Abstract
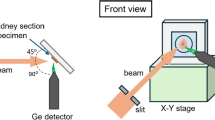
Aims of this study were to investigate gadolinium (Gd) in kidney tissue from a female patient with severe renal failure, who had a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with Gd-based contrast agent (GBCA) three times prior to kidney transplantation. Secondly to assess (semi-)quantitatively the Gd concentration in renal tissue and the spatial distribution of Gd in association to suspected co-elements such as calcium (Ca) and zinc (Zn). Archival paraffin embedded kidney tissue was investigated by micro Synchrotron X-ray fluorescence (µSRXRF) at the DORIS III storage ring at beamline L, HASYLAB/DESY(Hamburg, Germany). Elementary gadolinium (Gd) could be demonstrated in a near histological resolution in areas of about 2 × 1.5 mm2 of size. Mean Gd resulted in 200 ppm with a huge width of distribution (Gd-max: 2000 ppm). In kidney cortex Gd was in-homogeneously, but not randomly, distributed. Gd was verified throughout the investigated tissue. Low Gd was predominately concentrated either in areas with focally atrophic tubules or in areas with totally preserved uriniferous tubes. Moreover, strong correlations existed between Gd and calcium (Ca) or Gd and zinc (Zn) or Gd and strontium (Sr) distribution. Throughout our analysed areas copper (Cu) was nearly homogeneously distributed and Cu association to Gd could not be established, and also not for Gd to Fe. Gd in glomeruli was relatively reduced compared with mean Gd-values, while iron (Fe) distribution clearly demarks glomeruli mostly due to red blood cell iron in these capillary convolutes. Quantitative µSRXRF analysis provided an insight in element spatial distribution of Gd in the renal cortex. The strong correlation of the spatial distribution and associations between elements like Ca, Zn and Sr let us suspect that these elements are involved in the cell metabolism of GBCA. Low Gd in areas with extreme fibrosis and tubule atrophy or in areas with histologically intact tubes, let us suspect that on the one side Gd cannot be transported and deposited into these tissue areas and on the other side we assume that intact renal tubes do not reabsorb and store excreted Gd.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NSF:
-
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
- µSRXRF:
-
Microscopic synchrotron radiation X-ray fluorescence
- Gd:
-
Gadolinium
- GBCA:
-
Gadolinium based contrast agents
References
Abraham JL (2010) Detection of gadolinium (Gd) in tissues. Curr Rheumatol Rev 6(3):163–170. https://doi.org/10.2174/157339710791792784
Abraham JL, Thakral C, Skov L, Rossen K, Marckmann P (2008) Dermal inorganic gadolinium concentrations: evidence for in vivo transmetallation and long-term persistence in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Br J Dermatol 158(2):273–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08335.x
Akgun H, Gonlusen G, Cartwright J Jr, Suki WN, Truong LD (2006) Are gadolinium-based contrast media nephrotoxic? A renal biopsy study. Arch Pathol Lab Med 130(9):1354–1357. https://doi.org/10.1043/1543-2165(2006)130[1354:AGCMNA]2.0.CO;2
Boyd AS, Zic JA, Abraham JL (2007) Gadolinium deposition in nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy. J Am Acad Dermatol 56(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2006.10.048
Bussi S, Coppo A, Botteron C et al (2018) Differences in gadolinium retention after repeated injections of macrocyclic MR contrast agents to rats. J Magn Reson Imaging 47(3):746–752. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25822
El-Khatib AH, Radbruch H, Trog S et al (2019) Gadolinium in human brain sections and colocalization with other elements. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 6(1):e515. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXI.0000000000000515
Falkenberg G, Osterode W (2010) Räumliche Abbildung der Verteilung von Spurenelementen auf mikroskopischem Niveau. Wo sitzt das Blei im Knochen? Mikoroskopischen Röntgenfluoreszenzanalyse. In: Falta J, Möller T (ed) Forschung mit Synchrotronstrahlung. Vieweg + Teubner, Wiesbaden
Fingerhut S, Niehoff AC, Sperling M, Jeibmann A, Paulus W, Niederstadt T, Allkemper T, Heindel W, Holling M, Karst U (2018) Spatially resolved quantification of gadolinium deposited in the brain of a patient treated with gadolinium-based contrast agents. J Trace Elem Med Biol 45:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.10.004
George SJ, Webb SM, Abraham JL, Cramer SP (2010) Synchrotron X-ray analyses demonstrate phosphate-bound gadolinium in skin in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Br J Dermatol 163(5):1077–1081. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09918.x
Grobner T (2006) Gadolinium–a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:1104–1108
High WA, Ayers RA, Chandler J, Zito G, Cowper SE (2007a) Gadolinium is detectable within the tissue of patients with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 56(1):21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2006.10.047
High WA, Ayers RA, Cowper SE (2007b) Gadolinium is quantifiable within the tissue of patients with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 56(4):710–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2007.01.022
High WA, Ranville JF, Brown M, Punshon T, Lanzirotti A, Jackson BP (2010) Gadolinium deposition in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: an examination of tissue using synchrotron x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. J Am Acad Dermatol 62(1):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2009.07.018
Idee JM, Fretellier N, Robic C, Corot C (2014) The role of gadolinium chelates in the mechanism of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a critical update. Crit Rev Toxicol 44(10):895–913. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2014.955568
Kanal E, Tweedle MF (2015) Residual or retained gadolinium: practical implications for radiologists and our patients. Radiology 275(3):630–634. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015150805
Marckmann P, Skov L, Rossen K et al (2006) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: suspected causative role of gadodiamide used for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(9):2359–2362. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006060601
Mlinar B, Enyeart JJ (1993) Block of current through T-type calcium channels by trivalent metal cations and nickel in neural rat and human cells. J Physiol 469:639–652. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019835
Osterode W, Falkenberg G, Ferenci P, Wrba F (2019) Quantitative trace element mapping in liver tissue from patients with Wilson’s disease determined by micro X-ray fluorescence. J Trace Elem Med Biol 51:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2018.09.007
Osterode W, Falkenberg G, Petzelbauer P (2007) Two-dimensional distribution of gadolinium in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. https://hasyweb.desy.de/science/annual_reports/2007_reports/
Puttagunta NR, Gibby WA, Smith GT (1996) Human in vivo comparative study of zinc and copper transmetallation after administration of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Invest Radiol 31(12):739–742. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004424-199612000-00001
Rogosnitzky M, Branch S (2016) Gadolinium-based contrast agent toxicity: a review of known and proposed mechanisms. Biometals 29(3):365–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-016-9931-7
Sanyal S, Marckmann P, Scherer S, Abraham JL (2011) Multiorgan gadolinium (Gd) deposition and fibrosis in a patient with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis–an autopsy-based review. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(11):3616–3626. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr085
Semelka RC, Ramalho J, Vakharia A, AlObaidy M, Burke LM, Jay M, Ramalho M (2016) Gadolinium deposition disease: Initial description of a disease that has been around for a while. Magn Reson Imaging 34:1383–1390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2016.07.016
Sherry AD, Caravan P, Lenkinski RE (2009) Primer on gadolinium chemistry. J Magn Reson Imaging 30(6):1240–1248. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21966
Sieber MA, Pietsch H, Walter J, Haider W, Frenzel T, Weinmann HJ (2008) A preclinical study to investigate the development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a possible role for gadolinium-based contrast media. Invest Radiol 43(1):65–75. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0b013e31815e6277
Spencer AJ, Wilson SA, Batchelor J, Reid A, Rees J, Harpur E (1997) Gadolinium chloride toxicity in the rat. Toxicol Pathol 25(3):245–255. https://doi.org/10.1177/019262339702500301
Swaminathan S, High WA, Ranville J, Horn TD, Hiatt K, Thomas M, Brown HH, Shah SV (2008) Cardiac and vascular metal deposition with high mortality in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Kidney Int 73:1413–1418. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2008.76
Thakral C, Abraham JL (2009) Gadolinium-induced nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is associated with insoluble Gd deposits in tissues: in vivo transmetallation confirmed by microanalysis. J Cutan Pathol 36(12):1244–1254. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01283.x
Vekemans B, Janssens K, Vince L, Adams F, Van Espen P (1994) Analysis of X-ray spectra by iterative least squares (AXIL). New developments. X-Ray Spectr 23:278–285
Wagner B, Drel V, Gorin Y (2016) Pathophysiology of gadolinium-associated systemic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 311(1):F1–F11. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00166.2016
Wang YX, Schroeder J, Siegmund H et al (2015) Total gadolinium tissue deposition and skin structural findings following the administration of structurally different gadolinium chelates in healthy and ovariectomized female rats. Quant Imaging Med Surg 5(4):534–545. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2015.05.03
Wang S, Hesse B, Roman M et al (2019) Increased retention of gadolinium in the inflamed brain after repeated administration of gadopentetate dimeglumine: a proof-of-concept study in mice combining ICP-MS and micro- and nano-SR-XRF. Invest Radiol 54:617–626
Yang XC, Sachs F (1989) Block of stretch-activated ion channels in Xenopus oocytes by gadolinium and calcium ions. Science 243(4894 Pt 1):1068–1071. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2466333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial, consulting, or personal conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osterode, W., Falkenberg, G. & Regele, H. Gadolinium distribution in kidney tissue determined and quantified by micro synchrotron X-ray fluorescence. Biometals 34, 341–350 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-020-00284-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-020-00284-8