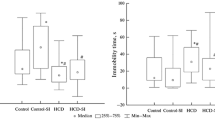
Stress response to physical exercise was studied in rats with alimentary obesity with and without caloric diet restriction. Daily excretion of corticosterone, progesterone, and testosterone, weights of internal organs, and serum levels of glucose, free fatty acids, triglycerides, corticosterone, and testosterone were estimated. Stress response to moderate exercise in rats with alimentary obesity was associated with predominance of anabolic influence of testosterone over the catabolic effects of corticosterone, which promoted the increase in the weight of reproductive organs. Exposure to physical loads against the background of restricted ration potentiated the response of the adrenocortical system and reduced the concentration and anabolic effects of testosterone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koubassov RV. Hormonal Changes in Response to Extreme Environment Factors. Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk. 2014;(9-10):102-109. Russian.
Filaretova LP. Stress in physiological studies. Ross. Fiziol. Zh. 2010;96(9):924-935. Russian.
Aswar U, Bodhankar SL, Mohan V, Thakurdesai PA. Effect of furostanol glycosides from Trigonella foenum-graecum on the reproductive system of male albino rats. Phytother. Res. 2010;24(10):1482-1488.
Bekaert M, Van Nieuwenhove Y, Calders P, Cuvelier CA, Batens AH, Kaufman JM, Ouwens DM, Ruige JB. Determinants of testosterone levels in human male obesity. Endocrine. 2015;50(1):202-211.
Cain DW, Cidlowski JA. Immune regulation by glucocorticoids. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017;17(4):233-247.
Gray M, Bingham B, Viau V. A comparison of two repeated restraint stress paradigms on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis habituation, gonadal status and central neuropeptide expression in adult male rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2010;22(2):92-101.
Polovynko ІS, Zajats LМ, Zukow W, Yanchij RI, Popovych ІL. Quantitative evaluation of integrated neuroendocrine and immune responses to chronic stress in rats male. J. Educat, Health Sport. 2016;6(8):154-166. doi: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.60023.
Retana-Márquez S, Vigueras-Villaseñor RM, Juárez-Rojas L, Aragón-Martínez A, Torres GR. Sexual behavior attenuates the effects of chronic stress in body weight, testes, sexual accessory glands, and plasma testosterone in male rats. Horm. Behav. 2014;66(5):766-778.
Sharma R, Biedenharn KR, Fedor JM, Agarwal A. Lifestyle factors and reproductive health: taking control of your fertility. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2013;11:66.
Toufexis D, Rivarola MA, Lara H, Viau V. Stress and the reproductive axis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2014;26(9):573-586.
Viau V, Soriano L, Dallman MF. Androgens alter corticotropin releasing hormone and arginine vasopressin mRNA within forebrain sites known to regulate activity in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2001;13(5):442-452.
Williamson M, Bingham B, Gray M, Innala L, Viau V. The medial preoptic nucleus integrates the central influences of testosterone on the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and its extended circuitries. J. Neurosci. 2010;30(35):11,762-11,770.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 164, No. 11, pp. 536-540, November, 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pal’chikova, N.A., Kuzminova, O.I. & Selyatitskaya, V.G. Stress Response to Physical Exercise in Rats with Alimentary Obesity. Bull Exp Biol Med 164, 587–590 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4037-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-018-4037-6