Abstract
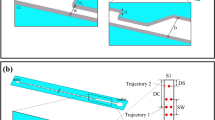
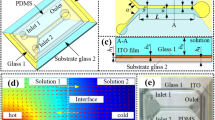
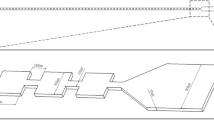
We report a contraction-expansion array (CEA) microchannel for rapidly and homogeneously mixing different types of fluids by multivortex induced in alternately formed rectangular structures of the channel. Rapid mixing can be achieved in a topologically simple and easily fabricated CEA microchannel, employing a synergetic combination of two kinds of vortices: (1) expansion-vortices being induced by flow separation due to an abrupt change of cross-sectional area of the channel in its expansion region, and (2) Dean-vortices being induced by centrifugal forces acting on a cornering fluid through the channel. We experimentally and numerically investigated expansion- and Dean-vortices, and demonstrated rapid mixing of an aqueous solution containing fluorescein or human red blood cells (RBCs) at different flow rates corresponding to Reynolds number (Re) ranging from 7.2 to 43.0. Over 90% mixing efficiency at a channel length of 14.4 and 19.5 mm was achieved at Re ≥ 28.6 (fluorescein solution and deionized water) and Re ≥ 21.5 (RBC suspension and phosphate buffered saline), respectively. The proposed CEA channel is expected to be useful for a wide range of applications where particles, cells and reagents must be rapidly and homogeneously mixed in microchannels.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Burns, B.N. Johnson, S.N. Brahmasandra, K. Handique, J.R. Webster, M. Krishnan, T.S. Sammarco, P.M. Man, D. Jones, D. Heldsinger, C.H. Mastrangelo, D.T. Burke, Science 282, 484–486 (1998)
D. Di Carlo, D. Irimia, R.G. Tompkins, M. Toner, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 18892–18897 (2007)
H. Chen, J. Meiners, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2193–2195 (2004)
W.J. Devenport, E.P. Sutton, Exp. Fluids 14, 423–432 (1993)
J.P.B. Howell, D.R. Mott, S. Fertig, C.R. Kaplan, J.P. Golden, E.S. Oran, F.S. Ligler, Lab Chip 5, 524–530 (2005)
T.J. Johnson, D. Ross, L.E. Locascio, Anal. Chem. 74, 45–51 (2002)
K. Kanno, H. Maeda, S. Izumo, M. Ikuno, K. Takeshita, A. Tashiro, M. Fujii, Lab Chip 2, 15–18 (2002)
D.S. Kim, S.H. Lee, T.H. Kwon, C.H. Ahn, Lab Chip 5, 739–747 (2005)
Y. Lee, C. Shih, P. Tabeling, C. Ho, J. Fluid Mech. 575, 425–448 (2007)
M.G. Lee, S. Choi, J.-K. Park, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 051902 (2009a)
M.G. Lee, S. Choi, J.-K. Park, Lab Chip 9, 3155–3160 (2009b)
R.H. Liu, J. Yang, M.Z. Pindera, M. Athavale, P. Grodzinski, Lab Chip 2, 151–157 (2002)
L.-H. Lu, K.S. Ryu, C. Liu, J. Microelectromech. Syst. 11, 462–469 (2002)
M. Miyazaki, H. Nakamura, H. Maeda, Chem. Lett. 30, 442–443 (2001)
W.Y. Ng, S. Goh, Y.C. Lam, C. Yang, I. Rodriquez, Lab Chip 9, 802–809 (2009)
N.T. Nguyen, Z. Wu, J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, R1–R16 (2005)
M.H. Oddy, J.G. Santiago, J.C. Mikkelsen, Anal. Chem. 73, 5822–5832 (2001)
M.S.N. Oliveira, L.E. Rodd, G.H. McKinley, M.A. Alves, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 5, 809–826 (2008)
J.M. Ottino, S. Wiggins, Science 305, 485–486 (2004)
A.M. Sallam, N.H. Hwang, Biorheology 21, 783–797 (1984)
P. Sethu, L.L. Moldawer, M.N. Mindrinos, P.O. Scumpia, C.L. Tannahill, J. Wilhelmy, P.A. Efron, B.H. Brownstein, R.G. Tompkins, M. Toner, Anal. Chem. 78, 5453–5461 (2006)
A.D. Stroock, S.K.W. Dertinger, A. Ajdari, I. Mezic, H.A. Stone, G.M. Whitesides, Science 295, 647–651 (2002)
A.P. Sudarsan, V.M. Ugaz, Lab Chip 6, 74–82 (2006a)
A.P. Sudarsan, V.M. Ugaz, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 7228–7233 (2006b)
E.Y. Tafti, R. Kumar, H.J. Cho, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 143504 (2008)
Y. Yamaguchi, F. Takagi, T. Watari, K. Yamashita, H. Nakamura, H. Shimizu, H. Maeda, Chem. Eng. J. 101, 367–372 (2004a)
Y. Yamaguchi, K. Takagi, H. Yamashita, H. Nakamura, H. Maeda, AlChE J. 50, 1530–1535 (2004b)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Research Laboratory (NRL) Program grant (R0A-2008-000-20109-0) and by the Converging Research Center Program grant (2009-0093663) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lee and Choi contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1969 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.G., Choi, S. & Park, JK. Rapid multivortex mixing in an alternately formed contraction-expansion array microchannel. Biomed Microdevices 12, 1019–1026 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9456-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9456-8