer elements of the G6PC promoter are critical for optimal G6PC expression in murine glycogen storage disease type Ia. Mol Genet Metab 110:275–280
Lennartson G, Lundblad A, Sjoblad S, Svensson S, Ockerman PA (1976) Quantitation of a urinary tetrasaccharide by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. Biomed Mass Spectrom 3:51–54
Luo X, Hall G, Li S et al (2011) Hepatorenal correction in murine glycogen storage disease type I with a double-stranded adeno-associated virus vector. Mol Ther 19:1961–1970
Manzia TM, Angelico R, Toti L et al (2011) Glycogen storage disease type Ia and VI associated with hepatocellular carcinoma: two case reports. Transplant Proc 43:1181–1183
Melis D, Rossi A, Pivonello R et al (2015) Glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSDIa) but not glycogen storage disease type Ib (GSDIb) is associated to an increased risk of metabolic syndrome: possible role of microsomal glucose 6-phosphate accumulation. Orphanet J Rare Dis 10:91
Minarich LA, Kirpich A, Fiske LM, Weinstein DA (2012) Bone mineral density in glycogen storage disease type Ia and Ib. Genet Med
Moraru E, Cuvinciuc O, Antonesei L et al (2007) Glycogen storage disease type I—between chronic ambulatory follow-up and pediatric emergency. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 16:47–51
Mutel E, Abdul-Wahed A, Ramamonjisoa N et al (2011) Targeted deletion of liver glucose-6 phosphatase mimics glycogen storage disease type 1a including development of multiple adenomas. J Hepatol 54:529–537
Nathwani AC, Tuddenham EG, Rangarajan S et al (2011) Adenovirus-associated virus vector-mediated gene transfer in hemophilia B. N Engl J Med 365:2357–2365
Oberholzer K, Sewell AC (1990) Unique oligosaccharide (apparently glucotetrasaccharide) in urine of patients with glycogen storage diseases. Clin Chem 36:1381
Okechuku GO, Shoemaker LR, Dambska M, Brown LM, Mathew J, Weinstein DA (2017) Tight metabolic control plus ACE inhibitor therapy improves GSD I nephropathy. J Inherit Metab Dis 40:703–708
Patnaik AK, Hurvitz AI, Lieberman PH, Johnson GF (1981) Canine hepatocellular carcinoma. Vet Pathol 18:427–438
Penhoat A, Fayard L, Stefanutti A, Mithieux G, Rajas F (2014) Intestinal gluconeogenesis is crucial to maintain a physiological fasting glycemia in the absence of hepatic glucose production in mice. Metabolism 63:104–111
Rake JP, Visser G, Labrune P, Leonard JV, Ullrich K, Smit GP (2002) Glycogen storage disease type I: diagnosis, management, clinical course and outcome. Results of the European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type I (ESGSD I). Eur J Pediatr 161(Suppl 1):S20–S34
Reddy SK, Kishnani PS, Sullivan JA et al (2007) Resection of hepatocellular adenoma in patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. J Hepatol 47:658–663
Sakellariou S, Al-Hussaini H, Scalori A et al (2012) Hepatocellular adenoma in glycogen storage disorder type I: a clinicopathological and molecular study. Histopathology 60:E58–E65
Schneider S, Breit SM, Grampp S et al (2004) Comparative assessment of bone mineral measurements obtained by use of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, peripheral quantitative computed tomography, and chemical-physical analyses in femurs of juvenile and adult dogs. Am J Vet Res 65:891–900
Sechi A, Deroma L, Lapolla A et al (2013) Fertility and pregnancy in women affected by glycogen storage disease type I, results of a multicenter Italian study. J Inherit Metab Dis 36:83–89
Sever S, Weinstein DA, Wolfsdorf JI, Gedik R, Schaefer EJ (2012) Glycogen storage disease type Ia: linkage of glucose, glycogen, lactic acid, triglyceride, and uric acid metabolism. J Clin Lipidol 6:596–600
Shestopaloff YK (2014) Method for finding metabolic properties based on the general growth law. Liver examples. A general framework for biological modeling. PLoS One 9:e99836
Sluiter W, van den Bosch JC, Goudriaan DA et al (2012) Rapid ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay for a characteristic glycogen-derived tetrasaccharide in Pompe disease and other glycogen storage diseases. Clin Chem 58:1139–1147
Sun B, Li S, Yang L et al (2009) Activation of glycolysis and apoptosis in glycogen storage disease type Ia. Mol Genet Metab 97:267–271
Talente GM, Coleman RA, Alter C et al (1994) Glycogen storage disease in adults. Ann Intern Med 120:218–226
van Dijk TH, Laskewitz AJ, Grefhorst A et al (2013) A novel approach to monitor glucose metabolism using stable isotopically labelled glucose in longitudinal studies in mice. Lab Anim 47:79–88
Visser G, Rake JP, Kokke FT, Nikkels PG, Sauer PJ, Smit GP (2002) Intestinal function in glycogen storage disease type I. J Inherit Metab Dis 25:261–267
Volmar KE, Burchette JL, Creager AJ (2003) Hepatic adenomatosis in glycogen storage disease type Ia: report of a case with unusual histology. Arch Pathol Lab Med 127:e402–e405
Wang DQ, Carreras CT, Fiske LM et al (2012) Characterization and pathogenesis of anemia in glycogen storage disease type Ia and Ib. Genet Med 14:795–799
Weinstein DA, Correia CE, Conlon T et al (2010) Adeno-associated virus-mediated correction of a canine model of glycogen storage disease type Ia. Hum Gene Ther 21:903–910
Yiu WH, Lee YM, Peng WT et al (2010) Complete normalization of hepatic G6PC deficiency in murine glycogen storage disease type Ia using gene therapy. Mol Ther 18:1076–1084
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge inspiration and support from Dr. Emory and Mrs. Mary Chapman and their son Christopher, and from Dr. John and Mrs. Michelle Kelly. We appreciate the care that these dogs received from the Duke Division of Laboratory Animal Resources staff, namely Ms. Laura Jordan and the veterinary support from Drs. Francis Sun, Amanda DeMaster, Sarah Faircloth, Shannon Smith, Feli Smith, Angela Garner, and Jai Tubbs, and veterinary technicians, namely Christian Marsini, Kelly Franke, Diego Zapata, and Jeff Lee. The collective support from the multiple students and staff in the dog feeding team over these years ensured a long, comfortable life for the GSD Ia dogs.
Funding
This work received funding provided by the Children’s Fund for GSD Research, Children’s Miracle Network, Association for Glycogen Storage Disease, For the Love of Christopher, and the Alice and YT Chen Center for Pediatric Genetics and Genomics, and grant R01DK105434-01A1 from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
E. D. Brooks, D. J. Landau, J. I. Everitt, T. T. Brown, K. M. Grady, L. Waskowicz, C. R. Bass, J. D’Angelo, Y. G. Asfaw, K. Williams, P. Kishnani, and D. D. Koeberl declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Animal rights
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Additional information
Communicating Editor: Terry G.J. Derks
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 12 kb)
Supplementary Figure 1
Area under the curve (AUC) of 8-hour fasted glucose curves over the lifetime of GSD Ia AAV-G6Pase treated dogs. *indicates glucose curve 2-4 weeks after last vector treatment. See Table 1 for vector therapy summary, excluding dog T, which had poor response to all vector therapies given and data is not included in main document. (JPG 957 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
a. Hepatic G6Pase from individual dogs at necropsy. b. Vector DNA copies/cell in dog liver at necropsy; mean ± SD for untreated dogs. (JPG 167 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
Serum enzyme concentrations of GSD Ia dogs throughout lifetime; Open symbols denote female dogs. Dotted lines denote enzyme concentrations for normal dogs. ^ denote that some values were higher than lab was able to detect. Dog De was >993 for ALP at 3 years of age, dogs De and H were >993 for ALP at 4 years of age, and dogs R and L were >993 for ALP at 6 years of age. Dog De was >450 for cholesterol at 3 years of age and dog L was >450 for cholesterol at 6 years of age. (JPG 432 kb)
Supplementary Figure 4
a. Urolithiasis detected in Dog L on Radiographs at 8 years of age, urinary bladder denoted by circle. b. Urolith surgically removed from Dog De at 4 years of age. c. Renal cysts from Dog R at 5.7 years of age. d. Polycystic Ovaries in GSD Ia carrier, Dog A at 5 years of age. (JPG 343 kb)
Supplementary Figure 5
Bone mineral densities of the femurs of GSD Ia dogs compared to a GSD Ia carrier. Mean ± SD of 5 different measurements through QCT. Dotted lines represent BMD range obtained from Schneider et al. 2006 in normal dog femurs. (PNG 43 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brooks, E.D., Landau, D.J., Everitt, J.I. et al. Long-term complications of glycogen storage disease type Ia in the canine model treated with gene replacement therapy. J Inherit Metab Dis 41, 965–976 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-018-0223-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-018-0223-y