Abstract
Objective
To develop a new and efficient biocatalytic synthesis method of imidazole-4-acetic acid (IAA) from l-histidine (l-His).
Results
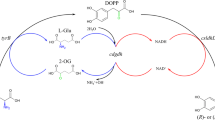
l-His was converted to imidazole-4-pyruvic acid (IPA) by an Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst expressing membrane-bound l-amino acid deaminase (ml-AAD) from Proteus vulgaris firstly. The obtained IPA was subsequently decarboxylated to IAA under the action of H2O2. Under optimum conditions, 34.97 mM IAA can be produced from 50 mM l-His, with a yield of 69.9%.
Conclusions
Compared to the traditional chemical synthesis, this biocatalytic method for IAA production is not only environmentally friendly, but also more cost effective, thus being promising for industrial IAA production.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 June 2018
In the original publication of the article, the affiliations of authors Jun Huang, Changjiang Lv and Jiaqi Mei were misplaced. The correct information for author affiliations is provided in this correction.
References
Chowdhury G, Dostalek M, Hsu EL, Nguyen LP, Stec DF, Bradfield CA, Guengerich FP (2009) Structural identification of diindole agonists of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor derived from degradation of indole-3-pyruvic acid. Chem Res Toxicol 22:1905–1912
Cooper AJ, Ginos JZ, Meister A (1983) Synthesis and properties of the alpha-keto acids. Chem Rev 83:321–358
Ding HR, Zhao WR, Lv CJ, Huang J, Hu S, Yao SJ, Mei LH, Wang JB (2017) Biosynthesis of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid from l-tyrosine using recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing membrane bound l-amino acid deaminase. Chin J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.08.009
Drozdzewski P, Pawlak B (2004) Coordination sphere vibrations in copper(II), nickel(II) and cobalt(II) complexes with 4-imidazoleacetic acid; metal isotope, deuteration, and density functional study. Spectrochim Acta A 60:1527–1532
Drozdzewski P, Pawlak B, Glowiak T (2002) Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of aquabis (imdazole-4-acetato) copper(II). J Coord Chem 55:735–744
Easson A, Pyman FL (1932) A general method for the preparation of 1-substituted glyoxalines from acetalylthiocarbimide and primary amines. J Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1039/JR9320001806
Ghosn B, Singh A, Li M, Vlassov AV, Burnett C, Puri N, Roy K (2010) Efficient gene silencing in lungs and liver using imidazole-modified chitosan as a nanocarrier for small interfering RNA. Oligonucleotides 20:163–172
Hossain GS, Li J, Shin H, Chen RR, Du G, Liu L, Chen J (2014a) Bioconversion of l-glutamic acid to alpha-ketoglutaric acid by an immobilized whole-cell biocatalyst expressing l-amino acid deaminase from Proteus mirabilis. J Biotechnol 169:112–120
Hossain GS, Li J, Shin H, Du G, Wang M, Liu L, Chen J (2014b) One-step biosynthesis of alpha-keto-gamma-methylthiobutyric acid from l-methionine by an Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst expressing an engineered l-amino acid deaminase from Proteus vulgaris. PLoS ONE 9(12):e11429112
Ju Y, Tong S, Gao Y, Zhao W, Liu Q, Gu Q, Xu J, Niu L, Teng M, Zhou H (2016) Crystal structure of a membrane-bound l-amino acid deaminase from Proteus vulgaris. J Struct Biol 195:306–315
Kulis-Horn RK, Persicke M, Kalinowski J (2014) Histidine biosynthesis, its regulation and biotechnological application in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb Biotechnol 7:5–25
Kurdziel K, Glowiak T, Materazzi S, Jezierska J (2003) Crystal structure and physico-chemical properties of cobalt(II) and manganese(II) complexes with imidazole-4-acetate anion. Polyhedron 22:3123–3128
Mehler AH, Tabor H, Bauer H (1952) The oxidation of histamine to imidazoleacetic acid in vivo. J Biol Chem 197:475–480
Niu P, Dong X, Wang Y, Liu L (2014) Enzymatic production of alpha-ketoglutaric acid from l-glutamic acid via l-glutamate oxidase. J Biotechnol 179:56–62
Pyman FL (1911) A new synthesis of 4 (or 5-)-beta-aminoethylglyoxaline, one of the active principles of ergot. J Chem Soc 99:668–682
Schayer RW (1952) The metabolism of ring-labeled histamine. J Biol Chem 196:469–475
Scott E, Peter F, Sanders J (2007) Biomass in the manufacture of industrial products—the use of proteins and amino acids. Appl Microbiol Biot 75:751–762
Song Y, Li J, Shin H, Du G, Liu L, Chen J (2015) One-step biosynthesis of alpha-ketoisocaproate from l-leucine by an Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst expressing an l-amino acid deaminase from Proteus vulgaris. Sci Rep 5:12614
Takahashi E, Ito K, Yoshimoto T (1999) Cloning of l-amino acid deaminase gene from Proteus vulgaris. Biosci Biotech Bioch 63:2244–2247
Teng Y, Scott EL, van Zeeland ANT, Sanders JPM (2011) The use of l-lysine decarboxylase as a means to separate amino acids by electrodialysis. Green Chem 13:624–630
Tunnicliff G (1998) Pharmacology and function of imidazole 4-acetic acid in brain. Gen Pharmacol 31:503–509
Valembois S, Krall J, Frolund B, Steffansen B (2017) Imidazole-4-acetic acid, a new lead structure for interaction with the taurine transporter in outer blood-retinal barrier cells. Eur J Pharm Sci 103:77–84
Wu XW, Li F, Wen J, Tian XS, Wu GY, Chen WD (2014) HPLC determination of 2-methylimidazole and 4-methylimidazolein imidazole. PTCA 9:1146–1148
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670804, 31470793, 21376217), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M592003), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (LY16B060008), and the General Scientific Research Project of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department (Y201432760).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Ding, H., Hu, S. et al. An efficient biocatalytic synthesis of imidazole-4-acetic acid. Biotechnol Lett 40, 1049–1055 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2569-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-018-2569-5