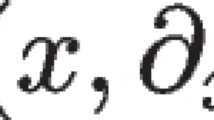Abstract
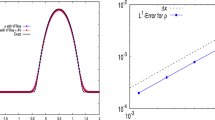
A finite element method for Burgers’ equation is studied. The method is analyzed using techniques from stabilized finite element methods and convergence to entropy solutions is proven under certain hypotheses on the artificial viscosity. In particular we assume that a discrete maximum principle holds. We then construct a nonlinear artificial viscosity that satisfies the assumptions required for convergence and that can be tuned to minimize artificial viscosity away from local extrema.
The theoretical results are exemplified on a numerical example.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Bertoluzza, The discrete commutator property of approximation spaces, C. R. Acad. Sci., Paris, Sér. I, Math., 329(12) (1999), pp. 1097–1102.
E. Burman and A. Ern, Nonlinear diffusion and discrete maximum principle for stabilized Galerkin approximations of the convection–diffusion-reaction equation, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 191(35) (2002), pp. 3833–3855.
E. Burman and A. Ern, The discrete maximum principle for stabilized finite element methods, in Numerical Mathematics and Advanced Applications, Springer, Milano, 2003, pp. 557–566.
E. Burman and A. Ern, Stabilized Galerkin approximation of convection–diffusion-reaction equations: discrete maximum principle and convergence, Math. Comput., 74 (2005), pp. 1637–1652 (electronic).
E. Burman and A. Ern, Continuous interior penalty hp-finite element methods for advection and advection–diffusion equations, Math. Comput. (2007).
P. G. Ciarlet and P.-A. Raviart, Maximum principle and uniform convergence for the finite element method, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 2 (1973), pp. 17–31.
B. Cockburn and C.-W. Shu, TVB Runge–Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws. II. General framework, Math. Comput., 52 (1989), pp. 411–435.
E. Godlewski and P.-A. Raviart, Numerical Approximation of Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws, Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 118, Springer, New York, 1996.
J. Jaffré, C. Johnson, and A. Szepessy, Convergence of the discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for hyperbolic conservation laws, Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci., 5(3) (1995), pp. 367–386.
C. Johnson and A. Szepessy, On the convergence of a finite element method for a nonlinear hyperbolic conservation law, Math. Comput., 49 (1987), pp. 427–444.
P. G. LeFloch, Hyperbolic systems of conservation laws, Lectures in Mathematics ETH Zürich, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 2002.
R. J. LeVeque, Numerical methods for conservation laws, Lectures in Mathematics ETH Zürich, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, 1990.
E. Y. Panov, Uniqueness of the solution of the Cauchy problem for a first-order quasilinear equation with an admissible strictly convex entropy, Mat. Zametki, 55(5) (1994), pp. 116–129, 159.
J. Smagorinsky, Some historical remarks on the use of nonlinear viscosities, in Large Eddy Simulation of Complex Engineering and Geophysical Flows, Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1993, pp. 3–36.
A. Szepessy, Convergence of a shock-capturing streamline diffusion finite element method for a scalar conservation law in two space dimensions, Math. Comput., 53 (1989), pp. 527–545.
V. Thomée, Galerkin finite element methods for parabolic problems, Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 25, Springer, Berlin, 1997.
J. Von Neumann and R. D. Richtmyer, A method for the numerical calculation of hydrodynamic shocks, J. Appl. Phys., 21 (1950), pp. 232–237.
J. Xu and L. Zikatanov, A monotone finite element scheme for convection–diffusion equations, Math. Comput., 68 (1999), pp. 1429–1446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
AMS subject classification (2000)
65M20, 65M12, 35L65, 76M10
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burman, E. On nonlinear artificial viscosity, discrete maximum principle and hyperbolic conservation laws . Bit Numer Math 47, 715–733 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-007-0147-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10543-007-0147-7