Abstract
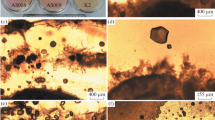
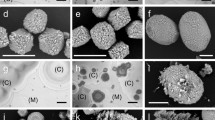
To obtain a restoring and protective calcite layer on degraded limestone, five different strains of the Bacillus sphaericus group and one strain of Bacillus lentus were tested for their ureolytic driven calcium carbonate precipitation. Although all the Bacillus strains were capable of depositing calcium carbonate, differences occurred in the amount of precipitated calcium carbonate on agar plate colonies. Seven parameters involved in the process were examined: calcite deposition on limestone cubes, pH increase, urea degrading capacity, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)-production, biofilm formation, ζ-potential and deposition of dense crystal layers. The strain selection for optimal deposition of a dense CaCO3 layer on limestone, was based on decrease in water absorption rate by treated limestone. Not all of the bacterial strains were effective in the restoration of deteriorated Euville limestone. The best calcite precipitating strains were characterised by high ureolytic efficiency, homogeneous calcite deposition on limestone cubes and a very negative ζ-potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amer F, Mahoud AA, Sabet V, (1985) Zeta-potential and surface-area of calcium carbonate as related to phosphate sorption Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 49(5): 1137–1142
Beushausen HD, Alexander MG, Mackechnie J, (2003) Aspekte der Dauerhaftigkeit des Betons in einem internationalen Vergleich Concrete Precast Plant Technol. 7: 22–33
Burne RA, Chen YY, (2000) Bacterial ureases in infectious diseases Microbes Infect. 2: 533–542
Castanier S, Le Métayer-Levrel G, Perthuisot J, (1999) Ca-carbonates precipitation and limestone genesis – the microbiogeologist point of view Sediment. Geol. 126: 9–23
Cultrone G, Sebastian E, Elert K, de la Torre MJ, Cazalla O, Rodriguez-Navarro C, (2004) Influence of mineralogy and firing temperature on the porosity of bricks J. Eur. Cer. Soc. 24: 547–564
Friedman LE, Passerini de Rossi BN, Messina MT, Franco MA, (2001) Phenotype evaluation of Bordetella bronchiseptica cultures by urease activity and congo red affinity Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 33: 285–290
Greenberg AE, Clesceri LS, Eaton ED, (1992) Standard methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, (18). American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Griffiths RI, Whitley AS, O’Donnell AG, Bailey MJ, (2000) Rapid method for coextraction of DNA and RNA from natural environments for analysis of ribosomal DNA- and rRNA-based microbial community composition AEM 66(12): 5488–5499
Hamilton WA, (2003) Microbially influenced corrosion as a model system for the study of metal microbe interactions: a unifying electron transfer hypothesis Biofouling 19(1): 65–76
Hammes F, Boon N, de Villiers J, Verstraete W, Siciliano SD, (2003) Strain-specific ureolytic microbial carbonate precipitation Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69(8): 4901–4909
Kawaguchi T, Decho AW, (2002). A laboratory investigation of cyanobacterial extracellular polymeric secretions (EPS) in influencing CaCO3 polymorphism J. Cryst. Growth 240: 230–235
Kowalchuk GA, Bodelier PLE, Heilig GHJ, Stephen JR, Laanbroek HJ, (1998) Community analysis of ammonia-oxidising bacteria, in relation to oxygen availability in soils and root oxygenated sediments, using PCR, DGGE and oligonucleotide probe hybridistation FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 27: 339–350
Merz-Preiss M, Riding R, (1999) Cyanobacterial tufa calcification in two freshwater streams: ambient environment, chemical thresholds and biological processes Sediment. Geol. 126(1–4): 103–124
Mobley HLY, Hausinger RP, (1989) Microbial ureases: significance, regulation and molecular characterization Microb. Rev. 53: 85–108
Molin J, Molin S, (1997) CASE: complex adaptive systems ecology Adv. Microb. Ecol. 15: 27–29
Prikryl R, Lokajicek T, Svobodova J, Weishauptova Z, (2003) Experimental weathering of marlstone from Predni Kopanina (Czech Republic) – historical building stone of Prague Build. Environ. 38: 1163–1171
Rowan NJ, Caldow G, Gemmell CG, Hunter IS, (2003) Production of diarrheal enterotoxins and other potential virulence factors by veterinary isolates of Bacillus species associated with nongastrointestinal infections Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69(4): 2372–2376
Stocks-Fischer S, Galinat JK, Bang SS, (1999) Microbiological precipitation of CaCO3 Soil Biol. Biochem. 31: 1563–1571
Tsuneda S, Jung J, Hayashi H, Aikawa H, Hirata A, Sasaki H, (2003) Influence of extracellular polymers on electrokinetic properties of heterotrophic bacterial cells examined by soft particle electrophoresis theory Colloid Surface B 29: 181–188
Udert KM, Larsen TA, Gujer W, (2003) Estimating the precipitation potential in urine-collecting systems Water Res. 37: 2667–2677
Warren LA, Maurice PA, Ferris FG, (2001) Microbially mediated calcium carbonate precipitation: implications for interpreting calcite precipitation and for solid-phase capture of inorganic contaminants Geomicrobiol. J. 18: 93–115
Warscheid T, Braams J, (2000) Biodeterioration of stone: a review Int Biodeter. Biodegr. 46: 343–368
Wen ZT, Burne RA, (2002) Functional genomics approach to identifying genes required for biofilm development by Streptococcus mutans Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68(3): 1196–1203
Yates KK, Robbins LL, (1999) Radioisotope tracer studies of inorganic carbon and Ca in microbially derived CaCO3 Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 63(1): 129–136
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Fund for Scientific Research – Flanders (project G.0054.02). The authors wish to thank Nico Boon, Sylvie Seurinck and Kim Windey for critically reading this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dick, J., De Windt, W., De Graef, B. et al. Bio-deposition of a calcium carbonate layer on degraded limestone by Bacillus species . Biodegradation 17, 357–367 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-005-9006-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-005-9006-x