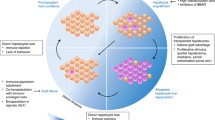
Abstract
The applications, outcomes and future strategies of hepatocyte transplantation (HTx) as a corrective intervention for inherited metabolic disease (IMD) are described. An overview of HTx in IMDs, as well as preclinical evaluations in rodent and other mammalian models, is summarized. Current treatments for IMDs are highlighted, along with short- and long-term outcomes and the potential for HTx to supplement or supplant these treatments. Finally, the advantages and disadvantages of HTx are presented, highlighted by long-term challenges with interorgan engraftment and expansion of transplanted cells, in addition to the future prospects of stem cell transplants. At present, the utility of HTx is represented by the potential to bridge patients with life-threatening liver disease to organ transplantation, especially as an adjuvant intervention where severe organ shortages continue to pose challenges.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AGT:
-
Alanine glyoxylate transaminase
- APOLT:
-
Auxiliary partial orthotopic liver transplant
- ASL:
-
Argininosuccinate lyase
- ASS:
-
Argininosuccinate synthetase
- BCAA:
-
Branched-chain amino acids
- BCKA:
-
Branched-chain keto acids
- BCKDH:
-
Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase complex
- CNSI:
-
Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I
- CPSI:
-
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
- FAH:
-
Fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase deficiency (tyrosinemia type I)
- GSD:
-
Glycogen storage disease
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- HDL:
-
High density lipoprotein
- HGF:
-
Hepatic growth factor
- HTx:
-
Hepatocyte transplantation
- KIC:
-
α-Ketoisocaproic acid
- LDL:
-
Low density lipoprotein
- MSUD:
-
Maple syrup urine disease
- NAGS:
-
N-acetylglutamate synthetase
- OLT:
-
Orthotopic liver transplantation
- OTC:
-
Ornithine transcarbamylase
- PFIC:
-
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis
- PHE:
-
Phenylalanine
- PH:
-
Primary Hyperoxaluria
- PKU:
-
Phenylketonuria
- UGT:
-
Bilirubin-UDP-glucuronosyl transferase
References
Al-Dhalimy M, Overturf K, Finegold M, Grompe M (2002) Long-term therapy with NTBC and tyrosine-restricted diet in a murine model of hereditary tyrosinemia type I. Mol Genet Metab 75:38–45. doi:10.1006/mgme.2001.3266
Allian-Sauer MU, Falko JM (2012) New treatments on the horizon for familial hypercholesterolemia. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 10:1227–1237. doi:10.1586/erc.12.112
Ambrosino G, Varotto S, Strom SC et al (2005) Isolated hepatocyte transplantation for Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1. Cell Transplant 14:151–157
Beck BB, Habbig S, Dittrich K et al (2012) Liver cell transplantation in severe infantile oxalosis–a potential bridging procedure to orthotopic liver transplantation? Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:2984–2989. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfr776
Bélanger-Quintana A, Burlina A, Harding CO, Muntau AC (2011) Up to date knowledge on different treatment strategies for phenylketonuria. Mol Genet Metab 104(Suppl):S19–S25. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.08.009
Burlina AB (2004) Hepatocyte transplantation for inborn errors of metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis 27:373–383. doi:10.1023/B:BOLI.0000031095.57411.8d
Campeau PM, Pivalizza PJ, Miller G et al (2010) Early orthotopic liver transplantation in urea cycle defects: follow up of a developmental outcome study. Mol Genet Metab 100(Suppl 1):S84–S87. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.02.012
Chen H-L, Chen H-L, Yuan R-H et al (2012) Hepatocyte transplantation in bile salt export pump-deficient mice: selective growth advantage of donor hepatocytes under bile acid stress. J Cell Mol Med 16:2679–2689. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01586.x
Chistiakov DA (2012) Liver regenerative medicine: advances and challenges. Cells Tissues Organs (Print) 196:291–312. doi:10.1159/000335697
Crigler JF, Najjar VA (1952) Congenital familial nonhemolytic jaundice with kernicterus. Pediatrics 10:169–180
Cubero FJ, Maganto P, Mula N et al (2007) Functional response of hepatocytes transplanted into Gunn rats stimulated with thyroid hormone. Dig Dis Sci 52:210–216. doi:10.1007/s10620-006-9614-2
De Vree JM, Ottenhoff R, Bosma PJ et al (2000) Correction of liver disease by hepatocyte transplantation in a mouse model of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology 119:1720–1730
Dhawan A, Mitry RR, Hughes RD et al (2004) Hepatocyte transplantation for inherited factor VII deficiency. Transplantation 78:1812–1814
Dyer CA (1999) Pathophysiology of phenylketonuria. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 5:104–112. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2779(1999)5:2<104::AID-MRDD2>3.0.CO;2–7
Ellis SR, Hulton SA, McKiernan PJ et al (2001) Combined liver-kidney transplantation for primary hyperoxaluria type 1 in young children. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:348–354
Erker L, Azuma H, Lee AY et al (2010) Therapeutic liver reconstitution with murine cells isolated long after death. Gastroenterology 139:1019–1029. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.05.082
Fenu M, Liggi M, Demelia E et al (2012) Kayser-Fleischer ring in Wilson’s disease: a cohort study. Eur J Intern Med 23:e150–e156. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2012.04.005
Fox IJ, Chowdhury JR, Kaufman SS et al (1998) Treatment of the Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I with hepatocyte transplantation. N Engl J Med 338:1422–1426. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805143382004
Gautschi M, Pavlovic M, Nuoffer J-M (2012) Fatal myocardial infarction at 4.5 years in a case of homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. JIMD Rep 2:45–50. doi:10.1007/8904_2011_45
Grossman M, Raper SE, Kozarsky K et al (1994) Successful ex vivo gene therapy directed to liver in a patient with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Nat Genet 6:335–341. doi:10.1038/ng0494-335
Guha C, Parashar B, Deb NJ et al (2002) Normal hepatocytes correct serum bilirubin after repopulation of Gunn rat liver subjected to irradiation/partial resection. Hepatology 36:354–362. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.34516
Guha C, Yamanouchi K, Jiang J et al (2005) Feasibility of hepatocyte transplantation-based therapies for primary hyperoxalurias. Am J Nephrol 25:161–170. doi:10.1159/000085408
Hamman K, Clark H, Montini E et al (2005) Low therapeutic threshold for hepatocyte replacement in murine phenylketonuria. Mol Ther 12:337–344. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2005.03.025
Hamman KJ, Winn SR, Harding CO (2011) Hepatocytes from wild-type or heterozygous donors are equally effective in achieving successful therapeutic liver repopulation in murine phenylketonuria (PKU). Mol Genet Metab 104:235–240. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.07.027
Harding CO (2010) New era in treatment for phenylketonuria: pharmacologic therapy with sapropterin dihydrochloride. Biologics 4:231–236
Homanics GE, Skvorak K, Ferguson C et al (2006) Production and characterization of murine models of classic and intermediate maple syrup urine disease. BMC Med Genet 7:33. doi:10.1186/1471-2350-7-33
Hoppe B (2012) An update on primary hyperoxaluria. Nat Rev Nephrol 8:467–475. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2012.113
Horslen SP, Fox IJ (2004) Hepatocyte transplantation. Transplantation 77:1481–1486
Horslen SP, McCowan TC, Goertzen TC et al (2003) Isolated hepatocyte transplantation in an infant with a severe urea cycle disorder. Pediatrics 111:1262–1267
Huether SE (2010) Structure and function of the digestive system. In: McCance KL, Huether SE, Brashers VL, Rote NS (eds) Pathophysiology: The biological basis for disease in adults and children, 6th edn, chap 38. Mosby Elsevier, pp 1420–1451
Irani AN, Malhi H, Slehria S et al (2001) Correction of liver disease following transplantation of normal rat hepatocytes into Long-Evans cinnamon rats modeling Wilson’s disease. Mol Ther 3:302–309. doi:10.1006/mthe.2001.0271
Jacquemin E (2012) Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 36(Suppl 1):S26–S35. doi:10.1016/S2210-7401(12)70018-9
Jankowska I, Socha P (2012) Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis and inborn errors of bile acid synthesis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 36:271–274. doi:10.1016/j.clinre.2012.03.020
Jiang J, Salido EC, Guha C et al (2008) Correction of hyperoxaluria by liver repopulation with hepatocytes in a mouse model of primary hyperoxaluria type-1. Transplantation 85:1253–1260. doi:10.1097/TP.0b013e31816de49e
Joseph B, Kapoor S, Schilsky ML, Gupta S (2009) Bile salt-induced pro-oxidant liver damage promotes transplanted cell proliferation for correcting Wilson disease in the Long-Evans Cinnamon rat model. Hepatology 49:1616–1624. doi:10.1002/hep.22792
Kakaei F, Nikeghbalian S, Kazemi K et al (2009) Liver transplantation for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: two case reports. Transplant Proc 41:2939–2941. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.07.028
Karnezis AN, Dorokhov M, Grompe M, Zhu L (2001) Loss of p27(Kip1) enhances the transplantation efficiency of hepatocytes transferred into diseased livers. J Clin Invest 108:383–390. doi:10.1172/JCI11933
Kawashita Y, Guha C, Moitra R et al (2008) Hepatic repopulation with stably transduced conditionally immortalized hepatocytes in the Gunn rat. J Hepatol 49:99–106. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2008.02.020
Kim PK (2009) Peroxisome assembly, degradation, and disease. In: Medicine IMASSE of PV of (ed) The liver. Wiley, New York, pp 191–200
Kochanek K, Xu J, Murphy S, Minino A (2011) Deaths: Final Data for 2009. National Vital Statistics Reports 60
LaClair CE, Ney DM, MacLeod EL, Etzel MR (2009) Purification and use of glycomacropeptide for nutritional management of phenylketonuria. J Food Sci 74:E199–E206. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01134.x
Lee K-W, Lee J-H, Shin SW et al (2007) Hepatocyte transplantation for glycogen storage disease type Ib. Cell Transplant 16:629–637
Legido-Quigley C, Cloarec O, Parker DA et al (2009) First example of hepatocyte transplantation to alleviate ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency, monitored by NMR-based metabonomics. Bioanalysis 1:1527–1535. doi:10.4155/bio.09.112
Li AP (2007) Human hepatocytes: isolation, cryopreservation and applications in drug development. Chem Biol Interact 168:16–29. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2007.01.001
Lysy P-A, Najimi M, Stephenne X et al (2008) Liver cell transplantation for Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I: update and perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 14:3464–3470
MacDonald A (2000) Diet and compliance in phenylketonuria. Eur J Pediatr 159(Suppl 2):S136–S141
Malhi H, Irani AN, Volenberg I et al (2002) Early cell transplantation in LEC rats modeling Wilson’s disease eliminates hepatic copper with reversal of liver disease. Gastroenterology 122:438–447
Mazariegos GV, Morton DH, Sindhi R et al (2012) Liver transplantation for classical maple syrup urine disease: long-term follow-up in 37 patients and comparative United Network for Organ Sharing experience. J Pediatr 160:116–121.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.06.033
McCandless DW (2011) The Gunn rat model. Kernicterus. Humana Press, pp 51–64
Meyburg J, Hoffmann GF (2010) Liver, liver cell and stem cell transplantation for the treatment of urea cycle defects. Mol Genet Metab 100(Suppl 1):S77–S83. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.01.011
Meyburg J, Das AM, Hoerster F et al (2009) One liver for four children: first clinical series of liver cell transplantation for severe neonatal urea cycle defects. Transplantation 87:636–641. doi:10.1097/TP.0b013e318199936a
Mitry RR, Dhawan A, Hughes RD et al (2004) One liver, three recipients: segment IV from split-liver procedures as a source of hepatocytes for cell transplantation. Transplantation 77:1614–1616
Mohamadnejad M, Pournasr B, Bagheri M et al (2010) Transplantation of allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Cytotherapy 12:566–568. doi:10.3109/14653240903511143
Muraca M, Gerunda G, Neri D et al (2002) Hepatocyte transplantation as a treatment for glycogen storage disease type 1a. Lancet 359:317–318. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07529-3
Muraca M, Ferraresso C, Vilei MT et al (2007) Liver repopulation with bone marrow derived cells improves the metabolic disorder in the Gunn rat. Gut 56:1725–1735. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.127969
Okura H, Saga A, Fumimoto Y et al (2011) Transplantation of human adipose tissue-derived multilineage progenitor cells reduces serum cholesterol in hyperlipidemic Watanabe rabbits. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 17:145–154. doi:10.1089/ten.TEC.2010.0139
Olivarez L, Caggana M, Pass KA et al (2001) Estimate of the frequency of Wilson’s disease in the US Caucasian population: a mutation analysis approach. Ann Hum Genet 65:459–463. doi:10.1017/S0003480001008764
Ordonez MP, Goldstein LSB (2012) Using human-induced pluripotent stem cells to model monogenic metabolic disorders of the liver. Semin Liver Dis 32:298–306. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1329898
Orejuela D, Jorquera R, Bergeron A et al (2008) Hepatic stress in hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 (HT1) activates the AKT survival pathway in the fah−/− knockout mice model. J Hepatol 48:308–317. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2007.09.014
Overturf K, Al-Dhalimy M, Finegold M, Grompe M (1999) The repopulation potential of hepatocyte populations differing in size and prior mitotic expansion. Am J Pathol 155:2135–2143. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65531-9
Ozçay F, Alehan F, Sevmiş S et al (2009) Living related liver transplantation in Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1. Transplant Proc 41:2875–2877. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.07.025
Park SM, Vo K, Lallier M et al (2006) Hepatocyte transplantation in the Long Evans cinnamon rat model of Wilson’s disease. Cell Transplant 15:13–22
Paulk NK, Wursthorn K, Haft A et al (2012) In vivo selection of transplanted hepatocytes by pharmacological inhibition of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase in wild-type mice. Mol Ther 20:1981–1987. doi:10.1038/mt.2012.154
Peña MMO, Lee J, Thiele DJ (1999) A delicate balance: homeostatic control of copper uptake and distribution. J Nutr 129:1251–1260
Popov Y, Patsenker E, Fickert P et al (2005) Mdr2 (Abcb4)−/− mice spontaneously develop severe biliary fibrosis via massive dysregulation of pro- and antifibrogenic genes. J Hepatol 43:1045–1054. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2005.06.025
Puppi J, Tan N, Mitry RR et al (2008) Hepatocyte transplantation followed by auxiliary liver transplantation—a novel treatment for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Am J Transplant 8:452–457. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.02058.x
Puppi J, Strom SC, Hughes RD et al (2012) Improving the techniques for human hepatocyte transplantation: report from a consensus meeting in London. Cell Transplant 21:1–10. doi:10.3727/096368911X566208
Quaglia A, Lehec SC, Hughes RD, Mitry RR, Knisely AS, Devereaux S, Richards J, Rela M, Heaton ND, Portmann BC, Dhawan A (2008) Liver after hepatocyte transplantation for liver-based metabolic disorders in children. Cell Transplant 17:1403–1414
Rela M, Muiesan P, Vilca-Melendez H et al (1999) Auxiliary partial orthotopic liver transplantation for Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I. Ann Surg 229:565–569
Ribes-Koninckx C, Pareja Ibars E, Agrasot MAC et al (2012) Clinical outcome of hepatocyte transplantation in four pediatric patients with inherited metabolic diseases. Cell Transplant. doi:10.3727/069368912X637505
Sampietro M, Iolascon A (1999) Molecular pathology of Crigler-Najjar type I and II and Gilbert’s syndromes. Haematologica 84:150–157
Schönberger S, Schweiger B, Schwahn B et al (2004) Dysmyelination in the brain of adolescents and young adults with maple syrup urine disease. Mol Genet Metab 82:69–75. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2004.01.016
Skvorak KJ, Hager EJ, Arning E et al (2009a) Hepatocyte transplantation (HTx) corrects selected neurometabolic abnormalities in murine intermediate maple syrup urine disease (iMSUD). Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:1004–1010. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.08.006
Skvorak KJ, Paul HS, Dorko K et al (2009b) Hepatocyte transplantation improves phenotype and extends survival in a murine model of intermediate maple syrup urine disease. Mol Ther 17:1266–1273. doi:10.1038/mt.2009.99
Skvorak KJ, Dorko K, Marongiu F et al (2013a) Placental stem cell correction of murine intermediate maple syrup urine disease. Hepatology 57:1017–1023. doi:10.1002/hep.26150
Skvorak KJ, Dorko K, Marongiu F, Tahan V, Hansel MC, Gramignoli R, Arning E, Bottiglieri T, Gibson KM, Strom SC (2013b) Improved amino acid, bioenergetic metabolite and neurotransmitter profiles following human amnion epithelial cell transplant in intermediate maple syrup urine disease. Mol Genet Metab 109:132–138
Sokal EM, Smets F, Bourgois A et al (2003) Hepatocyte transplantation in a 4-year-old girl with peroxisomal biogenesis disease: technique, safety, and metabolic follow-up. Transplantation 76:735–738. doi:10.1097/01.TP.0000077420.81365.53
Stéphenne X, Najimi M, Smets F et al (2005) Cryopreserved liver cell transplantation controls ornithine transcarbamylase deficient patient while awaiting liver transplantation. Am J Transplant 5:2058–2061. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.00935.x
Stéphenne X, Najimi M, Sibille C et al (2006) Sustained engraftment and tissue enzyme activity after liver cell transplantation for argininosuccinate lyase deficiency. Gastroenterology 130:1317–1323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.01.008
Stéphenne X, Debray FG, Smets F et al (2012) Hepatocyte transplantation using the domino concept in a child with tetrabiopterin nonresponsive phenylketonuria. Cell Transplant 21:2765–2770. doi:10.3727/096368912X653255
Strauss KA, Mazariegos GV, Sindhi R et al (2006a) Elective liver transplantation for the treatment of classical maple syrup urine disease. Am J Transplant 6:557–564. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01209.x
Strauss KA, Robinson DL, Vreman HJ et al (2006b) Management of hyperbilirubinemia and prevention of kernicterus in 20 patients with Crigler-Najjar disease. Eur J Pediatr 165:306–319. doi:10.1007/s00431-005-0055-2
Strauss KA, Wardley B, Robinson D et al (2010) Classical maple syrup urine disease and brain development: principles of management and formula design. Mol Genet Metab 99:333–345. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.12.007
Strom SC, Fisher RA, Rubinstein WS, Barranger JA, Towbin RB, Charron M, Mieles L, Pisarov LA, Dorko K, Thompson MT, Reyes J (1997) Transplantation of human hepatocytes. Transplantation Proc 29:2103–2106
Van Maldergem L, Moser AB, Vincent M-F et al (2005) Orthotopic liver transplantation from a living-related donor in an infant with a peroxisome biogenesis defect of the infantile Refsum disease type. J Inherit Metab Dis 28:593–600. doi:10.1007/s10545-005-0593-9
Wan Z, Zhang X-G, Liu Z-W, Lv Y (2013) Therapeutic liver repopulation for metabolic liver diseases: advances from bench to bedside. Hepatol Res 43:122–130. doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01081.x
Watanabe Y (1980) Serial inbreeding of rabbits with hereditary hyperlipidemia (WHHL-rabbit). Atherosclerosis 36:261–268
Weiss KH, Gotthardt D, Schmidt J et al (2007) Liver transplantation for metabolic liver diseases in adults: indications and outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:viii9–viii12. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfm658
Yoshida Y, Tokusashi Y, Lee GH, Ogawa K (1996) Intrahepatic transplantation of normal hepatocytes prevents Wilson’s disease in Long-Evans cinnamon rats. Gastroenterology 111:1654–1660
Yu Y, Fisher JE, Lillegard JB et al (2012) Cell therapies for liver diseases. Liver Transpl 18:9–21. doi:10.1002/lt.22467
Zhang KY, Tung BY, Kowdley KV (2007) Liver transplantation for metabolic liver diseases. Clin Liver Dis 11:265–281. doi:10.1016/j.cld.2007.04.002
Zhou H, Dong X, Kabarriti R et al (2012) Single liver lobe repopulation with wildtype hepatocytes using regional hepatic irradiation cures jaundice in Gunn rats. PLoS ONE 7:e46775. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046775
Zinnanti WJ, Lazovic J (2012) Interrupting the mechanisms of brain injury in a model of maple syrup urine disease encephalopathy. J Inherit Metab Dis 35:71–79. doi:10.1007/s10545-011-9333-5
Zinnanti WJ, Lazovic J, Griffin K et al (2009) Dual mechanism of brain injury and novel treatment strategy in maple syrup urine disease. Brain 132:903–918. doi:10.1093/brain/awp024
Zolotov D, Wagner S, Kalb K et al (2012) Long-term strategies for the treatment of Refsum’s disease using therapeutic apheresis. J Clin Apher 27:99–105. doi:10.1002/jca.21200
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Jerry Vockley
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogel, K.R., Kennedy, A.A., Whitehouse, L.A. et al. Therapeutic hepatocyte transplant for inherited metabolic disorders: functional considerations, recent outcomes and future prospects. J Inherit Metab Dis 37, 165–176 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-013-9656-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-013-9656-5