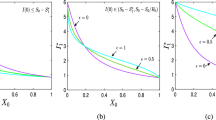
Abstract
A class of epidemic virus transmission population dynamic system is considered. Firstly, using the functional homotopic analysis method, an initial approximate function is selected. Then, the arbitrary order approximate analytic solutions are obtained successively. Finally, the accuracy of the obtained approximate analytic solutions is described. The influence of the various physical parameters for the epidemic virus transmission population dynamic system is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
May, R. M. Will a large complex system be stable. nature, 238, 413–414 (1972)
May, R. M. Biological populations with nonoverlapping generations: stable point, stable cycles, and chaos. Science, 186, 645–647 (1974)
De Ruiter, P. C., Neutel, A. M., and Moorre, J. C. Energetics, patterns of interaction strengths and stability in real ecosystems. Science, 269, 1257–1260 (1995)
Griffiths, J., Lowrie, D., and Williams, J. An age-structured model for the AIDS epidemic. European Journal of Operational Research, 124(1), 1–24 (2000)
Hyman, J. M., Li, J., and Stanley, E. A. The differential infectivity and staged progression models for the transmission of HIV. Mathematical Biosciences, 155(1), 77–109 (1999)
Hethcote, H. W. and Vanark, J. W. Modelling HIV Transmission and AIDS in the United States, Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1992)
Liu, M. X., Ruan, Y. H., Han, L. T., and Zhou, Y. C. The summary of dynamic models for HIV transmission. Journal of Biomathematics, 19(5), 551–560 (2004)
Barbu, L. and Morosanu, G. Singularly Perturbed Boundary-Value Problems, Birkhauserm Verlag AG, Basel (2007)
De Jager, E. M. and Jiang, F. R. The Theory of Singular Perturbation, North-Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam (1996)
Suzuki, R. Asymptotic behavior of solutions a semilinear heat equation with localized reaction. Advances in Differential Equations, 159(3/4), 283–314 (2010)
Ramos, M. On singular perturbation of superlinear elliptic systems. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 352(1), 246–258 (2009)
D’Aprile, T. and Pistoia, A. On the existence of some new positive interior spike solutions to a semilinear Nuumann problem. Journal of Differential Equations, 248(3), 556–573 (2010)
Kellogg, R. B. and Kopteva, N. A singularly perturbed semilinear reaction-diffusion problem in polygonal domain. Journal of Differential Equations, 248(1), 184–208 (2010)
Mo, J. Q. Singular perturbation for a class of nonlinear reaction diffusion systems. Science in China, Ser A, 32(11), 1306–1315 (1989)
Mo, J. Q. and Lin, W. T. Asymptotic solution of activator inhibitor systems for nonlinear reaction diffusion equations. Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 20(1), 119–128 (2008)
Mo, J. Q. and Wang, H. Nonlinear singularly perturbed approximate solution for generalized Lotke-Volterra ecological model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(10), 4366–4370 (2007)
Mo, J. Q. Yao, J. S., and Wang, H. The nonlinear species group singularly perturbed Robin problems for reaction diffusion system. Journal of Biomatheatics, 22(2), 193–199 (2007)
Mo, J. Q., Chen, X. F., and Xie, F. Asymptotic solution for a nonlinear singularly perturbed population problem. Journal of Biomatheatics, 22(4), 577–582 (2007)
Mo, J. Q. and Zhou, K. R. Singular perturbation for nonlinear species group reaction diffusion systems. Journal of Biomatheatics, 21(4), 481–488 (2006)
Mo, J. Q., Zhang, W. J., and He, M. Homotopic mapping solving method for dynamic study of HIV virus transmission (in Chinese). Mathematical Applicata, 20(3), 441–445 (2007)
Mo, J. Q. and Yao, J. S. Asymptotic solution to model for a class of virus transmission. Annals of Differential Equations, 26(4), 436–441 (2010)
Quyang, C., Yao, J. S., Shi, L. F., and Mo, J. Q. Solitary wave solution for a class of dusty plasma (in Chinese). Acta Physica Sinica, 63(11), 110203 (2014)
Ouyang, C., Cheng, L. H., and Mo, J. Q. Solving a class of burning disturbed problem with shock layer. Chinese Physics B, 21(5), 050203 (2012)
Ouyang, C., Lin, W. T., Cheng, R. J., and Mo, J. Q. A class of asymptotic solution of El Nino sea-air time delay oscillator (in Chinese). Acta Physica Sinica, 62, 060201 (2013)
Liao, S. J. Beyond Perturbation—Introduction to the Homotopy Analysis Method, Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton (2003)
Liao, S. J. Beyond Perturbation: Introduction to the Homotopy Analysis Method, CRC Press, New York (2004)
Liao, S. J. Homotopy Analysis Method in Nonlinear Differential Equations, Springer & Higher Education Press, Heidelberg (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41275062) and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (No. LY13A010005)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, C., Zhu, M. & Mo, J. A class of epidemic virus transmission population dynamic system. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 38, 1181–1190 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-017-2228-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-017-2228-9