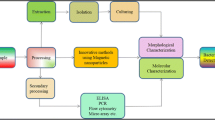
Abstract
Bacterial cell immobilization is a novel technique used in many areas of biosciences and biotechnology. Iron oxide nanoparticles have attracted much attention in bacterial cell immobilization due to their unique properties such as superparamagnetism, large surface area to volume ratio, biocompatibility and easy separation methodology. Adhesion is the basis behind many immobilization techniques and various types of interactions determine bacterial adhesion. Efficiency of bacterial cell immobilization using iron oxide nanoparticles (IONs) generally depends on the physicochemical properties of the IONs and surface properties of bacterial cells as well as environmental/culture conditions. Bacteria exhibit various metabolic responses upon interaction with IONs, and the potential applications of iron oxide nanoparticles in bacterial cell immobilization will be discussed in this work.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amemiya Y, Arakaki A, Staniland SS, Tanaka T, Matsunaga T (2007) Controlled formation of magnetite crystal by partial oxidation of ferrous hydroxide in the presence of recombinant magnetotactic bacterial protein Mms 6. Biomaterials 28:5381–5389
Ansari F, Grigoriev P, Libor S, Tothill IE, Ramsden JJ (2009) DBT degradation enhancement by decorating Rhodococcus erythropolis IGST8 with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1505–1512
Arakha M et al (2015) Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14813
Aruguete DM, Hochella MF (2010) Bacteria–nanoparticle interactions and their environmental implications. Environ Chem 7:3–9
Assa F, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H, Ajamein H, Anarjan N, Vaghari H, Sayyar Z, Berenjian A (2016) A biotechnological perspective on the application of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nano Res 9:2203–2225
Assa F, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H, Ajamein H, Vaghari H, Anarjan N, Ahmadi O, Berenjian A (2017) Chitosan magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery systems. Crit Rev Biotechnol 37:492–509
Auffan M et al (2008) Relation between the redox state of iron-based nanoparticles and their cytotoxicity toward Escherichia coli. Environ Sci Technol 42:6730–6735
Azam A, Ahmed AS, Oves M, Khan MS, Habib SS, Memic A (2012) Antimicrobial activity of metal oxide nanoparticles against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria: a comparative study. Int J Nanomed 7:6003–6009
Bharde A et al (2006) Extracellular biosynthesis of magnetite using fungi. Small 2:135–141
Bharde AA et al (2008) Bacteria-mediated precursor-dependent biosynthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide and iron sulfide nanoparticles. Langmuir 24:5787–5794
Borcherding J et al (2014) Iron oxide nanoparticles induce Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth, induce biofilm formation, and inhibit antimicrobial peptide function. Environ Sci 1:123–132
Borlido L, Azevedo A, Roque A, Aires-Barros M (2013) Magnetic separations in biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 31:1374–1385
Caccavo F, Schamberger PC, Keiding K, Nielsen PH (1997) Role of hydrophobicity in adhesion of the dissimilatory Fe (III)-reducing bacterium Shewanella alga to amorphous Fe (III) oxide. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3837–3843
Cassidy M, Lee H, Trevors J (1996) Environmental applications of immobilized microbial cells: a review. J Ind Microbiol 16:79–101
Chatterjee S, Bandyopadhyay A, Sarkar K (2011) Effect of iron oxide and gold nanoparticles on bacterial growth leading towards biological application. J Nanobiotechnol 9:1–7
Chen L, Razavi FS, Mumin A, Guo X, Sham T-K, Zhang J (2013) Multifunctional nanoparticles for rapid bacterial capture, detection, and decontamination. RSC Adv 3:2390–2397
Chua H, Wong P, Yu P, Li X (1998) The removal and recovery of copper (II) ions from wastewater by magnetite immobilized cells of Pseudomonas putida 5-X. Water Sci Technol 38:315–322
Czaczyk K, Myszka K (2007) Biosynthesis of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and its role in microbial biofilm formation. Pol J Environ Stud 16:799–806
Dickson JS, Koohmaraie M (1989) Cell surface charge characteristics and their relationship to bacterial attachment to meat surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:832–836
Dunhill P (1984) Immobilizing bacteria. Cell 36:796–797
Ebrahiminezhad A, Davaran S, Rasoul-Amini S, Barar J, Moghadam M, Ghasemi Y (2012a) Synthesis, characterization and anti-Listeria monocytogenes effect of amino acid coated magnetite nanoparticles. Curr Nanosci 8:868–874
Ebrahiminezhad A, Ghasemi Y, Rasoul-Amini S, Barar J, Davaran S (2012b) Impact of amino-acid coating on the synthesis and characteristics of iron-oxide nanoparticles (IONs). Bull Korean Chem Soc 33:3957–3962
Ebrahiminezhad A, Ghasemi Y, Rasoul-Amini S, Barar J, Davaran S (2013) Preparation of novel magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles using amino acids. Colloids Surf B 102:534–539
Ebrahiminezhad A, Rasoul-Amini S, Davaran S, Barar J, Ghasemi Y (2014) Impacts of iron oxide nanoparticles on the invasion power of Listeria monocytogenes. Curr Nanosci 10:382–388
Ebrahiminezhad A, Rasoul-Amini S, Kouhpayeh A, Davaran S, Barar J, Ghasemi Y (2015a) Impacts of amine functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles on HepG2 cell line. Curr Nanosci 11:113–119
Ebrahiminezhad A, Varma V, Yang S, Ghasemi Y, Berenjian A (2015b) Synthesis and application of amine functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles on Menaquinone-7 Fermentation: a step towards process intensification. Nanomaterials 6:1–9
Ebrahiminezhad A, Varma V, Yang S, Berenjian A (2016) Magnetic immobilization of Bacillus subtilis natto cells for menaquinone-7 fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:173–180
Ebrahiminezhad A, Barzegar Y, Ghasemi Y, Berenjian A (2017) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Alcea rosea flower extract as a new generation of antimicrobials. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 23:31–37
El-Boubbou K, Gruden C, Huang X (2007) Magnetic glyco-nanoparticles: a unique tool for rapid pathogen detection, decontamination, and strain differentiation. J Am Chem Soc 129:13392–13393
Fletcher M (1977) The effects of culture concentration and age, time, and temperature on bacterial attachment to polystyrene. Can J Microbiol 23:1–6
Fletcher M (1996) Bacterial attachment in aquatic environments : A diversity of surfaces and adhesion strategies. In: Fletcher M (ed) Bacterial adhesion: molecular and ecological diversity. Wiley, New York, pp 1–24
Galazzo JL, Bailey JE (1990) Growing Saccharomyces cerevisiae in calcium-alginate beads induces cell alterations which accelerate glucose conversion to ethanol. Biotechnol Bioeng 36:417–426
Gao J, Li L, Ho PL, Mak GC, Gu H, Xu B (2006) Combining fluorescent probes and biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles for rapid detection of bacteria in human blood. Adv Mater 18:3145–3148
Gholami A, Rasoul-amini S, Ebrahiminezhad A, Seradj SH, Ghasemi Y (2015) Lipoamino acid coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles concentration and time dependently enhanced growth of human hepatocarcinoma cell line (Hep-G2). J Nanomater 2015: Article No. 451405 https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/451405
Gholami A, Rasoul-Amini S, Ebrahiminezhad A, Abootalebi N, Niroumand U, Ebrahimi N, Ghasemi Y (2016) Magnetic properties and antimicrobial effect of amino and lipoamino acid coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Minerva Biotecnol 28:177–186
Gnanaprakash G, Mahadevan S, Jayakumar T, Kalyanasundaram P, Philip J, Raj B (2007) Effect of initial pH and temperature of iron salt solutions on formation of magnetite nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 103:168–175
Grasso D, Smets B, Strevett K, Machinist B, Van Oss C, Giese R, Wu W (1996) Impact of physiological state on surface thermodynamics and adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ Sci Technol 30:3604–3608
Gu H, Ho P-L, Tsang KW, Wang L, Xu B (2003) Using biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles to capture vancomycin-resistant enterococci and other gram-positive bacteria at ultralow concentration. J Am Chem Soc 125:15702–15703
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005a) Cytotoxicity suppression and cellular uptake enhancement of surface modified magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 26:1565–1573
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005b) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26:3995–4021
Hilge-Rotmann B, Rehm H-J (1991) Relationship between fermentation capability and fatty acid composition of free and immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34:502–508
Ho K-C, Tsai P-J, Lin Y-S, Chen Y-C (2004) Using biofunctionalized nanoparticles to probe pathogenic bacteria. Anal Chem 76:7162–7168
Huang Y-F, Wang Y-F, Yan X-P (2010) Amine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for rapid capture and removal of bacterial pathogens. Environ Sci Technol 44:7908–7913
Janot R, Guérard D (2002) One-step synthesis of maghemite nanometric powders by ball-milling. J Alloys Compd 333:302–307
Jirků V (1999) Whole cell immobilization as a means of enhancing ethanol tolerance. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 22:147–151
Kaittanis C, Naser SA, Perez JM (2007) One-step, nanoparticle-mediated bacterial detection with magnetic relaxation. Nano Lett 7:380–383
Kekutia S, Saneblidze L, Mikelashvili V, Markhulia J, Tatarashvili R, Daraselia D, Japaridze D (2015) A new method for the synthesis of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Eur Chem Bull 4:33–36
Khollam Y, Dhage S, Potdar H, Deshpande S, Bakare P, Kulkarni S, Date S (2002) Microwave hydrothermal preparation of submicron-sized spherical magnetite (Fe 3O4) powders. Mater Lett 56:571–577
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Vander Elst L, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108:2064–2110
Laurent S, Dutz S, Häfeli UO, Mahmoudi M (2011) Magnetic fluid hyperthermia: focus on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 166:8–23
Lee Y, Lee J, Bae CJ, Park JG, Noh HJ, Park JH, Hyeon T (2005) Large-scale synthesis of uniform and crystalline magnetite nanoparticles using reverse micelles as nanoreactors under reflux conditions. Adv Funct Mater 15:503–509
Lee C, Kim JY, Lee WI, Nelson KL, Yoon J, Sedlak DL (2008) Bactericidal effect of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ Sci Technol 42:4927–4933
Li Q, Mahendra S, Lyon DY, Brunet L, Liga MV, Li D, Alvarez PJ (2008) Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: potential applications and implications. Water Res 42:4591–4602
Li Y-G, Gao H-S, Li W-L, Xing J-M, Liu H-Z (2009) In situ magnetic separation and immobilization of dibenzothiophene-desulfurizing bacteria. Bioresour Technol 100:5092–5096
MacRae I (1985) Removal of pesticides in water by microbial cells adsorbed to magnetite. Water Res 19:825–830
MacRae I (1986) Removal of chlorinated hydrocarbons from water and wastewater by bacterial cells adsorbed to magnetite. Water Res 20:1149–1152
MacRae I, Evans SK (1983) Factors influencing the adsorption of bacteria to magnetite in water and wastewater. Water Res 17:271–277
Mahmoudi M, Sant S, Wang B, Laurent S, Sen T (2011) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:24–46
Martelli S et al (2000) Production of iron-oxide nanoparticles by laser-induced pyrolysis of gaseous precursors. Appl Surf Sci 154:353–359
Martins SCS, Martins CM, Fiúza LMCG, Santaella ST (2013) Immobilization of microbial cells: a promising tool for treatment of toxic pollutants in industrial wastewater. Afr J Biotechnol 12:4412–4418
McEldowney S, Fletcher M (1986a) Effect of growth conditions and surface characteristics of aquatic bacteria on their attachment to solid surfaces. Microbiology 132:513–523
McEldowney S, Fletcher M (1986b) Variability of the influence of physicochemical factors affecting bacterial adhesion to polystyrene substrata. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:460–465
Miller M, Prinz G, Cheng S-F, Bounnak S (2002) Detection of a micron-sized magnetic sphere using a ring-shaped anisotropic magnetoresistance-based sensor: a model for a magnetoresistance-based biosensor. Appl Phys Lett 81:2211–2213
Neuberger T, Schöpf B, Hofmann H, Hofmann M, Von Rechenberg B (2005) Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications: possibilities and limitations of a new drug delivery system. J Magn Magn Mater 293:483–496
Pal S, Alocilja EC (2009) Electrically active polyaniline coated magnetic (EAPM) nanoparticle as novel transducer in biosensor for detection of Bacillus anthracis spores in food samples. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1437–1444
Pascal C, Pascal J, Favier F, Elidrissi Moubtassim M, Payen C (1999) Electrochemical synthesis for the control of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticle size. Morphology, microstructure, and magnetic behavior. Chem Mater 11:141–147
Philipse AP, Maas D (2002) Magnetic colloids from magnetotactic bacteria: chain formation and colloidal stability. Langmuir 18:9977–9984
Prozorov T et al (2007) Protein-mediated synthesis of uniform superparamagnetic magnetite nanocrystals. Adv Funct Mater 17:951–957
Ranmadugala D, Ebrahiminezhad A, Manley-Harris M, Ghasemi Y, Berenjian A (2017a) The effect of iron oxide nanoparticles on Bacillus subtilis biofilm, growth and viability. Process Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2017.07.003 (In press)
Ranmadugala D, Ebrahiminezhad A, Manley-Harris M, Ghasemi Y, Berenjian A (2017b) Iron oxide nanoparticles in modern microbiology and biotechnology. Crit Rev Microbiol 43:493–507
Ravindranath SP, Mauer LJ, Deb-Roy C, Irudayaraj J (2009) Biofunctionalized magnetic nanoparticle integrated mid-infrared pathogen sensor for food matrixes. Anal Chem 81:2840–2846
Rijnaarts HH, Norde W, Bouwer EJ, Lyklema J, Zehnder AJ (1995a) Reversibility and mechanism of bacterial adhesion. Colloids Surf B 4:5–22
Rijnaarts HH, Norde W, Lyklema J, Zehnder AJ (1995b) The isoelectric point of bacteria as an indicator for the presence of cell surface polymers that inhibit adhesion. Colloids Surf B 4:191–197
Rishton S et al (1997) Magnetic tunnel junctions fabricated at tenth-micron dimensions by electron beam lithography. Microelectron Eng 35:249–252
Safarik I, Safarikova M (2007) Magnetically modified microbial cells: a new type of magnetic adsorbents. China Particuol 5:19–25
Sasaki T, Terauchi S, Koshizaki N, Umehara H (1998) The preparation of iron complex oxide nanoparticles by pulsed-laser ablation. Appl Surf Sci 127:398–402
Shan G, Xing J, Zhang H, Liu H (2005) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by microbial cells coated with magnetite nanoparticles. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4497–4502
Singh N, Jenkins GJ, Asadi R, Doak SH (2010) Potential toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION). Nano Rev Exp 1:5358. https://doi.org/10.3402/nano.v1i0.5358
Singh S, Barick K, Bahadur D (2011) Surface engineered magnetic nanoparticles for removal of toxic metal ions and bacterial pathogens. J Hazard Mater 192:1539–1547
Stenström T-A, Kjelleberg S (1985) Fimbriae mediated nonspecific adhesion of Salmonella typhimurium to mineral particles. Arch Microbiol 143:6–10
Sun S, Zeng H (2002) Size-controlled synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 124:8204–8205
Tartaj P, Gonzalez-Carreno T, Serna CJ (2001) Single-step nanoengineering of silica coated maghemite hollow spheres with tunable magnetic properties. Adv Mater 13:1620–1624
Tiberto P et al (2013) Magnetic properties of jet-printer inks containing dispersed magnetite nanoparticles. Eur Phys J B 86:1–6
Touhami A, Jericho MH, Boyd JM, Beveridge TJ (2006) Nanoscale characterization and determination of adhesion forces of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili by using atomic force microscopy. J Bacteriol 188:370–377
Tsuneda S, Aikawa H, Hayashi H, Yuasa A, Hirata A (2003) Extracellular polymeric substances responsible for bacterial adhesion onto solid surface. FEMS Microbiol Lett 223:287–292
Vaghari H, Eskandari M, Sobhani V, Berenjian A, Song Y, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H (2015) Process intensification for production and recovery of biological products. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 11:37–43
Vaghari H, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H, Mohammadlou M, Berenjian A, Anarjan N, Jafari N, Nasiri S (2016) Application of magnetic nanoparticles in smart enzyme immobilization. Biotechnol Lett 38:223–233
Van Iersel M, Brouwer-Post E, Rombouts F, Abee T (2000) Influence of yeast immobilization on fermentation and aldehyde reduction during the production of alcohol-free beer. Enzyme Microb Technol 26:602–607
Verma A, Stellacci F (2010) Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle–cell interactions. Small 6:12–21
Vijayakumar R, Koltypin Y, Felner I, Gedanken A (2000) Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of pure nanometer-sized Fe3O4 particles. Mater Sci Eng, A 286:101–105
Wang Y, Ravindranath S, Irudayaraj J (2011) Separation and detection of multiple pathogens in a food matrix by magnetic SERS nanoprobes. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:1271–1278
Weinstein JS et al (2010) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging and potential therapeutic applications in neurooncology and central nervous system inflammatory pathologies, a review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:15–35
Wiesner MR, Lowry GV, Alvarez P, Dionysiou D, Biswas P (2006) Assessing the risks of manufactured nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 40:4336–4345
Wu W, He Q, Jiang C (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res Lett 3:397–415
Zhang D, Tong Z, Li S, Zhang X, Ying A (2008) Fabrication and characterization of hollow Fe3O4 nanospheres in a microemulsion. Mater Lett 62:4053–4055
Zhao X, Hilliard LR, Mechery SJ, Wang Y, Bagwe RP, Jin S, Tan W (2004) A rapid bioassay for single bacterial cell quantitation using bioconjugated nanoparticles. PNAS 101:15027–15032
Zucca P, Sanjust E (2014) Inorganic materials as supports for covalent enzyme immobilization: methods and mechanisms. Molecules 19:14139–14194
Żur J, Wojcieszyńska D, Guzik U (2016) Metabolic Responses of Bacterial Cells to Immobilization. Molecules 21: Article Number: UNSP 958 https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070958
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranmadugala, D., Ebrahiminezhad, A., Manley-Harris, M. et al. Magnetic immobilization of bacteria using iron oxide nanoparticles. Biotechnol Lett 40, 237–248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2477-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2477-0