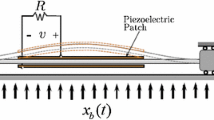
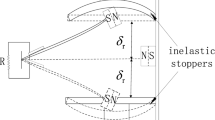
Abstract
A transition Fokker-Planck-Kolmogorov (FPK) equation describes the procedure of the probability density evolution whereby the dynamic response and reliability evaluation of mechanical systems could be carried out. The transition FPK equation of vibratory energy harvesting systems is a four-dimensional nonlinear partial differential equation. Therefore, it is often very challenging to obtain an exact probability density. This paper aims to investigate the stochastic response of vibration energy harvesters (VEHs) under the Gaussian white noise excitation. The numerical path integration method is applied to different types of nonlinear VEHs. The probability density function (PDF) from the transition FPK equation of energy harvesting systems is calculated using the path integration method. The path integration process is introduced by using the Gauss-Legendre integration scheme, and the short-time transition PDF is formulated with the short-time Gaussian approximation. The stationary probability densities of the transition FPK equation for vibratory energy harvesters are determined. The procedure is applied to three different types of nonlinear VEHs under Gaussian white excitations. The approximately numerical outcomes are qualitatively and quantitatively supported by the Monte Carlo simulation (MCS).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DAQAQ, M. F., MASANA, R., ERTURK, A., and QUINN, D. D. On the role of nonlinearities in vibratory energy harvesting: a critical review and discussion. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 66, 040801 (2014)
ELVIN, N. and ERTURK, A. Advances in Energy Harvesting Methods, Springer, New York (2013)
WANG, H. R., XIE, J. M., XIE, X., HU, Y. T., and WANG, J. Nonlinear characteristics of circular-cylinder piezoelectric power harvester near resonance based on flow-induced flexural vibration mode. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 35, 229–236 (2014) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-014-1786-6
HAJHOSSEINI, M. and RAFEEYAN, M. Modeling and analysis of piezoelectric beam with periodically variable cross-sections for vibration energy harvesting. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 37, 1053–1066 (2016) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-016-2117-8
LI, X., ZHANG, Y. W., DING, H., and CHEN, L. Q. Integration of a nonlinear energy sink and a piezoelectric energy harvester. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 38, 1019–1030 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-017-2220-6
COTTONE, F., VOCCA, H., and GAMMAITONI, L. Nonlinear energy harvesting. Physical Review Letters, 102, 080601 (2009)
DAQAQ, M. F. Transduction of a bistable inductive generator driven by white and exponentially correlated Gaussian noise. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 330, 2554–2564 (2011)
GREEN, P. L., WORDEN, K., ATALLAH, K., and SIMS, N. D. The benefits of Duffing-type nonlinearities and electrical optimisation of a mono-stable energy harvester under white Gaussian excitations. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 331, 4504–4517 (2012)
DAQAQ, M. F. On intentional introduction of stiffness nonlinearities for energy harvesting under white Gaussian excitations. Nonlinear Dynamics, 69, 1063–1079 (2012)
MASANA, R. and DAQAQ, M. F. Response of Duffing-type harvesters to band-limited noise. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 332, 6755–6767 (2013)
HE, Q. F. and DAQAQ, M. F. Influence of potential function asymmetries on the performance of nonlinear energy harvesters under white noise. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 33, 3479–3489 (2014)
HE, Q. F. and DAQAQ, M. F. New insights into utilizing bistability for energy harvesting under white noise. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 137, 021009 (2015)
XU, M., JIN, X. L., WANG, Y., and HUANG, Z. L. Stochastic averaging for nonlinear vibration energy harvesting system. Nonlinear Dynamics, 78, 1451–1459 (2014)
KUMAR, P., NARAYANAN, S., ADHIKARI, S., and FRISWELL, M. I. Fokker-Planck equation analysis of randomly excited nonlinear energy harvester. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 333, 2040–2053 (2014)
JIN, X. L., WANG, Y., XU, M., and HUANG, Z. L. Semi-analytical solution of random response for nonlinear vibration energy harvesters. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 340, 267–282 (2015)
JIANG, W. A. and CHEN, L. Q. Stochastic averaging of energy harvesting systems. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 85, 174–187 (2016)
JIANG, W. A. and CHEN, L. Q. Stochastic averaging based on generalized harmonic functions for energy harvesting systems. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 377, 264–283 (2016)
LIU, D., XU, Y., and LI, J. L. Randomly-disordered-periodic-induced chaos in a piezoelectric vibration energy harvester system with fractional-order physical properties. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 399, 182–196 (2017)
LIU, D., XU, Y., and LI, J. L. Probabilistic response analysis of nonlinear vibration energy harvesting system driven by Gaussian colored noise. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 104, 806–812 (2017)
XIAO, S. M. and JIN, Y. F. Response analysis of the piezoelectric energy harvester under correlated white noise. Nonlinear Dynamics, 90, 2069–2082 (2017)
YANG, Y. G. and XU, W. Stochastic analysis of monostable vibration energy harvesters with fractional derivative damping under Gaussian white noise excitation. Nonlinear Dynamics, 1–10 (2018)
SUN, Y., HONG, L., JIANG, J., and LI, Z. Estimation of critical conditions for noise-induced bifurcation in nonautonomous nonlinear systems by stochastic sensitivity function. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 26, 1650184 (2016)
CHEN, L. C., LIU, J., and SUN, J. Q. Stationary response probability distribution of SDOF nonlinear stochastic systems. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 84, 051006 (2017)
SUN, Y., HONG, L., YANG, Y., and SUN, J. Q. Probabilistic response of nonsmooth nonlinear systems under Gaussian white noise excitations. Physica A, 508, 111–117 (2018)
WEHNER, M. F. and WOLFER, W. G. Numerical evaluation of path-integral solution to Fokker-Plank equations. Physical Review A, 27, 2663–2670 (1983)
CRANDALL, S. H., CHANDIRAMANI, K. L., and COOK, R. G. Some first-passage problems in random vibration. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 33, 532–538 (1966)
HSU, C. S. and CHIU, H. M. A cell mapping method for non-linear deterministic and stochastic systems I: the method of analysis. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 53, 695–701 (1986)
HSU, C. S. and CHIU, H. M. A cell mapping method for nonlinear deterministic and stochastic systems II: examples of application. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 53, 702–710 (1986)
SUN, J. Q. and HSU, C. S. The generalized cell mapping method in nonlinear random vibration based upon short-time Gaussian approximation. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 57, 1018–1025 (1990)
NAESS, A. and JOHNSON, J. M. Response statistics of nonlinear, compliant offshore structures by the path integral solution method. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 8, 91–106 (1993)
IOURTCHENKOA, D. V., MO, E., and NAESS, A. Response probability density functions of strongly non-linear systems by the path integration method. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 41, 693–705 (2006)
FENG, G. M., WANG, B., and LU, Y. F. Path integral, functional method, and stochastic dynamical systems. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 7, 149–157 (1992)
YU, J. S., CAI, G. Q., and LIN, Y. K. A new path integration procedure based on Gauss-Legendre scheme. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 32, 759–768 (1997)
YU, J. S. and LIN, Y. K. Numerical path integration of a non-homogeneous Markov process. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 39, 1493–1500 (2004)
XIE, W. X., XU, W., and CAI, L. Study of the Duffing-Rayleigh oscillator subject to harmonic and stochastic excitations by path integration. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 172, 1212–1224 (2006)
WANG, Y. A path integration algorithm for stochastic structural dynamic systems. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 228, 423–431 (2014)
ZHU, H. T. and DUAN, L. L. Probabilistic solution of non-linear random ship roll motion by path integration. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 83, 1–8 (2016)
CAO, J. Y., ZHOU, S. X., WANG, W., and LIN, J. Influence of potential well depth on nonlinear tristable energy harvesting. Applied Physics Letters, 106, 173903 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Citation: JIANG, W. A., SUN, P., ZHAO, G. L., and CHEN, L. Q. Path integral solution of vibratory energy harvesting systems. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 40(4), 579–590 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2467-8
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11702119 and 51779111) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (Nos.BK20170565 and BK20170581)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Sun, P., Zhao, G. et al. Path integral solution of vibratory energy harvesting systems. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 40, 579–590 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2467-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2467-8