Abstract
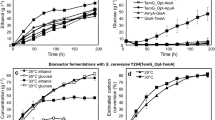
Amylolytic industrial polyploid strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ATCC 4126, ATCC 9763 and ATCC 24858) expressing a glucoamylase gene (GAM1) or an α-amylase gene (AMY) from Debaryomyces occidentalis were developed. The glucoamylase activity of S. cerevisiae ATCC 9763 expressing the GAM1 gene was 3.7-times higher than that of D. occidentalis. On the other hand, α-amylase activity in the corresponding strain expressing the D. occidentalis AMY gene increased 10-times relative to D. occidentalis. These two recombinant yeast strains expressing the GAM1 gene and AMY gene, respectively were cultured simultaneously to produce both glucoamylase and α-amylase for efficient one-step utilization of starch. Growth, substrate utilization and enzyme activity of these strains are described.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho KM, Yoo YJ, Kang HS (1999) δ-Integration of endo/exo-glucanase and β-glucosidase genes into the yeast chromosomes for direct conversion of cellulose to ethanol. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 25:23–30
Dohmen RJ, Strasser AWM, Dahlems UM, Hollenberg CP (1990) Cloning of the Schwanniomyces occidentalis glucoamylase gene (GAM1) and its expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 95:111–121
Eksteen JM, van Renseburg P, Cordero Otero RR, Pretorius IS (2003) Starch fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing the α-amylase and glucoamylase genes from Lipomyces kononenkoae and Saccharomycopsis fibuligera. Biotechnol Bioeng 84:639–646
Gietz D, St Jean A, Woods R, Schiestl RH (1992) Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res 20:1425
Hashida-Okado T, Ogawa A, Endo M, Yasumoto R, Takesako K, Kato I (1996) AUR1, a novel gene conferring aureobasidin resistance on Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a study of defective morphologies in Aur1p-depleted cells. Mol Gen Genet 251:236–244
Janse BJ, Pretorius IS (1995) One-step enzymatic hydrolysis of starch using a recombinant strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing α-amylase, glucoamylase and pullulanase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:876–883
Kang NY, Park JN, Chin JE, Lee HB, Im SY, Bai S (2003) Construction of an amylolytic industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing the Schwanniomyces occidentalis α-amylase gene. Biotechnol Lett 25:1847–1851
Kim K, Park CS, Mattoon JR (1988) High-efficiency, one-step utilization by transformed Saccharomyces cells which secrete both yeast glucoamylase and mouse α-amylase. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:966–971
Kim HO, Park JN, Sohn HJ, Shin DJ, Choi C, Im SY, Lee HB, Chun SB, Bai S (2000) Cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of a β-amylase gene from the oomycete Saprolegnia ferax. Biotechnol Lett 22:1493–1498
Lee FWF, Da Silva NA (1997) Improved efficiency and stability of multiple cloned gene insertions at the δ sequences of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:339–345
Lee HJ, Shin DJ, Cho NC, Kim HO, Shin SY, Im SY, Lee HB, Chun SB, Bai S (2000) Cloning, expression and nucleotide sequences of two xylanase genes from Paenibacillus sp. Biotechnol Lett 22:387–392
Ma Y, Lin LL, Chien HR, Hsu WH (2000) Effcient utilization of starch by a recombinant strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing glucoamylase and isoamylase. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 31:55–59
Marin D, Jimenez A, Lobato MF (2001) Construction of an efficient amylolytic industrial yeast strain containing DNA exclusively derived from yeast. FEMS microbiol Lett 201:249–253
Ness F, Lavallee F, Dubourdieu D, Aigle M, Dulau L (1993) Identification of yeast strains using the polymerase chain reaction. J Sci Food Agric 62:89–94
Nieto A, Prieto JA, Sanz P (1999) Stable high-copy number integration of Aspergillus orizae α-amylase cDNA in an industrial baker’s yeast strain. Biotechnol Prog 15:459–466
Park JN, Shin DJ, Kim HO, Kim DH, Lee HB, Chun SB, Bai S (1999) Expression of Schwanniomyces occidentalis α-amylase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. diastaticus. J Microbiol Biotechnol 9:668–671
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY
Steyn AJC, Pretorius IS (1991) Co-expression of a Saccharomyces diastaticus glucoamylase-encoding gene and a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens α-amylase-encoding gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 100:85–93
Wang X, Wang Z, Da Silva NA (1996) G418 selection and stability of cloned genes integrated at chromosomal δ sequences of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:45–51
Xie Q, Jimenez A (1996) Molecular cloning of a novel allele of SMR1 which determines sulfometuron methyl resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS microbiol Lett 137:165–168
Yamasaki Y, Suzuki Y, Ozawa J (1977) Three forms of α-glucosidase and a glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori. Agric Biol Chem 41:2149–2161
Zhu H, Qu F, Zhu LH (1993) Isolation of genomic DNAs from plant, fungi and bacteria using benzyl chloride. Nucleic Acids Res 21:5279–5280
Acknowledgement
This study was financially supported by Chonnam National University in the Program, 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghang, DM., Yu, L., Lim, MH. et al. Efficient one-step starch utilization by industrial strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the glucoamylase and α-amylase genes from Debaryomyces occidentalis . Biotechnol Lett 29, 1203–1208 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9371-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9371-0