Abstract
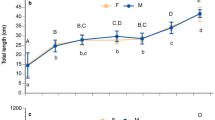
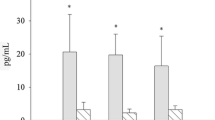
Profiles were generated of the sex hormones estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone in the marine snail Lobatus gigas every 2 months for 1 year. A non-invasive technique involving feces collection was used. Hormones were extracted from the feces with 80% methanol. After filtering, hormone concentrations were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography and a UV detector. All three sex hormones were present in L. gigas feces, and their concentrations increased contemporaneously with the conch reproductive period. Males and females showed the highest concentration of testosterone in May (1.8 ± 0.3 and 2.1 ± 0.8 ng/ml, respectively). Both sexes presented a maximum estrogen concentration in May (1.2 ± 0.7 and 1.0 ± 0.3 ng/ml). Progesterone in females remained constant from March to July. Pearson correlation between estrogen and spawning activity were r = 0.66 (p = 0.03) and for testosterone (r = 0.5216) and progesterone (r = 0.437). This study constitutes the first use of this technique in this species. Results show that sex hormones may be controlling this species’ reproductive events, as occurs in other gastropods. The understanding of the L. gigas reproductive process, this is one of several steps that will allow in the future improve aquaculture systems and supporting conservation of wild populations.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GnRH:
-
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
References
Acosta CA (2006) Impending trade suspensions of Caribbean queen conch under CITES. Fisheries 31:601–606. https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8446(2006)31[601:ITSOCQ]2.0.CO;2
Aldana Aranda D, Sanchez M, Reynaga Álvarez P, Patiño Suarez V, George Zamora A, Baqueiro Cárdenas E (2005) Crecimiento y temporada reproductiva del caracol rosa Strombus gigas en el parque Xel-Há, México. In: Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute. pp 741–754
Aldana Aranda D, Oxenford HA, Bissada C, Enriquez Díaz M, Brulé T, Delgado GA, Martínez Morales I, Frenkiel L (2014) Reproductive patterns of queen conch, Strombus gigas (Mollusca, Gastropoda), across the wider Caribbean region. Bull Mar Sci 90:813–831. https://doi.org/10.5343/bms.2013.1072
Alon G, Shore LS, Steinberger Y (2007) Correlation between levels of sex hormones (progesterone, testosterone, and estrogen) and ecophysiological-behavior stages in two species of desert snails (Sphincterochila zonata and Sphincterochila prophetarum) in the Northern Negev Desert. Gen Comp Endocrinol 151:122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2006.12.014
Amaral RS (2010) Use of alternative matrices to monitor steroid hormones in aquatic mammals: a review. Aquat Mamm 36:162–171
Aranda DA, Frenkiel L (2012) Digestive gland structure as a feed index for juveniles of the queen conch, Strombus gigas, reared with formulated food. Aquac Nutr 18:581–588. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2012.00936.x
Berg CJ (1975) Behavior and ecology of conch (superfamily Strombacea) on a deep subtidal algal plain. Bull Mar Sci 25:307–317
Biancani B, Da DL, Lacave G, Romagnoli S, Gabai G (2009) Measuring fecal progestogens as a tool to monitor reproductive activity in captive female bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Theriogenology 72:1282–1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2009.07.025
Brownell WN (1977) Reproduction, laboratory culture, and growth of Strombus Gigas, S. Costatus and S. Pugilus in Los Roques, Venezuela. Bull Mar Sci 27:668–680
Brownell WN, Stevely J (1983) The biology fisheries and management of the queen conch Strombus gigas. Mar Fish 43:1–12
Busso M, Ruiz R (2011) Excretion of steroid hormones in rodents: an overview on species differences for new biomedical animal research models. In: Contemporary aspects of endocrinology. InTech 376–389
Castillo SM, Bashaw MJ, Patton ML, Rieches R, Bercovitch FB (2005) Fecal steroid analysis of female giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis) reproductive condition and the impact of endocrine status on daily time budgets. Gen Comp Endocrinol 141:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.01.011
Castro LFC, Melo C, Guillot R, Mendes I, Queirós S, Lima D, Reis-Henriques MA, Santos MM (2007) The estrogen receptor of the gastropod Nucella lapillus: modulation following exposure to an estrogenic effluent? Aquat Toxicol 84:465–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.07.008
Chien TN, Khanh NH, Truong NX (2006) Endangered fish species and seed release strategies in Vietnam. In: Proceedings of the regional technical consultation on stock enhancement for threatened species of international concern pp 139–144
Cook PA (2016) Recent trends in worldwide abalone production. J Shellfish Res 35:581–583. https://doi.org/10.2983/035.035.0302
Cosmo AD, Di Cristo C, Paolucci M (2002) A estradiol-17β receptor in the reproductive system of the female of Octopus vulgaris: characterization and immunolocalization. Mol Reprod Dev 61:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.10014
D’aniello A, Di Cosmo A, Di Cristo C, Assisi L, Botte V, Di Fiore MM (1996) Occurrence of sex steroid hormones and their binding proteins in Octopus vulgaris Lam. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 227:782–788. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1996.1585
D’Asaro CN (1965) Organogenesis, development, and metamorphosis in the queen conch, Strombus gigas, with notes on breeding habits. Bull Mar Sci 15:359–416
De Lisa E, Paolucci M, Di Cosmo A (2012) Conservative nature of oestradiol signalling pathways in the brain lobes of Octopus vulgaris involved in reproduction, learning and motor coordination. J Neuroendocrinol 24:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2011.02240.x
Di Cristo C, Di Cosmo A (2007) Neuropeptidergic control of Octopus oviducal gland. Peptides 28:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2006.09.016
Di Rienzo J, Casanoves F, Balzarini M, Gonzalez L, Tablada M, Robledo C (2011) InfoStat. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Córdoba
Duncan NJ, Sonesson AK, Chavanne H (2013) Principles of finfish broodstock management in aquaculture: control of reproduction and genetic improvement. In: Advances in aquaculture hatchery technology. Woodhead Publishing, pp 23–75
Eick GN, Thornton JW (2011) Evolution of steroid receptors from an estrogen-sensitive ancestral receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol 334:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2010.09.003
FAO (2010) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture (SOFIA) 1:1–88
Fernandes D, Loi B, Porte C (2011) Biosynthesis and metabolism of steroids in molluscs. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 127:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.12.009
Gauthier-Clerc S, Pellerin J, Amiard JC (2006) Estradiol-17β and testosterone concentrations in male and female Mya arenaria (Mollusca bivalvia) during the reproductive cycle. Gen Comp Endocrinol 145:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.08.004
Gooding MP, LeBlanc GA (2001) Biotransformation and disposition of testosterone in the eastern mud snail Ilyanassa obsoleta. Gen Comp Endocrinol 122:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1006/gcen.2001.7630
Grilo TF, Rosa R (2017) Intersexuality in aquatic invertebrates: prevalence and causes. Sci Total Environ 592:714–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.099
Hogg CJ, Rogers TL, Shorter A, Barton K, Miller PJO, Nowacek D (2009) Determination of steroid hormones in whale blow: it is possible. Mar Mammal Sci 25:605–618. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-7692.2008.00277.x
Kim TH, Kim MA, Kim KS, Kim JW, Lim HK, Lee JS, Sohn YC (2017) Characterization and spatiotemporal expression of gonadotropin-releasing hormone in the Pacific abalone, Haliotis discus hannai. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 209:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.04.001
Kuramae A (2016) Population status and reproductive biology of the queen conch (Lobatus gigas) in the coastal waters of Anguilla. Univ Appl Sci Agora
Lafont R (1991) Reverse endocrinology, or “hormones” seeking functions. Insect Biochem 21:697–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-1790(91)90112-R
Lafont R, Mathieu M (2007) Steroids in aquatic invertebrates. Ecotoxicology 16:109–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-006-0113-1
Lehoux J-G, Sandor T (1970) The occurrence of steroids and steroid metabolizing enzyme systems in invertebrates. A review. Steroids 16:141–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-128X(70)80102-7
Li Q, Osada M, Suzuki T, Mori K (1998) Changes in vitellin during oogenesis and effect of estradiol-17β on vitellogenesis in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Invertebr Reprod Dev 33:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/07924259.1998.9652345
Lupica SJ, Turner JW (2009) Validation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for measurement of faecal cortisol in fish. Aquac Res 40:437–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2008.02112.x
Matzumoto T, Osada M, Osawa Y, Mori K (1997) Gonadal estrogen profile and immunohistochemical localization of steroidogenic enzymes in the oyster and scallop during sexual maturation. Comp Biochem Physiol 118:811–817
Mylonas CC, Duncan NJ, Asturiano JF (2017) Hormonal manipulations for the enhancement of sperm production in cultured fish and evaluation of sperm quality. Aquaculture 472:21–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.04.021
Nuurai P, Cummins SF, Botwright NA, Sobhon P (2016) Characterization of an abalone gonadotropin-releasing hormone and its effect on ovarian cell proliferation. Aquaculture 450:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.07.008
Ogino Y, Sato T, Iguchi T (2016) Gonadal steroids. In: Takei Y, Ando H, Tsutsui K (eds) Handbook of hormones. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 504–506
Palme RC, Touma N, Arias MF, Dominchin & Lepschy M (2013) Steroid extraction: get the best out of faecal samples. Wien. Tierärztl. Monatsschrift Spec Issue 100:238–246
Palme R (2005) Measuring fecal steroids: guidelines for practical application. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1046:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1343.007
Pérez Pérez M, Aldana Aranda D (2003) Actividad reproductiva de Strombus gigas (Mesogasteropoda: Strombidae) en diferentes hábitats del Arrecife Alacranes, Yucatán. Rev Biol Trop 51:119–126
Pradhan A, Olsson PE (2015) Zebrafish sexual behavior: role of sex steroid hormones and prostaglandins. Behav Brain Funct 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12993-015-0068-6
Reed S (1996) Reproductive anatomy and biology of the genus Strombus in the Caribbean. In: Proceedings of Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute, v 14, pp. 413–426
Rolland RM, Hunt KE, Kraus SD, Wasser SK (2005) Assessing reproductive status of right whales (Eubalaena glacialis) using fecal hormone metabolites. Gen Comp Endocrinol 142:308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.02.002
Santana Flores PA, Aldana Aranda D (2013) Temporalidad y Esfuerzo Reproductivo del Caracol Strombus gigas. In: Proceedings of Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute, v 66, pp. 458–460
Schwartz NB (2000) Neuroendocrine regulation of reproductive cyclicity. In: Neuroendocrinology in physiology and medicine. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp. 135–145
Serviere-Zaragosa E, Mazariegos-Villareal A, Aranda Aldana D (2009) Preliminary observation of natural feed of queen conch Strombus gigas. In: Proceedings of Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute, v 61, pp. 514–517
Shawl MD, Davis M (2004) Captive breeding behavior of four Strombidae conch. J Shellfish Res 23:157–164
Shawl A, Acosta-Salmon H, Davis M, Cape T, Riche MA 2008. Effect of protein origin in artificial diets on growth and survival of juvenile queen conch, Strombus gigas. In: Abstracts aquaculture America. p. 355
Sheriff MJ, Dantzer B, Delehanty B, Palme R, Boonstra R (2011) Measuring stress in wildlife: techniques for quantifying glucocorticoids. Oecologia 166:869–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-011-1943-y
Siah A, Pellerin J, Benosman A, Gagné JP, Amiard JC (2002) Seasonal gonad progesterone pattern in the soft-shell clam Mya arenaria. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 132:499–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1095-6433(02)00095-8
Siddal S (1983) Biological and economic outlook for hatchery production of juvenile queen conch. In: Proceedings of Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute, v 35, p 46–52
Sokal (1995) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics. In: Biological Research
Sternberg RM, Hotchkiss AK, LeBlanc GA (2008) The contribution of steroidal androgens and estrogens to reproductive maturation of the eastern mud snail Ilyanassa obsoleta. Gen Comp Endocrinol 156:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.12.002
Stoner AW, Ray-Culp M (2000) Evidence for Allee effects in an over-harvested marine gastropod: density-dependent mating and egg production. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 202:297–302. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps202297
Stoner AW, Waite JM (1991) Trophic biology of Strombus gigas in nursery habitats: diets and food sources in seagrass meadows. J Molluscan Stud 57:451–460. https://doi.org/10.1093/mollus/57.4.451
Stoner AW, Sandt VJ, Boidron-Metairon I (1992) Seasonality in reproductive activity and larval abundance of queen conch Strombus gigas. Fish Bull 90:161–170
Taves MD, Schmidt KL, Ruhr IM, Kapusta K, Prior NH, Soma KK (2010) Steroid concentrations in plasma, whole blood and brain: effects of saline perfusion to remove blood contamination from brain. PLoS One 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0015727
Turner JW, Nemeth R, Rogers C (2003) Measurement of fecal glucocorticoids in parrotfishes to assess stress. Gen Comp Endocrinol 133:341–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-6480(03)00196-5
Vardanyan R, Hruby V (2016) Steroid hormones. In: Synthesis of best-seller drugs. Academic Press, Boston, pp 459–493
Wang C, Croll RP (2006) Effects of sex steroids on spawning in the sea scallop, Placopecten magellanicus. Aquaculture 256:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.01.017
Wang HP, Gao Z, Beres B, Ottobre J, Wallat G, Tiu L, Rapp D, O’Bryant P, Yao H (2008) Effects of estradiol-17β on survival, growth performance, sex reversal and gonadal structure of bluegill sunfish Lepomis macrochirus. Aquaculture 285:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.08.041
Wasser SK, Azkarate JC, Booth RK, Hayward L, Hunt K, Ayres K, Vynne C, Gobush K, Canales-Espinosa D, Rodríguez-Luna E (2010) Non-invasive measurement of thyroid hormone in feces of a diverse array of avian and mammalian species. Gen Comp Endocrinol 168:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.04.004
Yan H, Liu W, Ke Q, Yu R, Kong L (2011) Seasonal changes of oestradiol-17b and testosterone concentrations in the gonad of the razor clam Sinonovacula Constricta (Lamarck, 1818). J Molluscan Stud 77:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1093/mollus/eyq045
Funding
This work was supported by a National Council for Science and Technology project (Ciencia Básica-CONACyT No. 181329), and a scholarship granted to Fabiola Chong Sanchez (Conacyt, Mexico). English translation service by John Lindsay-Edwards was supported by FOMIX Doctorado FOMIX-YUC-2014-C17-247043. Authors acknowledge to the Xel-Ha park for providing the space that allowed the taking of samples to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest that could affect the impartiality of the research reported here.
Statement of informed consent/Human and animal rights and informed consent
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Internal Committee for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Cicual) and accordance with the Official Mexican Standard NOM-062-ZOO-1999 and NOM-013-SAG / PESC-2016.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chong Sánchez, F., Enriquez Díaz, M., Murillo Rodríguez, E. et al. First use of a non-invasive technique for determination of sex hormones in the queen conch Lobatus gigas, Mollusca Gastropoda. Aquacult Int 27, 437–448 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-018-0336-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-018-0336-1