Summary
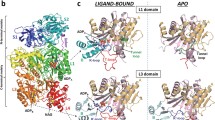
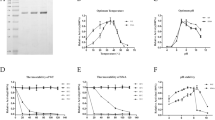
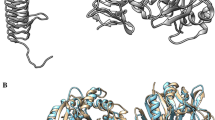
Human carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (hCPS) has evolved three features that allow it to remove excess, potentially neurotoxic ammonia via the urea cycle: inability to use glutamine as an alternative nitrogen donor; a K m for ammonia 100-fold lower than for CPSs that also use glutamine; and required allosteric activation by N-acetylglutamate (AGA), a sensor of excess amino acids. To determine the structural features of hCPS that allow its unique functioning, we have developed the first recombinant expression system for hCPS, utilizing Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Of several common single-nucleotide polymorphisms identified in the gene encoding hCPS, only the one resulting in substitution of threonine at position 1406 with asparagine has been linked to phenotypic effects. We have expressed and characterized both variants of hCPS. The asparagine polymorph, hCPS_N, consistently displayed inferior catalytic properties, but the K m and k cat values for overall and partial reactions varied only by a factor of 1.7 or less. We have designed and characterized an hCPS construction from which the N-terminal domain A is deleted. hCPS_ΔA was competent to bind AGA, demonstrating that domain A does not contain the AGA binding site. Thus, the site at the C/D boundary previously identified by AGA analogue labelling appears to be the functionally significant initial binding site for AGA. However, hCPS_ΔA was not able to fully assume the catalytically competent conformation, with specific activity of CP formation decreased 700-fold.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson PM (1995) Molecular aspects of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. In: Walsh PJ, Wright P, eds. Nitrogen Metabolism and Excretion. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 33–49.
Anderson PM, Meister A (1966) Bicarbonate-dependent cleavage of adenosine triphosphate and other reactions catalyzed by Escherichia coli carbamyl phosphate synthetase. Biochemistry 5: 3157–3163.
Batshaw ML (1994) Inborn errors of urea synthesis. Ann Neurol 35: 133–141.
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254.
Britton HG, Rubio V (1988) Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I. Kinetics of binding and dissociation of acetylglutamate and of activation and deactivation. Eur J Biochem 171: 615–622.
Cohen NS, Kyan FS, Kyan SS, Cheung CW, Raijman L (1985) The apparent K m of ammonia for carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (ammonia) in situ. Biochem J 229: 205–211.
Czerwinski RM, Mareya SM, Raushel FM (1995) Regulatory changes in the control of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase induced by truncation and mutagenesis of the allosteric binding domain. Biochemistry 34: 13920–13927.
Finckh U, Kohlschutter A, Schafer H, Sperhake K, Colombo J, Gal A (1998) Prenatal diagnosis of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency by identification of a missense mutation in CPSI. Hum Mutat 12, 206–211.
Guthohrlein G, Knappe J (1968) Modified determination of citrulline. Anal Biochem 26: 188–191.
Han J, Pope M, Borchers C, Graves LM (2002) Mapping of protein phosphorylation by dual enzyme digestion and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-quadrupole orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 310: 215–218.
Haraguchi Y, Uchino T, Takiguchi M, Endo F, Mori M, Matsuda I (1991) Cloning and sequence of a cDNA encoding human carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I: molecular analysis of hyperammonemia. Gene 107: 335–340.
Hosfield TS, Lu Q (1999) S. pombe expression vector with 6X (His) tag for protein purification and potential for ligation-independent cloning. Biotechniques 27: 58–60
Hoshide R, Matsuura T, Haraguchi Y, Endo F, Yoshinaga M, Matsuda I (1993) Carbamyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency. J Clin Invest 91: 1884–1887.
Kothe M, Purcarea C, Guy HI, Evans DR, Powers-Lee SG (2005) Direct demonstration of carbamoyl phosphate formation on the C-terminal domain of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. Prot Sci 14: 37–44 (Epub 2 Dec Epub 2004 Dec 2).
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Lawson FS, Charlesbois RL, Dillon JR (1996) Phylogenetic analysis of carbamoylphosphate synthetase genes: complex evolutionary history includes an internal duplication within a gene which can root the tree of life. Mol Biol Evol 13: 970–977.
Lim AL, Powers-Lee SG (1996) Requirement for the carboxyl-terminal domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem 271, 11400–11409.
Lusty CJ (1977) Carbamyl phosphate synthetase. Bicarbonate-dependent hydrolysis of ATP and potassium activation. J Biol Chem 253: 4270–4278.
Lusty CJ (1978) Carbamoylphosphate synthetase I of rat-liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem 85: 373–383.
McCudden CR, Powers-Lee SG (1996) Required allosteric effector site for N-acetylglutamate on carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I. J Biol Chem 271: 18285–18294.
Meister A, Powers-Lee SG (1978) Glutamine-dependent carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: catalysis and regulation. Adv Enzyme Regul 16: 289–315.
Mommsen TP, Walsh PJ (1989) Evolution of urea synthesis in vertebrates: the piscine connection. Science 243: 72–75.
Murzin AG (1996) Structural classification of proteins: new superfamilies. Curr Opin Struct Biol 6: 386–394.
Nyunoya H, Lusty CJ (1983) The carB gene of Escherichia coli: A duplicated gene coding for the large subunit of carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80: 4629–4633.
Nyunoya H, Broglie KE, Widgren EE, Lusty CJ (1985) Characterization and derivation of the gene coding for mitochondrial carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I of rat. J Biol Chem 260: 9346–9356.
Pearson DL, Dawling S, Walsh WF, et al (2001) Neonatal pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med 344: 1832–1838.
Penefsky HS (1977) Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem 252: 2891–2899.
Pierson DL, Brien JM (1980) Human carbamylphosphate synthetase I. J Biol Chem 255: 7891–7895.
Powers-Lee SG, Corina K (1986) Domain structure of rat liver carbamyl phosphate synthetase I. J Biol Chem 261: 15349–15353.
Powers-Lee SG, Meister A (1988) Urea synthesis and ammonia metabolism. In: Arias IM, Jakoby WB, Popper H, Schachter D, Shafritz DA, eds. The Liver: Biology and Pathology, 2nd edn. New York: Raven Press, 317–329
Rodriguez-Aparicio LB, Guadalajara AM, Rubio V (1989) Physical location of the site for N-acetyl-L-glutamate, the allosteric activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, in the 20-kilodalton COOH-terminal domain. Biochemistry 28: 3070–3074.
Rubio V, Britton HG, Grisolia S (1983a) Mitochondrial carbamoyl phosphate synthetase activity in the absence of N-acetyl-l-glutamate. Eur J Biochem 134: 337–343.
Rubio V, Britton HG., Grisolia S (1983b) Activation of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase by cryoprotectants. Mol Cell Biochem 53–54, 279–298.
Saeed-Kothe A, Powers-Lee SG (2002) Specificity determining residues in ammonia- and glutamine-dependent carbamoyl phosphate synthetases. J Biol Chem 277: 7231–7238.
Saeed-Kothe A, Powers-Lee SG (2003) Gain of glutaminase function in mutants of the ammonia-specific frog carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. J Biol Chem 278: 26722–26726.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Schofield JP (1993) Molecular studies on an ancient gene encoding for carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase. Clin Sci 84: 119–128.
Summar ML, Hall L, Christman B, et al (2004a) Environmentally determined genetic expression: clinical correlates with molecular variants of carbamyl phosphate synthetase I. Mol Genet Metab 81(Supplement 1): S12–S19.
Summar ML, Gainer JV, Pretorius M, et al (2004b) Relationship between carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase genotype and systemic vascular function. Hypertension 43: 186–191.
Thoden JB, Holden HM, Wesenberg G, Raushel FM, Rayment I (1997) Structure of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: a journey of 96 Å from substrate to product. Biochemistry 36: 6305–6316.
Thoden JB, Raushel FM, Benning MM, Rayment I, Holden HM (1999) The structure of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase determined to 2.1 Å resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 55: 8–24.
Vosatka RJ (2002) Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. N Engl J Med 346: 864.
Zalkin H, Smith JL (1998) Enzymes utilizing glutamine as an amide donor. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 72: 87–144.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: Michael Gibson
Competing interests: None declared
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahuja, V., Powers-Lee, S.G. Human carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase: Insight into N-acetylglutamate interaction and the functional effects of a common single nucleotide polymorphism. J Inherit Metab Dis 31, 481–491 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0913-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0913-y