Abstract
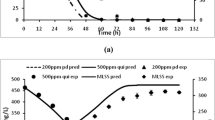
The proposed method of kinetic analysis of aqueous-phase biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) mixture presupposes representation of kinetic curves for each pair of mixture components, S x and S y , in double-logarithmic coordinates (ln S x ; ln S y ). If PAH mixture conversion corresponds to the multisubstrate model with a common active site, then the graphs in double-logarithmic coordinates are straight lines with the angular coefficients equal to the ratio of respective first-order rate constants \( k_{x}^{y} = {\frac{{V_{y} K_{x} }}{{K_{y} V_{x} }}} \), where K x and K y are half-saturation constants, V x and V y are the maximum conversion rates for substrates S x and S y ; the graph slope does not depend on any concentrations and remains constant during the change of reaction rates as a result of inhibition, induction/inactivation of enzymes or biomass growth. The formulated method has been used to analyze PAH mixture conversion by the culture of Sphingomonas sp. VKM B-2434. It has been shown that this process does not satisfy the multisubstrate model with a single active site. The results suggest that the strain VKM B-2434 contains at least two dioxygenases of different substrate specificity: one enzyme converts phenanthrene and fluoranthene and the other converts acenaphthene and acenaphthylene. The ratios of first-order rate constants have been obtained for these pairs of substrates.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baboshin MA, Akimov VN, Baskunov BP, Born TL, Khan SU, Golovleva LA (2008) Conversion of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Sphingomonas sp. VKM B-2434. Biodegradation 19:567–576
Baughman G, Paris DF (1981) Microbial bioconcentrations of organic pollutants from aquatic systems—a critical review. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol 8:205–228
Bouchez M, Blanchet D, Vandecasteele JP (1995) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by pure strains and defined strain associations: inhibition phenomena and cometabolism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:156–164
Casellas M, Grifoll M, Sebate J, Solanas AM (1998) Isolation and characterization of a fluorenone-degrading bacterial strain and its role in synergistic degradation of fluorene by a consortium. Can J Microbiol 44:734–742
Chevillard C, Cardenas ML, Cornish-Bowden A (1993) The competition plot: a simple test of whether two reactions occur at the same active site. Biochem J 289:599–604
Crabtree B, Newsholme EA (1987) A systematic approach to describing and analyzing metabolic control systems. Trends Biochem Sci 12:4–12
Demaneche S, Meyer C, Micoud J, Louwagie M, Willison JC, Jouanneau Y (2004) Identification and functional analysis of two aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases from a Sphingomonas strain that degrades various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6714–6725
Desai AM, Autenrieth RL, Dimitriou-Christidis P, McDonald TJ (2008) Biodegradation kinetics of select polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) mixtures by Sphingomonas paucimobilis EPA505. Biodegradation 19:223–233
Dimitriou-Christidis P, Autenrieth RL (2007) Kinetics of biodegradation of binary and ternary mixtures of PAHs. Biotech Bioeng 97:788–800
Grady CPL Jr, Smets BF, Barbeau DS (1996) Variability in kinetic parameter estimates: a review of possible causes and a proposed terminology. Water Res 30:742–748
Guha S, Peters CA, Jaffé PR (1999) Multisubstrate biodegradation kinetics of naphthalene, phenanthrene, and pyrene mixtures. Biotech Bioeng 65:491–499
Juhasz AL, Naidu R (2000) Bioremediation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review of microbial degradation of benzo[a]pyrene. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 45:57–88
Kazunga C, Aitken MD (2000) Products of incomplete metabolism of pyrene by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1917–1922
Kim S-J, Kweon O, Freeman JP, Jones RC, Adjei MD, Jhoo J-W, Edmondson RD, Cerniglia CE (2006) Molecular cloning and expression of genes encoding a novel dioxygenase involved in low- and high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1045–1054
Knightes CD, Peters CA (2006) Multisubstrate biodegradation kinetics for binary and complex mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1746–1756
Krivobok S, Kuony S, Meyer C, Louwagie M, Willison JC, Jouanneau Y (2003) Identification of pyrene-induced proteins in Mycobacterium sp. strain 6PY1: evidence for two ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases. J Bacteriol 185:3828–3841
Lotfabad SK, Gray MR (2002) Kinetics of biodegradation mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:361–366
Molina M, Araujo R, Hodson RE (1999) Cross-induction of pyrene and phenanthrene in a Mycobacterium sp. isolated from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated river sediments. Can J Microbiol 45:520–529
Segel IH (1975) Enzyme kinetics. Wiley, New York
Seo J-S, Keum Y-S, Li QX (2009) Bacterial degradation of aromatic compounds. Int J Environ Res Public Health 6:278–309
Stringfellow WT, Aitken MD (1995) Competitive metabolism of naphthalene, methylnaphthalene and fluorene by phenanthrene-degrading pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:357–362
Wammer KH, Peters CA (2005) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation rates: a structure-based study. Environ Sci Technol 39:2571–2578
Wammer KH, Peters CA (2006) A molecular modeling analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation by naphthalene dioxygenase. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:912–920
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baboshin, M., Golovleva, L. Multisubstrate kinetics of PAH mixture biodegradation: analysis in the double-logarithmic plot. Biodegradation 22, 13–23 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9370-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9370-z