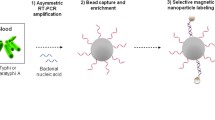
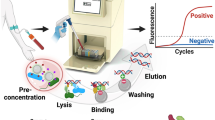
Abstract
Enteric fever is one of the leading causes of infection and subsequent fatality (greater than 1.8 million) (WHO 2018), especially in the developing countries due to contaminated water and food inter twinned with unhygienic practices. Clinical gold standard technique of culture-based method followed by biochemical tests demand 72+ hours for diagnosis while newly developed techniques (like PCR, RT-PCR, DNA microarray etc.) suffer from high limit of detection or involve high-cost infrastructure or both. In this work, a quick and highly specific method, SMOL was established for simultaneous detection of Salmonella paratyphi A and Salmonella typhi in clinical blood samples. SMOL consists of (i) pre-concentration of S. typhi and S. paratyphi A cells using magnetic nanoparticles followed by (ii) cell lysis and DNA extraction (iii) amplification of select nucleic acids by LAMP technique and (iv) detection of amplified nucleic acids using an affordable portable device (costs less than $70). To identify the viability of target cells at lower concentrations, the samples were processed at two different time periods of t = 0 and t = 4 h. Primers specific for the SPA2539 gene in S. paratyphi A and STY2879 gene in S. typhi were used for LAMP. Within 6 h SMOL was able to detect positive and negative samples from 55 human clinical blood culture samples and detect the viability of the cells. The results were concordant with culture and biochemical tests as well as by qPCR. Statistical power analysis yielded 100%. SMOL results were concordant with culture and biochemical tests as well as by qPCR. The sensitive and affordable system SMOL will be effective for poor resource settings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Abdullah, N. Saffie, F.A.R. Sjasri, A. Husin, Z. Abdul-Rahman, A. Ismail, et al., Rapid detection of Salmonella Typhi by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method. Braz. J. Microbiol. 45(4), 1385–1391 (2014)
D. Acheson, E.L. Hohmann, Nontyphoidal Salmonellosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32(2), 263–269 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1086/318457
S.A. Besuschio, M. Llano Murcia, A.F. Benatar, S. Monnerat, I. Cruz Mata, A. Picado de Puig, et al., Analytical sensitivity and specificity of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) kit prototype for detection of Trypanosoma cruzi DNA in human blood samples. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 11(7) (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0005779
C. Carter, K. Akrami, D. Hall, D. Smith, E. Aronoff-Spencer, Lyophilized visually readable loop-mediated isothermal reverse transcriptase nucleic acid amplification test for detection Ebola Zaire RNA. J. Virol. Methods 244, 32–38 (2017)
CLSI document M47-A, Principles and procedures for blood cultures; approved guideline. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. (2007)
B.A. Connor, E. Schwartz, Typhoid and paratyphoid fever in travellers. Lancet Infect. Dis. 5(10), 623–628 (2005)
P.B. Crichton, Enterobacteriaceae: Escherichia, Klebsiella, proteus and other genera. Mackie and McCartney Practical Medical Microbiology 14, 361–384 (1996)
J.A. Crump, E.D. Mintz, Global trends in typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Clinical Infectious Diseases : An Official Publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America 50(2), 241–246 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1086/649541
J.A. Crump, S.P. Luby, E.D. Mintz, The global burden of typhoid fever. Bull. World Health Organ. 82(5), 346–353 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0042-96862004000500008
S. Dahiya, P. Sharma, B. Kumari, S. Pandey, R. Malik, N. Manral, et al., Characterisation of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonellae during 2014–2015 from four centres across India: An ICMR antimicrobial resistance surveillance network report. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 35(1), 61–68 (2017)
S. Dutta, S. Das, U. Mitra, P. Jain, I. Roy, S.S. Ganguly, et al., Antimicrobial resistance, virulence profiles and molecular subtypes of Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A blood isolates from Kolkata, India during 2009-2013. PLoS ONE 9(8) (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101347
E. Eriksson, A. Aspan, Comparison of culture, ELISA and PCR techniques for salmonella detection in faecal samples for cattle, pig and poultry. BMC Vet. Res. 3 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-6148-3-21
A. Eyigor, K.T. Carli, Rapid detection of Salmonella from poultry by real-time polymerase chain reaction with fluorescent hybridization probes. Avian Dis. 47(2), 380–386 (2003)
L. Fabre, S. Le Hello, C. Roux, S. Issenhuth-Jeanjean, F.-X. Weill, CRISPR is an optimal target for the design of specific PCR assays for Salmonella enterica serotypes Typhi and Paratyphi A. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 8(1), 1–11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002671
F. Fan, P. Du, B. Kan, M. Yan, The development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the rapid detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. PLoS ONE 10(4) (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124507
M. Fangtham, H. Wilde, Emergence of Salmonella Paratyphi A as a major cause of enteric fever: need for early detection, preventive measures, and effective vaccines. Journal of Travel Medicine 15(5), 344–350 (2008)
N.A. Feasey, K. Gaskell, V. Wong, C. Msefula, G. Selemani, S. Kumwenda, et al., Rapid emergence of multidrug resistant, H58-lineage Salmonella Typhi in Blantyre, Malawi. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9(4), e0003748 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003748
V. Gupta, J. Kaur, J. Chander, et al., An increase in enteric fever cases due to Salmonella Paratyphi A in & around Chandigarh. Indian J. Med. Res. 129(1), 95–98 (2009)
K. Hajian-Tilaki, Sample size estimation in diagnostic test studies of biomedical informatics. J. Biomed. Inform. 48, 193–204 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2014.02.013
A. Kaur, R. Das, M.R. Nigam, R. Elangovan, D. Pandya, S. Jha, D. Kalyanasundaram, Rapid detection device for Salmonella typhi in milk, juice, water and calf serum. Indian J. Microbiol. 58(3), 381–392 (2018a). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-018-0730-4
A. Kaur, A. Kapil, R. Elangovan, S. Jha, D. Kalyanasundaram, Highly-sensitive detection of Salmonella typhi in clinical blood samples by magnetic nanoparticle-based enrichment and in-situ measurement of isothermal amplification of nucleic acids. PLoS One 13(3) (2018b). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194817
Y.T. Kim, Y. Chen, J.Y. Choi, W.-J. Kim, H.-M. Dae, J. Jung, T.S. Seo, Integrated microdevice of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction with colorimetric immunochromatographic detection for rapid gene expression analysis of influenza A H1N1 virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 33(1), 88–94 (2012)
J.-S. Lee, V.V. Mogasale, V. Mogasale, K. Lee, Geographical distribution of typhoid risk factors in low and middle income countries. BMC Infect. Dis. 16(1), 732 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-016-2074-1
T.R. Liu, K. Liljebjelke, E. Bartlett, C. Hofacre, S. Sanchez, J.J. Maurer, Application of nested polymerase chain reaction to detection of Salmonella in poultry environment. J. Food Prot. 65(8), 1227–1232 (2002). https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X-65.8.1227
C. Manjunatha, S. Sharma, D. Kulshreshtha, S. Gupta, K. Singh, S.C. Bhardwaj, R. Aggarwal, Rapid detection of Puccinia triticina causing leaf rust of wheat by PCR and loop mediated isothermal amplification. PLoS ONE 13(4) (2018)
W. Mokhtari, S. Nsaibia, D. Majouri, A. Ben Hassen, A. Gharbi, M. Aouni, Detection and characterization of Shigella species isolated from food and human stool samples in Nabeul, Tunisia, by molecular methods and culture techniques. J. Appl. Microbiol. 113(1), 209–222 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05324.x
M. Mukhtar, S.S. Ali, S.A. Boshara, A. Albertini, S. Monnerat, P. Bessell, et al., Sensitive and less invasive confirmatory diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in Sudan using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 12(2) (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006264
K. Nagamine, T. Hase, T. Notomi, Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 16, 223–229 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/mcpr.2002.0415
T. Notomi, H. Okayama, H. Masubuchi, T. Yonekawa, K. Watanabe, N. Amino, T. Hase, Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 28(12), E63 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.12.e63
C.R. Phaneuf, B. Mangadu, H.M. Tran, Y.K. Light, A. Sinha, F.W. Charbonier, et al., Integrated LAMP and immunoassay platform for diarrheal disease detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 120, 93–101 (2018)
P. Phumkhachorn, P. Rattanachaikunsopon, Detection of viable Salmonella Typhi by reverse transcription-multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture 29(4), 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.9755/ejfa.2016-12-1867
N.-E. Saffie, J. Abdullah, Z.A. Rahman, A. Hussin, A. Ismail, M. Mohamed, Establishment of an in-house loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for a rapid detection of Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi A at low-resource settings. J. Food Saf. 34(1), 69–75 (2014)
E. Sheikhzadeh, M. CHamsaz, A.P.F. Turner, E.W.H. Jager, V. Beni, Label-free impedimetric biosensor for Salmonella Typhimurium detection based on poly [pyrrole-co-3-carboxyl-pyrrole] copolymer supported aptamer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 80, 194–200 (2016)
B. Shu, C. Zhang, D. Xing, A sample-to-answer, real-time convective polymerase chain reaction system for point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 97, 360–368 (2017)
S. Singh, M. Upadhyay, J. Sharma, S. Gupta, P. Vivekanandan, R. Elangovan, A portable immunomagnetic cell capture system to accelerate culture diagnosis of bacterial infections. Analyst 141(11), 3358–3366 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AN00291A
Sood, S., Kapil, A., Dash, N., Das, B. K., Goel, V., & Seth, P. Paratyphoid fever in India: An emerging problem [3]. Emerg. Infect. Dis. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0503.990329 (1999)
M.C. Soria, M.A. Soria, D.J. Bueno, H.R. Terzolo, Comparison of 3 culture methods and PCR assays for Salmonella gallinarum and Salmonella pullorum detection in poultry feed. Poult. Sci. 92(6), 1505–1515 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2012-02926
S.M. Tennant, D. Toema, F. Qamar, N. Iqbal, M.A. Boyd, J.M. Marshall, et al., Detection of typhoidal and paratyphoidal salmonella in blood by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Clin. Infect. Dis. 61, S241–S250 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ726
Wan, L., Gao, J., Chen, T., Dong, C., Li, H., Wen, Y. Z., … Martins, R. P. LampPort: a handheld digital microfluidic device for loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Biomed. Microdevices https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0354-9 (2019)
Y.-P. Wong, S. Othman, Y.-L. Lau, S. Radu, H.-Y. Chee, Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): a versatile technique for detection of micro-organisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 124(3), 626–643 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13647
C.W. Woods, D.R. Murdoch, M.D. Zimmerman, W.A. Glover, B. Basnyat, L. Wolf, et al., Emergence of Salmonella enterica serotype Paratyphi A as a major cause of enteric fever in Kathmandu, Nepal. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 100(11), 1063–1067 (2006)
Y. Zhao, F. Chen, Q. Li, L. Wang, C. Fan, Isothermal Amplification of Nucleic Acids. Chem. Rev. 115(22), 12491–12545 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00428
L. Zhou, A.J. Pollard, A fast and highly sensitive blood culture PCR method for clinical detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 9(1), 14 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from the Department of Science and Technology (YSS/2014/000880, and IDP/MED/05/2014), Indo-German Science and Technology Centre (IGSTC/Call 2014/Sound4All/24/2015-16), Naval research board (NRB/4003/PG/359), BIRAC, Department of Biotechnology (BIRAC/BT/AIR0275/PACE-12/17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, A., Ruhela, A., Sharma, P. et al. Simultaneous and high sensitive detection of Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi a in human clinical blood samples using an affordable and portable device. Biomed Microdevices 21, 95 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0441-6
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0441-6