Abstract
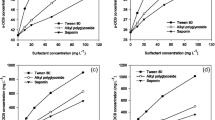
Environmental biodegradation of several chlorinated pesticides is limited by their low solubility and sorption to soil surfaces. To mitigate this problem we quantified the effect of three biosurfactant viz., rhamnolipid, sophorolipid and trehalose-containing lipid on the dissolution, bioavailability, and biodegradation of HCH-isomers in liquid culture and in contaminated soil. The effect of biosurfactants was evaluated through the critical micelle concentration (CMC) value as determined for each isomer. The surfactant increased the solubilization of HCH isomers by 3–9folds with rhamnolipid and sophorolipid being more effective and showing maximum solubilization of HCH isomers at 40 μg/mL, compared to trehalose-containing lipid showing peak solubilization at 60 μg/mL. The degradation of HCH isomers by Sphingomonas sp. NM05 in surfactant-amended liquid mineral salts medium showed 30% enhancement in 2 days as compared to degradation in 10 days in the absence of surfactant. HCH-spiked soil slurry incubated with surfactant also showed around 30–50% enhanced degradation of HCH which was comparable to the corresponding batch culture experiments. Among the three surfactants, sophorolipid offered highest solubilization and enhanced degradation of HCH isomers both in liquid medium and soil culture. The results of this study suggest the effectiveness of surfactants in improving HCH degradation by increased bioaccessibility.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awasthi N, Kumar A, Makkar R, Cameotra SS (1999) Biodegradation of soil-applied endosulfan in the presence of a biosurfactant. J Environ Sci Health B 34(5):793–803
Bardi L, Mattei A, Steffan S, Marzona M (2000) Hydrocarbon degradation by a soil microbial population with b-cyclodextrin as surfactant to enhance bioavailability. Enzyme Microb Technol 27:709–713
Billingsley KA, Backus SM, Ward OP (1999) Effect of surfactant solubilization on biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners by Pseudomonas LB400. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:255–260
Chrzanowski Ł, Wick LY, Meulenkamp R, Kaestner M, Heipieper HJ (2009) Rhamnolipid biosurfactants decrease the toxicity chlorinated phenols to Pseudomonas putida DOT-1TE. Lett Appl Microbiol 48:756–762
Chrzanowski L, Owsianiak M, Szulc A, Marecik R, Piotrowska-Cyplik A, Olejnik-Schmidt AK, Staniewski J, Lisiecki P, Ciesielczyk F, Jesionowski T, Heipieper HJ (2011) Interactions between rhamnolipid biosurfactants and toxic chlorinated phenols enhance biodegradation of a model hydrocarbon-rich effluent. Int. Biodeter Biodegr 65:605–611
Desai JD, Banat AM (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61(1):47–64
Fava F, Di Gioia D (1998) Effects of triton X-100 and quillaya saponin on the ex-situ bioremediation of chronically polychlorobiphenyl contaminated soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:623–630
Frank N, Libner A, Winkelmann M, Hüttl R, Mertens FO, Kaschabek SR, Schlömann M (2010) Degradation of selected (bio-) surfactants by bacterial cultures monitored by calorimetric methods. Biodegradation 21:179–191
Franzetti A, Bestetti G, Caredda P, La Colla P, Tamburini E (2008) Surface-active compounds and their role in the access to hydrocarbons in Gordonia strains. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 63:238–248
Frister A (2006) Trehalosetetraester aus Rhodococcus erythropolisB7g: Optimierung der Herstellung Abbaubarkeitund Beeinflussung des Abbaus organischer Schadstoffe Diploma thesis TU Bergakademie Freiberg
Gobbert U, Lang S, Wagner F (1984) Sophorose lipid formation by resting cells of Torulopsis bombicola. Biotechnol Lett 6:225–230
Hommel RK, Stuwer O, Stuber W, Haferburg D, Kleber HP (1987) Production of water-soluble surface-active exolipids by Torulopsis apicola. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:199–205
Kang SW, Kim YB, Shin JD, Kim EK (2010) Enhanced biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil by microbial biosurfactant sophorolipid. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:780–790
Kumari R, Subudhi S, Suar M, Dhingra G, Raina V, Dogra C, Lal S, van der Meer JR, Holliger C, Lal R (2002) Cloning and characterization of lin genes responsible for the degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain B90. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6021–6028
Lai CC, Huang YC, Wei YH, Chang JS (2009) Biosurfactant-enhanced removal of total petroleum hydrocarbons from contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 167:609–614
Lajoie CA, Layton AC, Easter JP, Menn FM, Sayler GS (1997) Degradation of nonionic surfactants and polychlorinated biphenyls by recombinant field application vectors. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 19:252–262
Lal R, Pandey G, Sharma P, Kumari K, Malhotra S, Pandey R, Raina V, Kohler HPE, Holliger C, Jackson C, Oakeshott JG (2010) Biochemistry of microbial degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane and prospects for bioremediation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 74:58–80
Manickam N, Reddy MK, Saini HS, Shanker R (2008) Isolation of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas sp. by dehalogenase assay and characterization of genes involved in gamma-HCH degradation. J Appl Microbiol 104:952–960
Mata-Sandoval JC, Karns JS, Torrents A (1999) High-performance liquid chromatography method for the characterization of rhamnolipid mixtures produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2 on corn oil. J Chromatogr A 864:211–220
Mata-Sandoval JC, Karns JS, Torrents A (2000) Effect of rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2 on the solubilization of pesticides. Environ Sci Technol 34:4923–4930
Mata-Sandoval JC, Karns JS, Torrents A (2001) Influence of rhamnolipids and triton X-100 on the biodegradation of three pesticides in aqueous phase and soil slurries. J Agric Food Chem 49(7):3296–3303
Mata-Sandoval JC, Karns JS, Torrents A (2002) Influence of rhamnolipids and triton X-100 on the desorption of pesticides from soils. Environ Sci Technol 36:4669–4675
Nagata Y, Miyauchi K, Takagi M (1999) Complete analysis of genes and enzymes for hexachlorocyclohexane degradation in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:380–390
Owsianiak M, Chrzanowski L, Szulc A, Staniewski J, Olszanowski A, Olejnik-Schmidt AK, Heipieper HJ (2009) Biodegradation of diesel/biodiesel blends by a consortium of hydrocarbon degraders: effect of the type of blend and the addition of biosurfactants. Bioresour Technol 100:1497–1500
Pacwa-Płociniczak M, Płaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS (2011) Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. Int J Mol Sci 12:633–654
Rapp P, Bock H, Wray V, Wagner F (1979) Formation isolation and characterization of trehalose dimycolates from Rhodococcus erythropolis grown on n-alkanes. J Gen Microbiol 115:491–503
Schwartz A, Bar R (1995) Cyclodextrin-enhanced degradation of toluene and p-toluic acid by Pseudomonas putida. Appl Microb Biotechnol 6:2727–2731
Semple KT, Doick KJ, Jones KC, Burauel P, Craven A, Harms H (2004) Defining bioavailability and bioaccessibility of contaminated soil and sediment is complicated. Environ Sci Technol 38(12):228A–231A
Sharma S, Singh P, Raj M, Chadha BS, Saini HS (2009) Aqueous phase partitioning of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) isomers by biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa WH-2. J Hazard Mater 171:1178–1182
Sifour M, Al-Jilawi MH, Aziz GM (2007) Emulsification properties of biosurfactant produced from Pseudomonas aeruginosa RB. Pak J Biol Sci 10:1331–1335
Sivaram H, Cumaraswamy V (2011) Effects of surfactants on solubilization of perchloroethylene (PCE) and trichloroethylene (TCE). Ind Eng Chem Res 50(9):5831–5837
Thomas JC, Berger F, Jacquier M, Bernillon D, Baud-Grasset F, Truffaut N, Normand P, Vogel TM, Simonet P (1996) Isolation and characterization of a novel gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading bacterium. J Bacteriol 178:6049–6055
Urum K, Grigson S, Pekdemir T, McMenamy SA (2006) Comparison of the efficiency of different surfactants for removal of crude oil from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 62:1403–1410
Uysal A, Türkman A (2005) A Effect of biosurfactant on 24-dichlorophenol biodegradation in an activated sludge bioreactor. Process Biochem 40:2745–2749
Wang JM, Marlowe EM, Miller-Maier RM, Brusseau ML (1998) Cyclodextrin-enhanced biodegradation of phenanthrene. Environ Sci Technol 32:1907–1912
Zhang Y, Maier WJ, Miller RM (1997) Effect of rhamnolipids on the dissolution bioavailability and biodegradation of phenanthrene. Environ Sci Technol 31:2211–2217
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Stefan Kaschabek, Department of Environmental Microbiology, Technical University-Bergakademie Freiberg, Germany, for his generous gift of biosurfactants. Dr. Deepak Agarwal, Former Scientist at Indian Institute of Toxicology Research, Lucknow, India is appreciated for his valuable suggestions and critical reading of the manuscript. This manuscript carries IITR communication number 2956.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manickam, N., Bajaj, A., Saini, H.S. et al. Surfactant mediated enhanced biodegradation of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) isomers by Sphingomonas sp. NM05. Biodegradation 23, 673–682 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9543-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9543-z