Abstract
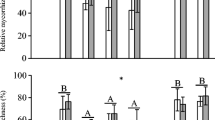
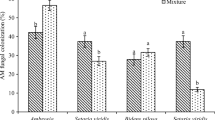
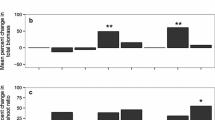
Introduced, non-native organisms are of global concern, because biological invasions can negatively affect local communities. Arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungal communities have not been well studied in this context. AM fungi are abundant in most soils, forming symbiotic root-associations with many plant species. Commercial AM fungal inocula are increasingly spread worldwide, because of potentially beneficial effects on plant growth. In contrast, some invasive plant species, such as the non-mycorrhizal Alliaria petiolata, can negatively influence AM fungi. In a greenhouse study we examined changes in the structure of a local Canadian AM fungal community in response to inoculation by foreign AM fungi and the manipulated presence/absence of A. petiolata. We expected A. petiolata to have a stronger effect on the local AM fungal community than the addition of foreign AM fungal isolates. Molecular analyses indicated that inoculated foreign AM fungi successfully established and decreased molecular diversity of the local AM fungal community in host roots. A. petiolata did not affect molecular diversity, but reduced AM fungal growth in the greenhouse study and in a in vitro assay. Our findings suggest that both introduced plants and exotic AM fungi can have negative impacts on local AM fungi.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal AA, Kotanen PM, Mitchell CE, Power AG, Godsoe W, Klironomos J (2005) Enemy release? An experiment with congeneric plant pairs and diverse above- and belowground enemies. Ecol 86:2979–2989
Antunes PM, Koch AM, Dunfield KE, Hart MM, Downing A, Rillig MC, Klironomos JN (2009) Influence of commercial inoculation with Glomus intraradices on the structure and functioning of an AM fungal community from an agricultural site. Plant Soil 317:257–266
Arim M, Abades SR, Neill PE, Lima M, Marquet PA (2006) Spread dynamics of invasive species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:374–378
Avis PG, Dickie IA, Mueller GM (2006) A ‘dirty’ business: testing the limitations of terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (TRFLP) analysis of soil fungi. Mol Ecol 15:873–882
Bais HP, Vepachedu R, Gilroy S, Callaway RM, Vivanco JM (2003) Allelopathy and exotic plant invasion: From molecules and genes to species interactions. Science 301:1377–1380
Barto EK, Cipollini D (2009) Half-lives and field soil concentrations of Alliaria petiolata secondary metabolites. Chemosphere 76:71–75
Becard G, Fortin JA (1988) Early events of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhiza formation on Ri T-DNA transformed roots. New Phytol 108:211–218
Broennimann O, Treier UA, Muller-Scharer H, Thuiller W, Peterson AT, Guisan A (2007) Evidence of climatic niche shift during biological invasion. Ecol Lett 10:701–709
Burke DJ (2008) Effects of Alliaria petiolata (garlic mustard; Brassicaceae) on mycorrhizal colonization and community structure in three herbaceous plants in a mixed deciduous forest. Am J Bot 95:1416–1425
Callaway RM, Ridenour WM (2004) Novel weapons: invasive success and the evolution of increased competitive ability. Front Ecol Environ 2:436–443
Callaway RM, Thelen GC, Rodriguez A, Holben WE (2004) Soil biota and exotic plant invasion. Nature 427:731–733
Callaway RM, Cipollini D, Barto K, Thelen GC, Hallett SG, Prati D, Stinson K, Klironomos J (2008) Novel weapons: Invasive plant suppresses fungal mutualists in America but not in its native Europe. Ecol 89:1043–1055
Croll D, Sanders IR (2009) Recombination in Glomus intraradices, a supposed ancient asexual arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. BMC Evolutionary Biology 9:13
Croll D, Wille L, Gamper HA, Mathimaran N, Lammers PJ, Corradi N, Sanders IR (2008) Genetic diversity and host plant preferences revealed by simple sequence repeat and mitochondrial markers in a population of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices. New Phytol 178:672–687
Croll D, Giovannetti M, Koch AM, Sbrana C, Ehinger M, Lammers PJ, Sanders IR (2009) Nonself vegetative fusion and genetic exchange in the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices. New Phytol 181:924–937
Desprez-Loustau M-L, Robin C, Buée M, Courtecuisse R, Garbaye J, Suffert F, Sache I, Rizzo DM (2007) The fungal dimension of biological invasions. Trends Ecol Evol 22:472–480
Dorning M, Cipollini D (2006) Leaf and root extracts of the invasive shrub, Lonicera maackii, inhibit seed germination of three herbs with no autotoxic effects. Plant Ecol 184:287–296
Dunbar J, Ticknor LO, Kuske CR (2001) Phylogenetic specificity and reproducibility and new method for analysis of terminal restriction fragment profiles of 16S rRNA genes from bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:190–197
Ehinger M, Koch AM, Sanders IR (2009) Changes in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal phenotypes and genotypes in response to plant species identity and phosphorus concentration. New Phytol 184:412–423
Enright SM, Cipollini D (2007) Infection by powdery mildew Erysiphe cruciferarum (Erysiphaceae) strongly affects growth and fitness of Alliaria petiolata (Brassicaceae). Am J Bot 94:1813–1820
Funk JL, Vitousek PM (2007) Resource-use efficiency and plant invasion in low-resource systems. Nature 446:1079–1081
Gimsing AL, Sorensen JC, Tovgaard L, Jorgensen AMF, Hansen HCB (2006) Degradation kinetics of glucosinolates in soil. Environ Tox Chem 25:2038–2044
Gimsing AL, Sorensen JC, Strobel BW, Hansen HCB (2007) Adsorption of glucosinolates to metal oxides, clay minerals and humic acid. Appl Clay Sci 35:212–217
Gollotte A, van Tuinen D, Atkinson D (2004) Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonising roots of the grass species Agrostis capillaris and Lolium perenne in a field experiment. Mycorrhiza 14:111–117
Grime JP, Mackey JML, Hillier SH, Read DJ (1987) Floristic diversity in a model system using experimental microcosms. Nature 328:420–422
Hart MM, Klironomos JN (2002) Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and ecosystem functioning. In: van der Heijden MGA, Sanders IR (eds) Mycorrhizal Ecology. Springer, pp, pp 225–242
Hawkes CV, Belnap J, D’Antonio C, Firestone MK (2006) Arbuscular mycorrhizal assemblages in native plant roots change in the presence of invasive exotic grasses. Plant Soil 281:369–380
Hooper DU, Chapin FS, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecol Monogr 75:3–35
Jansa J, Smith FA, Smith SE (2008) Are there benefits of simultaneous root colonization by different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi? New Phytol 177:779–789
Johnson NC, Graham JH, Smith FA (1997) Functioning of mycorrhizal associations along the mutualism-parasitism continuum. New Phytol 135:575–586
Klironomos JN (2002) Feedback with soil biota contributes to plant rarity and invasiveness in communities. Nature 417:67–70
Klironomos JN (2003) Variation in plant response to native and exotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Ecol 84:2292–2301
Koch AM, Kuhn G, Fontanillas P, Fumagalli L, Goudet J, Sanders IR (2004) High genetic variability and low local diversity in a population of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2369–2374
Koch AM, Croll D, Sanders IR (2006) Genetic variability in a population of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi causes variation in plant growth. Ecol Lett 9:103–110
Lankau RA, Nuzzo V, Spyreas G, Davis AS (2009) Evolutionary limits ameliorate the negative impact of an invasive plant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:15362–15367
Lee CE (2002) Evolutionary genetics of invasive species. Trends Ecol Evol 17:386–391
Legendre P, Anderson MJ (1999) Distance-based redundancy analysis: Testing multispecies responses in multifactorial ecological experiments. Ecol Monogr 69:1–24
Lockwood JL, Cassey P, Blackburn T (2005) The role of propagule pressure in explaining species invasions. Trends Ecol Evol 20:223–228
Maherali H, Klironomos JN (2007) Influence of phylogeny on fungal community assembly and ecosystem functioning. Science 316:1746–1748
Martin F, Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Hijri M, Lammers P, Requena N, Sanders IR, Shachar-Hill Y, Shapiro H, Tuskan GA, Young JPW (2008) The long hard road to a completed Glomus intraradices genome. New Phytol 180:747–750
McGonigle TP, Miller MH, Evans DG, Fairchild GL, Swan JA (1990) A new method which gives an objective-measure of colonization of roots by vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 115:495–501
Meekins JF, McCarthy BC (1999) Competitive ability of Alliaria petiolata (garlic mustard, Brassicaceae), an invasive, nonindigenous forest herb. Int J Plant Sci 160:743–752
Mummey DL, Rillig MC (2006) The invasive plant species Centaurea maculosa alters arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in the field. Plant Soil 288:81–90
Mummey DL, Rillig MC (2007) Evaluation of LSU rRNA-gene PCR primers for analysis of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities via terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J Microbiol Methods 70:200–204
Mummey DL, Antunes PM, Rillig MC (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi pre-inoculant identity determines community composition in roots. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1173–1179
Newsham KK, Fitter AH, Watkinson AR (1995) Multi-functionality and biodiversity in arbuscular mycorrhizas. Trends Ecol Evol 10:407–411
Opik M, Moora M, Liira J, Zobel M (2006) Composition of root-colonizing arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in different ecosystems around the globe. J Ecol 94:778–790
Prati D, Bossdorf O (2004) Allelopathic inhibition of germination by Alliaria petiolata (Brassicaceae). Am J Bot 91:285–288
Rees GN, Baldwin DS, Watson GO, Perryman S, Nielsen DL (2004) Ordination and significance testing of microbial community composition derived from terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms: application of multivariate statistics. Antonie Van Leewenhoek Int J Gen Mol Biol 86:339–347
Remy W, Taylor TN, Hass H, Kerp H (1994) Four-hundred-million-year-old vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11841–11843
Ridenour WM, Callaway RM (2001) The relative importance of allelopathy in interference: the effects of an invasive weed on a native bunchgrass. Oecologia 126:444–450
Rillig MC (2004) Arbuscular mycorrhizae and terrestrial ecosystem processes. Ecol Lett 7:740–754
Roberts KJ, Anderson RC (2001) Effect of garlic mustard Alliaria petiolata (Beib. Cavara & Grande) extracts on plants and arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi. Am Midland Nat 146:146–152
Schlaepfer MA, Sherman PW, Blossey B, Runge MC (2005) Introduced species as evolutionary traps. Ecol Lett 8:241–246
Schwartz MW, Hoeksema JD, Gehring CA, Johnson NC, Klironomos JN, Abbott LK, Pringle A (2006) The promise and the potential consequences of the global transport of mycorrhizal fungal inoculum. Ecol Lett 9:501–515
Sikes BA, Cottenie K, Klironomos JN (2009) Plant and fungal identity determines pathogen protection of plant roots by arbuscular mycorrhizas. J Ecol 97:1274–1280
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. Academic Press, London, U.K
Stinson KA, Campbell SA, Powell JR, Wolfe BE, Callaway RM, Thelen GC, Hallett SG, Prati D, Klironomos JN (2006) Invasive plant suppresses the growth of native tree seedlings by disrupting belowground mutualisms. PLoS Biology 4:727–731
Trouvelot S, van Tuinen D, Hijri M, Gianinazzi-Pearson V (1999) Visualization of ribosomal DNA loci in spore interphasic nuclei of glomalean fungi by fluorescence in situ hyhridization. Mycorrhiza 8:203–206
Tsao R, Yu Q, Friesen I, Potter J, Chiba M (2000) Factors affecting the dissolution and degradation of oriental mustard-derived sinigrin and allyl isothiocyanate in aqueous media. J Agri Food Chem 48:1898–1902
van der Heijden MGA (2004) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as support systems for seedling establishment in grassland. Ecol Lett 7:293–303
van der Heijden MGA, Klironomos JN, Ursic M, Moutoglis P, Streitwolf-Engel R, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1998) Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature 396:69–72
van der Putten WH, Klironomos JN, Wardle DA (2007) Microbial ecology of biological invasions. ISME J 1:28–37
van Tuinen D, Jacquot E, Zhao B, Gollotte A, Gianinazzi-Pearson V (1998) Characterization of root colonization profiles by a microcosm community of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi using 25S rDNA-targeted nested PCR. Mol Ecol 7:879–887
Vaughn SF, Berhow MA (1999) Allelochemicals isolated from tissues of the invasive weed garlic mustard (Alliaria petiolata). J Chem Ecol 25:2495–2504
Wehner J, Antunes PM, Powell JR, Mazukatow J, Rillig MC (2010) Plant pathogen protection by mycorrhizas: diversity takes central role. Pedobiol. 53:197–201
Wolfe BE, Rodgers VL, Stinson KA, Pringle A (2008) The invasive plant Alliaria petiolata (garlic mustard) inhibits ectomycorrhizal fungi in its introduced range. J Ecol 96:777–783
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis, 2nd Ed edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA
Zhang Q, Yao LJ, Yang RY, Yang XY, Tang JJ, Chen X (2007) Potential allelopathic effects of an invasive species Solidago canadensis on the mycorrhizae of native plant species. Allelopath J 20:71–77
Acknowledgments
We thank Michael Mucci and Lindsay Wilson for technical assistance. Isabelle Meusnier and the Biodiversity Institute of Ontario helped us with the T-RFLP analysis. A.M.K. was supported by fellowships from the Swiss National Science Foundation (PBLAA-114210 and PAOOA-119519) and the Roche Research Foundation. D.L.M. was supported by grants from National Science Foundation Ecology (0515904) and United States Department of Agriculture—Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (2005-35320-16267). We also thank the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Alexander M. Koch and Pedro M. Antunes contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koch, A.M., Antunes, P.M., Kathryn Barto, E. et al. The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungal and garlic mustard introductions on native AM fungal diversity. Biol Invasions 13, 1627–1639 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-010-9920-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-010-9920-7