Summary
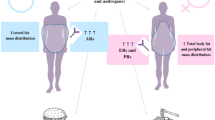
The natural history of inborn errors of protein metabolism and the long-term effects of prescribed semisynthetic therapeutic diets are largely unknown. We assessed body composition, measuring body-fat mass and distribution, fat-free mass, total body protein, total body potassium, bone density and skeletal muscle mass, in young adults (age > 18 years; 6 female, 5 male) with inborn errors of protein metabolism maintained on long-term low-protein diets, compared with controls. Female patients were significantly shorter (159.4 cm vs 169.2 cm, p = 0.013) and had higher BMI (25.3 vs 22.0 kg/m2, p < 0.05), abdominal to gluteal circumference ratio (0.84 vs 0.73, p = 0.011), percentage body fat (42.3% vs 29.5%, p < 0.005) and ratio of central to peripheral body fat (1.15 vs 0.86, p < 0.05) than controls. Male patients had lower height-adjusted total body bone mineral content (0.9 vs 1.02 g/m2, p < 0.04) and skeletal muscle mass (31.1 vs 36.3 kg, p < 0.04) than controls. Compared with controls, patients’nitrogen index was significantly lower (0.91 vs 1.03, p < 0.01), consistent with lower total body protein. Potassium index was significantly higher (121.2% vs 110.4%, p < 0.03), consistent with higher body cell mass, or intracellular water. Documentation of body composition in larger patient series is important to elucidate whether these results reflect increased risks (hence opportunities for prevention) of bone disease, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease in this population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlercreutz H, Hockerstedt K, Bannwart C, et al (1987) Effect of dietary components, including lignans and phytoestrogens, on enterohepatic circulation and liver metabolism of estrogens and on sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). J Steroid Biochem 27: 1135–1344.
Anderson KE, Conney AH, Kappas A (1984) The influence of dietary protein and carbohydrate on the principal oxidative biotransformations of estradiol in normal subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 59: 103–107.
Bergstrom J, Hultman E (1987) Determination of water and electrolytes in muscle biopsies in the nutritional assessment of clinical disorders. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 11 (5 supplement): 51S–54S.
Berrino F, Bellati C, Secreto G, et al (2001) Reducing bioavailable sex hormones through a comprehensive change in diet: the diet and androgens (DIANA) randomized trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10: 25–33.
Bisnuth C, Elford M, van Prooyen G (1992) Calibration of a shadow shield detector. MSc thesis, Swinburne Institute of Technology, Victoria, Australia.
Bjorntorp P (1997) Body fat distribution, insulin resistance, and metabolic diseases. Nutrition 13: 795–803.
Bruce A, Andersson M, Arvidsson B, Isaksson B (1980) Body composition. Prediction of normal body potassium, body water and body fat in adults on the basis of body height, body weight and age. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 40: 461–473.
Bushinsky DA, Ori Y (1993) Effects of metabolic and respiratory acidosis on bone. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2: 588–596.
Domrongkitchaiporn S, Pongsakul C, Stitchantrakul W, et al (2001) Bone mineral density and histology in distal renal tubular acidosis. Kidney Int 59: 1086–1093. %%Brown C, Clevidence BA, Campbell WS, Nair PP, Franz C, Kahle L, Taylor PR
Dorgan JF, Judd JT, Longcope C, et al (1996) Dietary fat and fiber effects on plasma and urine androgen and estrogen levels in men: a controlled feeding study. Am J Clin Nutr 64: 850–855.
Eiam-ong S, Kurtzman NA (1994) Metabolic acidosis and bone disease. Miner Electrolyte Metab 20: 72–80.
Fruehwald-Schultes B, Kern W, Born J, Fehm HL, Peters A (2001) Hyperinsulinemia causes activation of the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis in humans. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25 (supplement 1): S38–S40.
Goldin BR, Woods MN, Spiegelman DL, et al (1994) The effect of dietary fat and fiber on serum estrogen concentrations in premenopausal women under controlled dietary conditions. Cancer 74: S1125–S1131.
Goran MI (1997) Energy expenditure, body composition, and disease risk in children and adolescents. Proc Nutr Soc 56: 195–209.
Infante D, Tormo R (2000) Risk of inadequate bone mineralization in diseases involving long term suppression of dairy products. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 30: 310–313.
Kim J Wang Z, Heymsfield SB, Baumgartner RN, Gallagher D (2002) Total body skeletal muscle mass: estimation by a new dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry method. Am J Clin Nutr 76: 378–383.
Kerstetter JE, Svastisalee CM, Caseria DM, Mitnick MAE, Insogna KL (2000) A threshold for low-protein-diet-induced elevations in parathyroid hormone. Am J Clin Nutr 72: 168–173.
Leidig-Bruckner G, Ziegler R (2001) Diabetes mellitus a risk for osteoporosis? Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 109 (supplement 2): 493–514.
Lindberg JS, Moe SM (1999) Osteoporosis in end-state renal disease. Semin Nephrol 19: 115–122.
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorel R, eds (1988) Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual. Illinois: Human Kinetics Books.
Luke A, Schoeller DA (1992) Basal metabolic rate, fat-free mass, and body cell mass during energy restriction. Metabolism 41: 450–456.
Mazess RB, Bardin HS, Bisek JP, Hanson J (1990) Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry for total body and regional bone-mineral and soft tissue composition. Am J Clin Nutr 51: 1106–1112.
McDevitt RM, Poppitt SD, Murgatroyd PR, Prentice AM (2000) Macronutrient disposal during controlled overfeeding with glucose, fructose, sucrose, or fat in lean and obese women. Am J Clin Nutr 72: 369–377.
Muller MJ, Bosy-Westphal A, Kutzner D, Heller M (2002) Metabolically active components of fat-free mass and resting energy expenditure in humans: recent lessons from imaging technologies. Obes Rev 3: 113–122.
Noguchi T (2000) Protein nutrition and insulin-like growth factor system. Br J Nutr 84 (supplement 2): S241–S244.
Parrot F, Redonnet-Vernhet I, Lacombe D, Gin H (2000) Osteoporosis in late-diagnosed adult homocystinuric patients. J Inherit Metab Dis 23: 338–340.
Poehlman ET, Dvorak RV, DeNino WF, Brochu M, Ades PA (2000) Effects of resistance training and endurance training on insulin sensitivity in nonobese, young women: a controlled randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85: 2463–2468.
Rayner HC, Stroud DB, Salamon KM, et al (1991) Anthropometry underestimates body protein depletion in haemodialysis patients. Nephron 59: 33–40.
Rennie MJ (1998) Nutritional and pathophysiological modulation of body protein. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 1: 67–71.
Ross RJ (2000) GH, IGF-I and binding proteins in altered nutritional states. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24 (supplement 2): S92–95.
Russell DM, Prendergast PJ, Darby PL, Garfinkel PE, Whitwell J, Jeejeebhoy KN (1983) A comparison between muscle function and body composition in anorexia nervosa: the effect of refeeding. Am J Clin Nutr 38: 229–237.
Simoni RD, Hill RL, Vaughan M (2002) The amino-acid minimum for maintenance and growth, as exemplified by further experiments with lysine and tryptophane (Osborne, T. B., and Mendel, L. B. (1916) J. Biol. Chem. 25, 1–12) and The role of vitamines in the diet (Osborne, T. B., and Mendel, L. B. (1917) J Biol Chem 31: 149–163). J Biol Chem 277: e7.
Stroud DB, Borovnicar DJ, Lambert JR, et al (1990) Clinical studies of total body nitrogen in an Australian hospital. In: Yasumura S, Harrison JE, McNeill KG, Woodhead AD, Dilmanian FA, eds. In Vivo Body Composition Studies: Recent Advances. New York: Plenum Press, 177–185.
Toida S, Takahashi M, Shimizu H, Sato N, Shimomura Y, Kobayashi I (1996) Effect of high sucrose feeding on fat accumulation in the male Wistar rat. Obes Res 4: 561–568.
Truswell AS, ed (1990) Recommended Nutrient Intakes: Australian Papers. Sydney: Australian Professional Publications.
Vartsky D, Prestwich WV, Thomas BJ, et al (1979) The use of body hydrogen as an internal standard in the measurement of nitrogen in vivo by prompt neutron gamma-ray analysis. J Radioanal Chem 48: 243–252.
Widdowson EM, Dickerson JW (1981) Composition of the body. In: Lentner C, ed. Geigy Scientific Tables, 8th edn. Basle: Ciba-Geigy, Vol. 1, 217–225.
Wyshak G (2000) Teenaged girls, carbonated beverage consumption, and bone fractures. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 154: 610–613.
Young VR (2001) Protein and amino acids. In: Bowman BA, Russell RM, eds. Present Knowledge in Nutrition, 8th edn. Washington DC: ILSI Press, 43–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented in part at the SSIEM annual symposium, Prague, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilcox, G., Strauss, B.J.G., Francis, D.E.M. et al. Body composition in young adults with inborn errors of protein metabolism—A pilot study. J Inherit Metab Dis 28, 613–626 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-005-0036-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-005-0036-7