Abstract
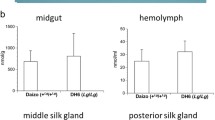
Carotenoids are the precursors of Vitamin A. They are cleaved by carotenoid oxygenase and then isomerized by retinoid isomerase. In this study, we identified a gene, Bombyx mori Carotenoid Oxygenases and Retinal Isomerase (BmCORI), which was the homolog of β-carotene 15,15′-monooxygenase and the retinal pigment epithelium protein of 65 kD. Further analysis indicated that the expression of BmCORI in silkworms was significantly higher in females than in males. We also found that the β-carotene content in BmCORI-expressed human embryonic kidney 293 cells was significantly lower than in the controls, while the lutein content showed a slight difference. These results suggested that BmCORI is related to carotenoid depletion, especially β-carotene depletion. Our research provides new insight into the study of BmCORI function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Pee S, Bloem MW (2007) The bioavailability of (pro) vitamin A carotenoids and maximizing the contribution of homestead food production to combating vitamin A deficiency. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 77:182–192
Dong XL, Liu TH, Wang W, Pan CX, Wu YF, Du GY, Chen P, Lu C, Pan MH (2015) BmREEPa is a novel gene that facilitates BmNPV entry into silkworm cells. PLoS ONE 10:14
Dong XL, Liu TH, Wang W, Pan CX, Du GY, Wu YF, Pan MH, Lu C (2016) Bm NHR96 participate BV entry of BmN-SWU1 cells via affecting the cellular cholesterol level. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482:1484–1490
Gao BX (2004) Natural pigment. Chemical Industrial Press, Beijing
Giguere V, Ong ES, Segui P, Evans RM (1987) Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature 330:624–629
Glover J, Redfearn ER (1954) The mechanism of the transformation of beta-carotene into vitamin A in vivo. Biochem J 58:xv–xvi
Gu G, Yang J, Mitchell KA, O’Tousa JE (2004) Drosophila ninaB and ninaD act outside of retina to produce rhodopsin chromophore. J Biol Chem 279:18608–18613
Hui B (2005) Chemistry and biochemistry of carotenoids. China Light Industry Publishing House, Beijing
Khan NC, West CE, de Pee S, Bosch D, Phuong HD, Hulshof PJ, Khoi HH, Verhoef H, Hautvast JG (2007) The contribution of plant foods to the vitamin A supply of lactating women in Vietnam: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 85:1112–1120
Krinsky NI (1998) Overview of lycopene, carotenoids, and disease prevention. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 218:95–97
Lietz G, Lange J, Rimbach G (2010) Molecular and dietary regulation of beta, beta-carotene 15,15′-monooxygenase 1 (BCMO1). Arch Biochem Biophys 502:8–16
Oberhauser V, Voolstra O, Bangert A, von Lintig J, Vogt K (2008) NinaB combines carotenoid oxygenase and retinoid isomerase activity in a single polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:19000–19005
O’Sullivan SM, Woods JA, O’Brien NM (2004) Use of Tween 40 and Tween 80 to deliver a mixture of phytochemicals to human colonic adenocarcinoma cell (CaCo-2) monolayers. Br J Nutr 91:757–764
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Von Lintig J, Vogt K (2004) Vitamin A formation in animals. J Nutr 134:5
von Lintig J, Dreher A, Kiefer C, Wernet MF, Vogt K (2001) Analysis of the blind Drosophila mutant ninaB identifies the gene encoding the key enzyme for vitamin A formation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1130–1135
Voolstra O, Kiefer C, Hoehne M, Welsch R, Vogt K, von Lintig J (2006) The Drosophila class B scavenger receptor NinaD-I is a cell surface receptor mediating carotenoid transport for visual chromophore synthesis. Biochemistry 45:13429–13437
Wang W, Huang MH, Dong XL, Chai CL, Pan CX, Tang H, Chen YH, Dai FY, Pan MH, Lu C (2014) Combined effect of Cameo2 and CBP on the cellular uptake of lutein in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS ONE 9:e86594
Yang J, O’Tousa JE (2007) Cellular sites of Drosophila NinaB and NinaD activity in vitamin A metabolism. Mol Cell Neurosci 35:49–56
Yasmeen R, Jeyakumar SM, Reichert B, Yang F, Ziouzenkova O (1821) The contribution of vitamin A to autocrine regulation of fat depots. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012:190–197
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (Grant No. 2452016204) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. K3320215183). We would like to thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for providing linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Xl., Pan, Cx. & Zhang, Mj. A Novel Gene Bombyx mori Carotenoid Oxygenases and Retinal Isomerase (BmCORI) Related to β-Carotene Depletion. Biochem Genet 58, 509–517 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-018-9853-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-018-9853-x