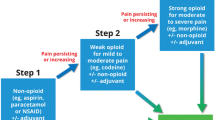
The analgesic effects of inert gas xenon were examined on rats. The formalin model of inflammatory pain, tail-flick test, and hot-plate test revealed the antinociceptive effects of subanesthetizing doses of inhalation anesthetic xenon. Inhalation of 50/50 xenon/oxygen mixture moderated the nociceptive responses during acute and tonic phases of inflammatory pain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burov NE, Potapov VN. Xenon in Medicine: Essays on the History of Medical Xenon. Moscow, 2012. Russian.
Igon’kina SI, Vetrile LA, Kukushkin ML. Intrathecal administration of antibodies to excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate decreases spontaneous pain episodes in rats with neuropathic pain. Patogenez. 2014;12(3):48-49. Russian.
Kukushkin ML, Igonkina SI. Effect of L-lysine escinate on pain sensitivity in rats. Ros. Zh. Boli. 2015;(2):9-11. Russian.
Kukushkin ML, Igonkina SI. Significance of GABA in pain syndrome pathogenes. Patol. Fiziol. Eksper. Ter. 2014;(1):68-78. Russian.
Kukushkin ML, Khitrov NK. General Pathology of Pain. Moscow, 2004. Russian.
Stryapko NV, Sazontova TG, Potievskaya VI, Khairullina AA, Vdovina IB, Kulikov AN, Arkhipenko YuV, Molchanov IV. Adaptation effect of repeated Xenon application. 2014;10(2):50-56.
Dickinson R, Peterson BK, Banks P, Simillis C, Martin JC, Valenzuela CA, Maze M, Franks NP. Competitive inhibition at the glycine site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor by the anesthetics xenon and isoflurane: evidence from molecular modeling and electrophysiology. Anesthesiology. 2007;107(5):756-767.
Esencan E, Yuksel S, Tosun YB, Robinot A, Solaroglu I, Zhang JH. XENON in medical area: emphasis on neuroprotection in hypoxia and anesthesia. Med. Gas Res. 2013;3(1):4. doi: 10.1186/2045-9912-3-4.
Franks NP, Dickinson R, de Sousa SL, Hall AC, Lieb WR. How does xenon produce anaesthesia. Nature. 1998;396:324.
Froeba G, Georgieff M, Linder EM, Föhr KJ, Weigt HU, Holsträter TF, Kölle MA, Adolph O. Intranasal application of xenon:describing the pharmacokinetics in experimental animals and the increased pain tolerance within a placebo-controlledexperimental human study. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010. doi:10.1093/bja/aep395.
Georgiev SK, Furue H, Baba H, Kohno T. Xenon inhibits excitatory but not inhibitory transmission in rat spinal cord dorsal horn neurons. Mol. Pain. 2010;6:25. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 162, No. 10, pp. 445-447, October, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kukushkin, M.L., Igon’kina, S.I., Potapov, S.V. et al. Analgesic Effect of Xenon in Rat Model of Inflammatory Pain. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 451–453 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3637-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3637-x