Abstract
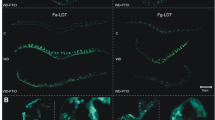
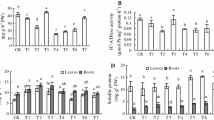
Calcium ion (Ca2+) is essential secondary messenger in plant signaling networks. In this study, the effect of Ca2+ on oxidative damage caused by a high irradiance (HI) was investigated in the leaves of two cultivars of tall fescue (Arid3 and Houndog5). Pretreatment of the tall fescue leaves with a CaCl2 solution significantly increased Ca2+ content and intrinsic HI tolerance due to a decreased ion leakage and content of malondialdehyde, hydrogen peroxide, and superoxide radicals. Moreover, the activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase increased in both the cultivars in the presence of Ca2+ under the HI stress. In contrast, treatments with a Ca2+ chelator ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) or a plasma membrane Ca2+ channel blocker LaCl3 reversed these effects. On the other hand, a pronounced increase in nitric oxide synthase-like activity and NO release by exogenous Ca2+ treatment was observed in the tolerant Arid3 plants after exposure to the HI, whereas only a small increase was observed in more sensitive Houndog5. Moreover, the inhibition of NO production by 2-(4-carboxy-2-phenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide or N ω-nitro-L-arginine blocked the protective effect of exogenous Ca2+, whereas the inhibition of Ca2+ by EGTA or LaCl3 had no influence on the protective effect of NO. The results indicate that NO might be involved in the Ca2+-induced activities of antioxidant enzymes further protecting against HI-induced oxidative damage. This protective mechanism was found to be more efficient in Arid3 than in Houndog5.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
abscisic acid
- APX:
-
ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
catalase
- EGTA:
-
ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
- GR:
-
glutathione reductase
- HI:
-
high irradiance
- LI:
-
low irradiance
- LNNA:
-
N ω-nitro-L-arginine
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
nitric oxide synthase
- PPFD:
-
photosynthetic photon flux density
- PTIO:
-
2-(4-carboxy-2-phenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide
- PVP:
-
polyvinylpyrrolidone
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SNP:
-
sodium nitroprusside
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
References
Aebi, H.: Catalase in vitro. — Methods Enzymol. 105: 121–126, 1984.
Ali, M.B., Hahn, E.J., Paek, K.Y.: Effects of light intensities on antioxidant enzymes and malondialdehyde content during short-term acclimatization on micropropagated Phalaenopsis plantlet. — Environ. exp. Bot. 54: 109–120, 2005.
Al-Whaibi, M.H., Siddiqui, M.H., Basalah, M.O.: Salicylic acid and calcium-induced protection of wheat against salinity. — Protoplasma 249: 769–778, 2012.
An, L.Z., Liu, Y.H., Zhang, M.X., Chen, T., Wang, X.L.: Effects of nitric oxide on growth of maize seedling leaves in the presence or absence of ultraviolet-B radiation. — J. Plant Physiol. 162: 317–326, 2005.
Apel, K., Hirt, H.: Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress and signal transduction. — Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 55: 373–399, 2004.
Asada, K.: Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. — Plant Physiol. 141: 391–396, 2006.
Bai, X.Y., Dong, Y.J., Wang, Q.H., Xu, L.L., Kong, J., Liu, S.: Effect of lead and nitric oxide on photosynthesis, antioxidative ability, and mineral element content of perennial ryegrass. — Biol. Plant 59: 163–170, 2015.
Beauchamp, C., Fridovich, I.: Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. — Anal. Biochem. 44: 276–287, 1971.
Beligni, M.V., Lamattina, L.: Nitric oxide stimulates seed germination and de-etiolation, and inhibits hypocotyl elongation, three light-inducible responses in plants. — Planta 210: 215–221, 2000.
Bhattacharjee, S.: Calcium-dependent signaling pathway in the heat-induced oxidative injury in Amaranthus lividus. — Biol. Plant. 52: 137–140, 2008.
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. — Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254, 1976.
Bright, J., Desikan, R., Hancock, J.T., Weir, I.S., Neill, S.J.: ABA-induced NO generation and stomatal closure in Arabidopsis are dependent on H2O2 synthesis. — Plant J. 45: 113–122, 2006.
Buege, J.A., Aust, S.D.: Microsomal lipid peroxidation. — Methods Enzymol. 52: 302–310, 1978.
Burritt, D.J., Mackenzie, S.: Antioxidant metabolism during acclimation of Begonia × erythrophylla to high light levels. — Ann. Bot. 91: 783–794, 2003.
Chandok, M.R., Ytterberg, A.J., Van Wijk, K.J., Klessig, D.F.: The pathogen-inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in plants is a variant of the P protein of the glycine decarboxylase complex. — Cell 113: 469–482, 2003.
Chen, Y.H., Kao, C.H.: Calcium is involved in nitric oxide- and auxin-induced lateral root formation in rice. — Protoplasma 249: 187–195, 2012.
Courtois, C., Besson, A., Dahan, J., Bourque, S., Dobrowolska, G., Pugin, A., Wendehenne, D.: Nitric oxide signalling in plants: interplays with Ca2+ and protein kinases. — J. exp. Bot. 59: 155–163, 2008.
Corpas, F.J., Leterrier, M., Valderrama, R., Airakia, M., Chaki, M., Palma, J.M., Barroso, J.B.: Nitric oxide imbalance provokes a nitrosative response in plants under abiotic stress. — Plant Sci. 181: 604–611, 2011.
Elstner, E.F., Heupel, A.: Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxyllammonium chloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. — Anal. Biochem. 70: 616–620, 1976.
Foyer, C.H., Halliwell, B.: The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: a proposed role on ascorbic acid metabolism. — Planta 133: 21–25, 1976.
Garcia-Mata, C., Lamattina L.: Abscisic acid (ABA) inhibits light-induced stomatal opening through calcium- and nitric oxide-mediated signaling pathways. — Nitric Oxide 17: 143–151, 2007.
Gong, M., Chen, S.N., Song, Y.Q., Li, Z.G.: Effect of calcium and calmodulin on intrinsic heat tolerance in relation to antioxidant system in maize seedlings. — Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 24: 371–379, 1997.
Gong M., Van der Luit, A.H., Knight, M.R., Trewavas, A.J.: Heat-shock-induced changes in intracellular Ca2+ level in tobacco seedlings in relation to thermotolerance. — Plant Physiol. 116: 429–437, 1998.
Guo, F.Q., Okamoto, M., Crawford, N.M.: Identification of a plant nitric oxide synthase gene involved in hormonal signaling. — Science 302: 100–103, 2003.
Jiang, M., Zhang, J.: Cross-talk between calcium and reactive oxygen species originated from NADPH oxidase in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defense in leaves of maize seedlings. — Plant Cell Environ. 26: 929–939, 2003.
Jiang, Y.W., Huang, B.R.: Effects of calcium on antioxidant activities and water relations associated with heat tolerance in two cool-season grasses. — J. exp. Bot. 52: 341–349, 2001.
Lanteri, M.L., Pagnussat, G.C., Lamattina, L.: Calcium and calcium-dependent protein kinases are involved in nitric oxide-and auxin-induced adventitious root formation in cucumber. — J. exp. Bot. 57: 1341–1351, 2006.
Laspina, N.V., Groppa, M.D., Tomaro, M.L., Benavides, M.P.: Nitric oxide protects sunflower leaves against Cd-induced oxidative stress. — Plant Sci. 169: 323–330, 2005.
Murphy, M.E., Noack, E.: Nitric oxide assay using hemoglobin method. — Methods Enzymol. 233: 240–250, 1994.
Nakano, Y., Asada K.: Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. — Plant Cell Physiol. 22: 867–880, 1981.
Nasir Khan, M., Siddiqui, M.H., Mohammad, F., Naeem, M.: Interactive role of nitric oxide and calcium chloride in enhancing tolerance to salt stress. — Nitric Oxide 27: 210–218, 2012.
Neill, S.J., Desikan, R., Hancock, J.T.: Nitric oxide signalling in plants. — New Phytol. 159: 11–35, 2003.
Sairam, R.K., Srivastava, G.C.: Changes in antioxidant activity in sub-cellular fractions of tolerant and susceptible wheat genotypes in response to long term salt stress. — Plant Sci. 162: 897–904, 2002.
Shi, H.T., Ye, T.T., Zhong, B., Liu, X., Chan, Z.L.: Comparative proteomic and metabolomic analyses reveal mechanisms of improved cold stress tolerance in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.) by exogenous calcium. — J. Integr. Plant Biol. 56: 1064–1079, 2014.
Tossi, V., Cassia, R., Bruzzone, S., Zocchi, E., Lamattina, L.: ABA says NO to UV-B: a universal response? — Trends Plant Sci. 17: 510–517, 2012.
Veljovic-Jovanovic, S., Noctor, G., Foyer, C.H.: Are leaf hydrogen peroxide concentrations commonly overestimated? The potential influence of artefactual interference by tissue phenolics and ascorbate. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 40: 501–507, 2002.
Wu, S.J., Wu, J.Y.: Extracellular ATP-induced NO production and its dependence on membrane Ca2+ flux in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. — J. exp. Bot. 59: 4007–4016, 2008.
Xu, Y.F., Fu, J.J., Chu, X.T., Sun, Y.F., Zhou, H., Hu, T.M.: Nitric oxide mediates abscisic acid induced light-tolerance in leaves of tall fescue under high-light stress. — Sci. Hort. 162: 1–10, 2013.
Xu, Y.F., Sun, X.L, Jin, J.W., Zhou, H.: Protective effect of nitric oxide on light-induced oxidative damage in leaves of tall fescue. — J. Plant Physiol. 167: 512–518, 2010.
Zhao, L., He, J.X., Wang, X.M., Zhang, L.X.: Nitric oxide protects against polyethylene glycol-induced oxidative damage in two ecotypes of reed suspension cultures. — J. Plant Physiol. 165: 182–191, 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31402129) and Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program in the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (No. 2011BAD17B05).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y.F., Chu, X.T., Fu, J.J. et al. Crosstalk of nitric oxide with calcium induced tolerance of tall fescue leaves to high irradiance. Biol Plant 60, 376–384 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0597-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0597-3