Abstract
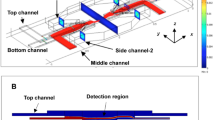
Conventional flow cytometers employ hydrodynamic focusing method to insure detection accuracy by forcing cells go through detected position. However, an increased flow velocity will significantly reduce detection precision due to a fact that cells will deviate center position and are easily silted in choke point. In an effort to overcome this limitation, a two-dimension ultrasonic particle focusing method are presented in this work to enhance the performance of flow cytometer. Two piezoelectric transducers are used to attach to a 250 μm × 250 μm rectangular fused silica flow channel to realize the modification. Finite element model simulation is performed for parametrical analysis and simplifying experiment design. 3 μm polystyrene fluorescent particles are adopted to test focusing effect. One dimension acoustic focusing is achieved at 2.95 MHz with single focusing node as well as 2, 3, 4 nodes focusing near 6, 9, 12 MHz respectively. The 2D focusing particle stream width in two dimensions is less than 10 μm. Results verified that this method is applicable for Jurkat cells. Sample flow maintains its stability without clogging up even at high sample concentration. Focusing still works at flow velocity over 100 μl/min. All these results certify this acoustic particles focusing method can enhance the performance of hydrodynamic flow cytometer by minor modification.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Adan, G. Alizada, Y. Kiraz, Y. Baran, A. Nalbant, Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 37, 163–176 (2017)
D. Carugo, T. Octon, W. Messaoudi, A.L. Fisher, M. Carboni, N.R. Harris, et al., Lab Chip 14, 3830 (2014)
D.A. DeAngelis, G.W. Schulze, Phys. Procedia 87, 85–92 (2016)
M. Evander, J. Nilsson, Lab Chip 12, 4667–4676 (2012)
E.I. Galanzha, V.P. Zharov, Methods 57, 280–296, 7 (2012)
E.I. Galanzha, M.G. Viegas, T.I. Malinsky, A.V. Melerzanov, M.A. Juratli, M. Sarimollaoglu, D.A. Nedosekin, V.P. Zharov, Sci. Rep. 6, 21531 (2016)
G. Goddard, J.C. Martin, S.W. Graves, G. Kaduchak, Cytometry Part A 69A, 66–74 (2006)
G.R. Goddard, C.K. Sanders, J.C. Martin, G. Kaduchak, S.W. Graves, Anal. Chem. 79, 8740–8746 (2007)
J. Greenhall, F.G. Vasquez, B. Raeymaekers, Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 074103 (2013)
O. Jakobsson, M. Antfolk, T. Laurell, Anal. Chem. 86, 6111–6114 (2014)
J.S. Jeong, J.W. Lee, C.Y. Lee, S.Y. Teh, A. Lee, K.K. Shung, Biomed. Microdevices 13, 779–788 (2011)
L. Johansson, J. Enlund, S. Johansson, I. Katardjiev, V. Yantchev, Biomed. Microdevices 14, 279–289 (2012)
J.T. Karlsen, H. Bruus, Physical Review E Statistical Nonlinear & Soft Matter Physics 85, 043010 (2011)
F.W. Kuckuck, B.S. Edwards, L.A. Sklar, Cytometry Part B Clinical Cytometry 44, 83–90 (2001)
W.M. Lee, K. Grindle, T. Pappas, D.J. Marshall, M.J. Moser, E.L. Beaty, J. Clin. Microbiol. 45, 2626–2634 (2007)
H. Li, J.R. Friend, L.Y. Yeo, Biomed. Microdevices 9, 647–656 (2007)
Z. Li, P. Li, J. Xu, W. Shao, C. Wang, Y. Cui, IEEE international Ultrasonics symposium (IUS) (2017), pp. 1–4
S. Liu, Y. Yang, Z. Ni, X. Guo, L. Luo, J. Tu, et al., Sensors 17, 1664 (2017)
G. Liu, F. He, Y. Li, H. Zhao, X. Li, H. Tang, et al., Biomed. Microdevices 21 (2019)
X. Ma, Q.L. Jun, R.S. Brock, M.J. Kenneth, Y. Ping, H. Xin-Hua, Phys. Med. Biol. 48, 4165 (2003)
F.G. Mitri, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 56, 1059–1064 (2009)
F.G. Mitri, Z.E.A. Fellah, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 55, 2469–2478 (2008)
R.J. Olson, A. Shalapyonok, D.J. Kalb, S.W. Graves, H.M. Sosik, Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 15 (2017)
M.E. Piyasena, P.P.A. Suthanthiraraj, R.W. Applegate Jr., A.M. Goumas, T.A. Woods, G.P. López, Anal. Chem. 84, 1831–1839 (2012)
J. Shi, H. Huang, Z. Stratton, Y. Huang, T.J. Huang, Lab Chip 9, 3354–3359 (2009)
G.T. Silva, H. Bruus, Physical Review E Statistical Nonlinear & Soft Matter Physics 90, 063007 (2014)
Y. Sriphutkiat, Y. Zhou, Sensors Actuators A Phys. 263, 521–529 (2017)
T. Stratoudaki, M. Clark, P.D. Wilcox, Opt. Express 24, 21921 (2016)
P.P.A. Suthanthiraraj, M.E. Piyasena, T.A. Woods, M.A. Naivar, G.P. Lόpez, S.W. Graves, Methods 57, 259–271 (2012)
M. Ward, P. Turner, M. Dejohn, G. Kaduchak, Curr. Protocols Cytometry 49, 1.22.1–1.22.12 (2009a)
M. Ward, P. Turner, M. DeJohn, G. Kaduchak, Curr. Protocols Cytometry 1.22, 1–1.22. 12 (2009b)
J. Xia, J. Yao, L.V. Wang, Electromagnetic Waves (Cambridge, Mass.) 147, 1–22 (2014)
A. Yang, W. Hsieh, Biomed. Microdevices 9, 113–122 (2007)
C. Yang, Z. Li, P. Li, W. Shao, P. Bai, Y. Cui, IEEE international Ultrasonics symposium (IUS), 1–4 (2017)
L.Y. Yeo, J.R. Friend, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 46, 379–406 (2014)
Y. Yu, W. Qiu, L. Sun, 2013 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS) (2013), pp. 2118–2121
S. Yue, F. Lin, Q. Zhang, N. Epie, S. Dong, X. Shan, X. Shan, D. Liu, W. Chu, Z. Wang, J. Bao, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 116, 6580–6585 (2019)
Q. Zhang, Y. Han, W. C. W, L. Zhang, J. Chang, Eur. Polym. J. 45, 550–556 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.11704397). The fluorescence labeled microspheres are supplied by Pengli Bai, who is also a faculty researcher with the Bio-Medical Diagnostics department, Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Some of observing equipment are supported by Medical Optical Department of Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Li, P., Xu, J. et al. Hydrodynamic flow cytometer performance enhancement by two-dimensional acoustic focusing. Biomed Microdevices 22, 27 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00481-9
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00481-9