Abstract
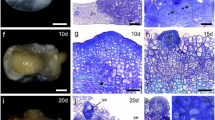
Non-transformed and transformed embryogenic cultures of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L. cv. Zaječarska 83), long-term maintained on growth regulator-free medium, were histologically analyzed. In all examined cultures, somatic embryos at various stages of development were observed and secondary embryos were formed in the cotyledonary, hypocotylary and radicular region of the primary embryos. Detailed histological analysis of the torpedo shape somatic embryo revealed that secondary somatic embryos arose directly from single epidermal cells of hypocotylary axis after an unequal periclinal division. Bipolar proembryos were composed of one smaller cytoplasm rich cell and one larger more vacuolated cell. Further cell division pattern was similar for both non-transformed and transformed embryos. However, multicellular origin of secondary embryos in a direct process and even from callus can not be excluded.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- nptII:
-
neomycin phospho-transferase II
- OCII:
-
oryzacistatin II
References
Chaudhary, B., Kumar, S., Prasad, K.V.S.K., Oinam, G.S., Burma, P.K., Pental, D.: Slow desiccation leads to high-frequency shoot recovery from transformed somatic embryos of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. cv. Coker 310 FR).-Plant Cell Rep. 21: 955–960, 2003.
Dos Santos, A.V.P., Cutter, E.G., Davey, M.R.: Origin and development of somatic embryos in Medicago sativa L. (alfalfa).-Protoplasma 117: 107–115, 1983.
Gamborg, O.L., Miller, R.A., Ojima, K.: Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells.-Exp. Cell Res. 50: 151–158, 1968.
Griga, M.: Morphology and anatomy of Pisum sativum somatic embryos.-Biol. Plant. 45: 173–182, 2002.
Maheswaran, G., Williams, E.G.: Primary and secondary somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of Brassica campestris.-J. Plant Physiol. 124: 455–463, 1986.
Milivojević, S., Mitrović, A., Ćulafić, Lj.: Somatic embryogenesis in Chenopodium rubrum and Chenopodium murale in vitro.-Biol. Plant. 49: 35–39, 2005.
Mohan, M.L., Krishnamurthy, K.V.: Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in pigeonpea.-Biol. Plant. 45: 19–25, 2002.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F.: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures.-Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497, 1962.
Ninković, S., Miljuš-Djukić, J., Nešković, M.: Genetic transformation of alfalfa somatic embryos and their clonal propagation through repetitive somatic embryogenesis.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 42: 255–260, 1995.
Ninković, S., Miljuš-Đukić, J., Nešković, M.: Genetic engineering of herbicide-resistant alfalfa (Medicago sativa L. cv. Zaječarska 83).-In: S. Stamenković (ed.): Proc. of 2nd Balkan Symp. on Field Crops. Vol. 1. Pp. 457–460, Institute of Field and Vegetable Crops, Novi Sad 1998.
Polito, V.S., McGranahan, G., Pinney, K., Leslie, C.: Origin of somatic embryos from repetitively embryogenic cultures of walnut (Juglans regia L.): implications for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation.-Plant Cell Rep. 8: 219–221, 1989.
Puigderrajols, P., Fernández-Guijarro, B., Toribio, M., Molinas, M.: Origin and early development of secondary embryos in Quercus suber L.-Int. J. Plant Sci. 157: 674–684, 1996.
Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R., Fuentes-Cerda, C.F.J., Rojas-Herrera, R., Loyola-Vargas, V.M.: Histological studies on the developmental stages and differentiation of two different somatic embryogenesis systems of Coffea arabica.-Plant Cell Rep. 20: 1141–1149, 2002.
Sagare, A.P., Suhasini, K., Krishnamurthy, K.V.: Histology of somatic embryo initiation and development in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.).-Plant Sci. 109: 87–93, 1995.
Samac, D.A., Smigocki, A.C.: Expression of oryzacystatin I and II in alfalfa increases resistance to the root-lesion nematode.-Phytopathology 93: 799–804, 2003.
Sauer, U., Wilhelm, E.: Somatic embryogenesis from ovaries, developing ovules and immature zygotic embryos, and improved embryo development of Castanea sativa.-Biol. Plant. 49: 1–6, 2005.
Williams, E.G., Maheswaran, G.: Somatic embryogenesis: factors influencing coordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group.-Ann. Bot. 57: 443–462, 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uzelac, B., Ninković, S., Smigocki, A. et al. Origin and development of secondary somatic embryos in transformed embryogenic cultures of Medicago sativa . Biol Plant 51, 1–6 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0001-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0001-4