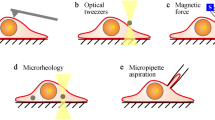
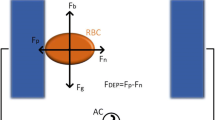
Abstract
Blood flow presents several interesting phenomena in microcirculation that can be used to develop microfluidic devices capable to promote blood cells separation and analysis in continuous flow. In the last decade there have been numerous microfluidic studies focused on the deformation of red blood cells (RBCs) flowing through geometries mimicking microvessels. In contrast, studies focusing on the deformation of white blood cells (WBCs) are scarce despite this phenomenon often happens in the microcirculation. In this work, we present a novel integrative microfluidic device able to perform continuous separation of a desired amount of blood cells, without clogging or jamming, and at the same time, capable to assess the deformation index (DI) of both WBCs and RBCs. To determine the DI of both WBCs and RBCs, a hyperbolic converging microchannel was used, as well as a suitable image analysis technique to measure the DIs of these blood cells along the regions of interest. The results show that the WBCs have a much lower deformability than RBCs when subjected to the same in vitro flow conditions, which is directly related to their cytoskeleton and nucleus contents. The proposed strategy can be easily transformed into a simple and inexpensive diagnostic microfluidic system to simultaneously separate and assess blood cells deformability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.C. Agbangla, É. Climent, P. Bacchin, Sep. Purif. Technol. 101, 42–48 (2012)
E.L. Bradley, L. Bernard, P. Thomas, J. Brian, J. Micromech. Microeng. 22, 025009 (2012)
X. Chen, D. Cui, C. Liu, H. Li, J. Chen, Anal. Chim. Acta 584, 237–243 (2007)
X. Chen, D.F. Cui, C.C. Liu, H. Li, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 130, 216–221 (2008)
R. Covar, M. Gleason, B. Macomber, L. Stewart, P. Szefler, K. Engelhardt, J. Murphy, A. Liu, S. Wood, S. DeMichele, E.W. Gelfand, S.J. Szefler, Clin. Exp. Allergy 40, 1163–1174 (2010)
V. Faustino, D. Pinho, T. Yaginuma, R. Calhelha, I.F.R. Ferreira, R. Lima, BioChip J. 8, 42–47 (2014)
A.E. Frampton, C.E. Fletcher, T.M. Gall, L. Castellano, C.L. Bevan, J. Stebbing, J. Krell, Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 13, 425–430 (2013)
J. Fu, B.E. Sha, L.L. Thomas, J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 56, 16–25 (2011)
K. Georgieva, D.J. Dijkstra, H. Fricke, N. Willenbacher, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 352, 265–277 (2010)
D.R. Gossett, W.M. Weaver, A.J. Mach, S.C. Hur, H.T. Tse, W. Lee, H. Amini, D. Di Carlo, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 397, 3249–3267 (2010)
D.R. Gossett, H.T.K. Tse, S.A. Lee, Y. Ying, A.G. Lindgren, O.O. Yang, J. Rao, A.T. Clark, D. Di Carlo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109, 7630–7635 (2012)
H.W. Hou, A.A. Bhagat, A.G. Chong, P. Mao, K.S. Tan, J. Han, C.T. Lim, Lab Chip 10, 2605–2613 (2010)
H.M. Ji, V. Samper, Y. Chen, C.K. Heng, T.M. Lim, L. Yobas, Biomed. Microdevices 10, 251–257 (2008)
Z. Jinlong, G. Qiuquan, L. Mei, Y. Jun, J. Micromech. Microeng. 18, 125025 (2008)
D.B. Khismatullin, in Leukocyte rolling and adhesion: Current topics in membranes, ed. by K. Ley, vol. 64 (Academic, New York, 2009), pp. 47–111
M. Kim, S. Mo Jung, K.H. Lee, Y. Jun Kang, S. Yang, Artif. Organs 34, 996–1002 (2010)
V. Leble, R. Lima, R. Dias, C. Fernandes, T. Ishikawa, Y. Imai, T. Yamaguchi, Biomicrofluidics 5, 044120-044120-044115 (2011)
S. Lee, Y. Yim, K. Ahn, S. Lee, Biomed. Microdevices 11, 1021–1027 (2009)
R. Lima, S. Wada, S. Tanaka, M. Takeda, T. Ishikawa, K. Tsubota, Y. Imai, T. Yamaguchi, Biomed. Microdevices 10, 153–167 (2008)
X.H. Liu, X. Wang, J. Biomech. 37, 1079–1085 (2004)
W. Luttmann, K. Bratke, M. Kupper, D. Myrtek, Immunology, vol. 1 (Elsevier, Philadelphia, 2006)
E. Maes, B. Landuyt, I. Mertens, L. Schoofs, PLoS One 8, e61933 (2013)
E. Meijering, I. Smal, G. Danuser, IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 23, 46–53 (2006)
S. Metz, C. Trautmann, A. Bertsch, R. Ph, J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 324 (2004)
S.K. Murthy, P. Sethu, G. Vunjak-Novakovic, M. Toner, M. Radisic, Biomed. Microdevices 8, 231–237 (2006)
E. Ortega, R. Gilabert, I. Nuñez, M. Cofán, A. Sala-Vila, E. de Groot, E. Ros, Atherosclerosis 221, 275–281 (2012)
T.G. Papaioannou, C. Stefanadis, Hellenic J. Cardiol. 46, 9–15 (2005)
D. Pinho, T. Yaginuma, R. Lima, BioChip J. 7, 367–374 (2013)
A. Sabo, V. Jakovljevic, M. Stanulovic, L. Lepsanovic, D. Pejin, Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 31, 1–5 (1993)
S.S. Shevkoplyas, T. Yoshida, L.L. Munn, M.W. Bitensky, Anal. Chem. 77, 933–937 (2005)
Sigma-Aldrich, Histopaque-1077: product information. St. Louis, MO, USA, (2011)
R. Suwanarusk, B.M. Cooke, A.M. Dondorp, K. Silamut, J. Sattabongkot, N.J. White, R. Udomsangpetch, J. Infect. Dis. 189, 190–194 (2004)
K. Tae Goo, Y. Yong-Jin, J. Hongmiao, L. Pei Yi, C. Yu, J. Micromech. Microeng. 24, 087001 (2014)
M. Tanino, R. Matoba, S. Nakamura, H. Kameda, K. Amano, T. Okayama, H. Nagasawa, K. Suzuki, K. Matsubara, T. Takeuchi, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 387, 261–265 (2009)
V. VanDelinder, A. Groisman, Anal. Chem. 78, 3765–3771 (2006)
V. VanDelinder, A. Groisman, Anal. Chem. 79, 2023–2030 (2007)
T. Yaginuma, M.S.N. Oliveira, R. Lima, T. Ishikawa, T. Yamaguchi, Biomicrofluidics 7, 054110 (2013)
X. Yang, J.M. Yang, Y.-C. Tai, C.-M. Ho, Sensors Actuators A Phys. 73, 184–191 (1999)
Y.T. Yaylali, I. Susam, E. Demir, M. Bor-Kucukatay, B. Uludag, E. Kilic-Toprak, G. Erken, D. Dursunoglu, J. Coron. Artery Dis. 24, 11–15 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by PTDC/SAU-ENB/116929/2010 and EXPL/EMS-SIS/2215/2013 from FCT (Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia), COMPETE, QREN and European Union (FEDER). R. O. Rodrigues, D. Pinho and V. Faustino acknowledge respectively, the PhD scholarships SFRH/BD/97658/2013, SFRH/BD/89077/2012 and SFRH/BD/99696/2014 granted by FCT. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Ângela Fernandes for providing the blood samples and Dr. Ricardo Calhelha for supplying the tissue culture medium used in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
supplementary video 1
Trajectories of both RBC and PBMC flowing around the cross-flow pillars. RBCs deform and pass through the pillars into the branch channel whereas a PBMC rolls along the pillars in the direction of the primary flow. (AVI 8910 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, R.O., Pinho, D., Faustino, V. et al. A simple microfluidic device for the deformability assessment of blood cells in a continuous flow. Biomed Microdevices 17, 108 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-0014-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-015-0014-2