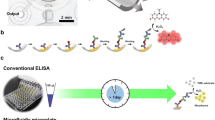
Abstract
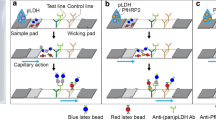
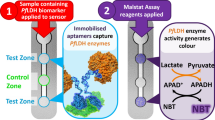
In this study, a novel film-based immunochromatographic microfluidic device (IMD) has been developed for malaria diagnosis. A microfluidic channel was patterned on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) double-sided adhesive film using a plotting cutter and was assembled with a polycarbonate (PC) film. The PC film used for the probe immobilization layer was activated using oxygen plasma treatment to modify the film surface with avidin-biotin linker to immobilize a capture antibody. A fluorescent labeled Pan type mAb conjugate was prepared for signal indicator after undergoing a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Target antigens include Plasmodium falciparum (P. falciparum) lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and Plasmodium vivax (P. vivax) LDH which were injected into the sample inlet. Target antigens combined with the conjugate and then flowed to the detection chamber where two test dots and a control dot (Ctrl) exist. In the presence of P. falciparum LDH, three detection dots including test dot 1 (T1), test dot 2 (T2) and Ctrl revealed fluorescence signals where P. falciparum mAb, Pan type pLDH mAb and goat anti-mouse IgG were immobilized, respectively. When P. vivax LDH was present, T2 and Ctrl dots showed fluorescence signals while no signal was detected with the negative control. P. falciparum LDH and P. vivax LDH were successfully detected on the IMD with a detection limit of 50 ng/mL and 100 ng/mL, respectively. The IMD provides a point-of-care diagnosis platform which is able to analyze pathogenic bacteria and viruses that can be applied in the field of clinical diagnosis and food safety testing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.K. Baird, Resistance to therapies for infection by Plasmodium vivax. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 22, 508–534 (2009)
A. Bobenchik, R. Shimiz-Cohen, R.M. Humphries, Use of rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosis of malaria in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 51, 379 (2013)
K.H. Chua, P.C. Lee, H.C. Chai, Development of insulated isothermal PCR for rapid on-site malaria detection. Malar. J. 15, 134 (2016)
M.A. DiMaio, I.T. Pereira, T.I. George, N. Banaei, Performance of BinaxNOW for diagnosis of malaria in a U.S. hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 50, 2877–2880 (2012)
L.A. Fraser, A.B. Kinghorn, R.M. Dirkzwager, S. Liang, Y.-W. Cheung, B. Lim, S.C.-C. Shiu, M.S.L. Tang, D. Andrew, J. Manitta, J.S. Richards, J.A. Tanner, A portable microfluidic aptamer-tethered enzyme capture (APTEC) biosensor for malaria diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 100, 591–596 (2018)
M.J. Gardner, N. Hall, E. Fung, O. White, M. Berriman, R.W. Hyman, J.M. Carlton, A. Pain, K.E. Nelson, S. Bowman, I.T. Paulsen, K. James, J.A. Eisen, K. Rutherford, S.L. Salzberg, A. Craig, S. Kyes, M.-S. Chan, V. Nene, S.J. Shallom, B. Suh, J. Peterson, S. Angiuoli, M. Pertea, J. Allen, J. Selengut, D. Haft, M.W. Mather, A.B. Vaidya, D.M.A. Martin, A.H. Fairlamb, M.J. Fraunholz, D.S. Roos, S.A. Ralph, G.I. McFadden, L.M. Cummings, G.M. Subramanian, C. Mungall, J.C.venter, D.J. Carucci, S.L. Hoffman, C. Newbold, R.W. Davis, C.M. Fraser, B. Barrell, genome sequence of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 419, 498–511 (2002)
C.G. Haanshuus, S. Chandy, A. Manoharan, R. Vivek, D. Mathai, D. Xena, A. Singh, N. Langeland, B. Blomberg, G. Vasanthan, U. Sitaram, J. Appasamy, J. Nesaraj, A. Henry, S. Patil, G. Alvarez-Uria, L. Armstrong, K. Mørch, PLoS One 17, e0158816 (2016)
A. Jimenez, R.R. Rees-Channer, R. Perera, D. Gamboa, P.L. Chiodini, I.J. González, A. Mayor, X.C. Ding, Analytical sensitivity of current best-in-class malaria rapid diagnostic tests. Malar. J. 16, 128 (2017)
J.-M. Kang, P.-Y. Cho, M. Moe, J. Lee, H. Jun, H.-W. Lee, S.K. Ahn, T.I. Kim, J.H. Pak, M.K. Myint, K. Lin, T.-S. Kim, B.K. Na, Comparison of the diagnostic performance of microscopic examination with nested polymerase chain reaction for optimum malaria diagnosis in upper Myanmar. Malar. J. 16, 119 (2017)
D.L. Kasper, E. Braunwald, S. Hauser, D. Longo, J.L. Jameson, A.S. Fauci, Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 16 th Edition (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2005)
C. Koepfli, W. Nguitragool, N.E. Hofmann, L.J. Robinson, M. Ome-Kaius, J. Sattabongkot, I. Felger, I. Mueller, Sensitive and accurate quantification of human malaria parasites using droplet digital PCR (ddPCR). Sci. Rep. 6, 39183 (2016)
T.F. Kong, W. Ye, W.K. Peng, H.W. Hou, P.R. Marcos, N.-T. Preiser, J.H. Nguyen, Enhancing malaria diagnosis through microfluidic cell enrichment and magnetic resonance relaxometry detection. Sci. Rep. 5, 11425 (2015)
C. Mahende, B. Ngasala, J. Lusingu, T.-S. Yong, P. Lushino, M. Lemnge, B. Mmbando, Z. Premji, Performance of rapid diagnostic test blood-film microscopy and PCR for the diagnosis of malaria infection among febrile children from Korogwe District. Tanzania. Malar. J. 15, 391 (2016)
R. Mao, G. Ge, Z. Wang, R. Hao, G. Zhang, Z. Yang, B. Lin, Y. Ma, H. Liu, Y. Du, A multiplex microfluidic loop-meidated isothermal amplification array for detection of malaria-related parasites and vectors. Acta Trop. 178, 86–92 (2018)
A. Moody, Rapid diagnostic tests for malaria parasites. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 15, 66–78 (2002)
J.C. Mouatcho, J.P.D. Goldring, Malaria rapid diagnostic tests: Challenges and prospects. J. Med. Microbiol. 62, 1491–1505 (2013)
C.J.L. Murray, L.C. Rosenfeld, S.S. Lim, K.G. Andrews, K.J. Foreman, D. Haring, N. Fullman, M. Naghavi, R. Lozano, A.D. Lopez, Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: A systematic analysis. Lancet 379, 413–431 (2012)
J. Nam, Y. Shin, J.K.S. Tan, Y.B. Lim, C.T. Lim, S. Kim, High-throughput malaria parasite separation using a viscoelastic fluid for ultrasensitive PCR detection. Lab Chip 16, 2086–2092 (2016)
S. Proux, R. Suwanarusk, M. Barends, J. Zwang, R.N. Price, M. Leimanis, L. Kiricharoen, N. Laochan, B. Russell, F. Nosten, G. Snounou, Considerations on the use of nucleic acid-based amplification for malaria parasite detection. Malar. J. 10, 323 (2011)
N. Ranadive, S. Kunene, S. Darteh, N. Ntshalintshali, N. Nhlabathi, N. Dlamini, S. Chitundu, M. Saini, M. Murphy, A. Soble, A. Schwartz, B. Greenhouse, M.S. Hsiang, Limitations of rapid diagnostic testing in patients with suspected malaria: A diagnostic accuracy evaluation from Swaziland, a low-endemicity country aiming for malaria elimination. Clin. Infect. Dis. 64, 1221–1227 (2017)
G.G. Rutledge, U. Böhme, M. Sanders, A.J. Reid, J.A. Cotton, O. Maiga-Ascofare, A.A. Djimdé, T.O. Apinjoh, L. Amenga-Etego, M. Manske, J.W. Barnwell, F. Renaud, B. Ollomo, F. Prugnolle, N.M. Anstey, S. Auburn, R.N. Price, J.S. McCarthy, D.P. Kwiatkowski, C.I. Newbold, M. Berriman, T.D. Otto, Plasmodium malariae and P. ovale genomes provide insights into malaria parasite evolution. Nature 542, 101–104 (2017)
C. Rypien, B. Chow, W.W. Chan, D.L. Church, D.R. Pillai, Detection of Plasmodium infection by the illumigene malaria assay compared to reference microscopy and real-time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 55, 3037–3045 (2017)
G. Snounou, S. Viriyakosol, X.P. Zhu, W. Jarra, L. Pinheiro, V.E. do Rosario, S. Thaithong, K.N. Brown, High sensitive of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 61, 315–320 (1993)
M.E. Warkiani, A.K.P. Tay, B.L. Khoo, X. Xiafeng, J. Han, C.T. Lim, Malaria detection using inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 15, 1101–1109 (2015)
WHO-Regional Office for the Western Pacific/TDR, Evaluating diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, s34–s38 (2006)
M.L. Wilson, Malaria rapid diagnostic tests. Clin. Infect. Dis. 54, 1673–1641 (2012)
World Health Organization, Basic malaria microscopy: part II. Tutor’s guide (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2010)
World Health Organization, World Malaria Report 2013 (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2013)
World Health Organization, World Malaria Report 2018 (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2018)
World Health Organization, High Burden to High Impact: A Targeted Malaria Response (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2019)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2017R1A6A1A03015562), Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (P002007, The Competency Development Program for Industry Specialist), and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF-2018R1C1B5085897).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J., Cho, SJ., Kim, Y.T. et al. Development of a film-based immunochromatographic microfluidic device for malaria diagnosis. Biomed Microdevices 21, 86 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0431-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-019-0431-8