Abstract
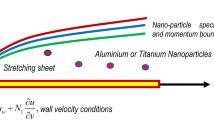
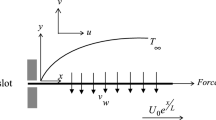
The present paper deals with the multiple solutions and their stability analysis of non-Newtonian micropolar nanofluid slip flow past a shrinking sheet in the presence of a passively controlled nanoparticle boundary condition. The Lie group transformation is used to find the similarity transformations which transform the governing transport equations to a system of coupled ordinary differential equations with boundary conditions. These coupled set of ordinary differential equation is then solved using the Runge- Kutta-Fehlberg fourth-fifth order (RKF45) method and the ode15s solver in MATLAB. For stability analysis, the eigenvalue problem is solved to check the physically realizable solution. The upper branch is found to be stable, whereas the lower branch is unstable. The critical values (turning points) for suction (0 < s c < s) and the shrinking parameter (χ c < χ < 0) are also shown graphically for both no-slip and multiple-slip conditions. Multiple regression analysis for the stable solution is carried out to investigate the impact of various pertinent parameters on heat transfer rates. The Nusselt number is found to be a decreasing function of the thermophoresis and Brownian motion parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eastman, J. A., Choi, S. U. S., Li, S., Yu, W., and Thompson, L. J. Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Applied Physics Letters, 78, 718–720 (2001)
Keblinski, P., Prasher, R., and Eapen, J. Thermal conductance of nanofluids: is the controversy over? Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 10, 1089–1097 (2008)
Chen, H., Ding, Y., and Tan, C. Rheological behaviour of nanofluids. New Journal of Physics, 9, 367 (1–24) (2007)
Lee, J. H., Lee, S. H., Choi, C., Jang, S., and Choi, S. A review of thermal conductivity data, mechanisms and models for nanofluids. International Journal of Micro-Nano Scale Transport, 1, 269–322 (2010)
Wong, K. V. and de Leon, O. Applications of nanofluids: current and future. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2, 519659 (2010)
Tombcz, E., Bica, D., Hajdu, A., Ills, E., Majzik, A., and Vks, L. Surfactant double layer stabilized magnetic nanofluids for biomedical application. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 20, 204103 (2008)
Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. Journal of Heat Transfer, 128, 240–250 (2006)
Crane, L. J. Flow past a stretching plate. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Physik, 21, 645–647 (1970)
Miklavcic, M. and Wang, C. Y. Viscous flow due to a shrinking sheet. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 64, 283–290 (2006)
Wang, C. Y. Stagnation flow towards a shrinking sheet. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 43, 377–382 (2008)
Fang, T. and Zhang, J. Closed-form exact solutions of MHD viscous flow over a shrinking sheet. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 14, 2853–2857 (2009)
Khan, W. A. and Pop, I. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 53, 2477–2483 (2010)
Rana, P. and Bhargava, R. Flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet: a numerical study. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 17, 212–226 (2012)
Kuznetsov, A. V. and Nield, D. A. Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 49, 243–247 (2010)
Sheikholeslami, M., Gorji-Bandpy, M., Ganji, D. D., Rana, P., and Soleimani, S. Magnetohydrodynamic free convection of Al2O3-water nanofluid considering thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects. Computers and Fluids, 94, 147–160 (2014)
Rana, P., Bhargava, R., and Bég, O. A. Finite element simulation of unsteady magnetohydrodynamic transport phenomena on a stretching sheet in a rotating nanofluid. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part N: Journal of Nanoengineering and Nanosystems, 227, 77–99 (2013)
Dhanai, R., Rana, P., and Kumar, L. Multiple solutions of MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer behavior of nanofluids induced by a power-law stretching/shrinking permeable sheet with viscous dissipation. Powder Technology, 273, 62–70 (2015)
Bachok, N., Ishak, A., and Pop, I. Unsteady boundary-layer flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 55, 2102–2109 (2012)
Malvandi, A., Hedayati, F., and Ganji, D. D. Slip effects on unsteady stagnation point flow of a nanofluid over a stretching sheet. Powder Technology, 253, 377–384 (2014)
Freidoonimehr, N., Rashidi, M. M., and Mahmud, S. Unsteady MHD free convective flow past a permeable stretching vertical surface in a nanofluid. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 87, 136–145 (2015)
Ellahi, R. The effects of MHD and temperature dependent viscosity on the flow of non-Newtonian nanofluid in a pipe: analytical solutions. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37, 1451–1467 (2013)
Uddin, M. J., Yusoff, N. M., Bg, O. A., and Ismail, A. I. M. Lie group analysis and numerical solutions for non-Newtonian nanofluid flow in a porous medium with internal heat generation. Physica Scripta, 87, 025401 (2013)
Dhanai, R., Rana, P., and Kumar, L. Critical values in slip flow and heat transfer analysis of non- Newtonian nanofluid utilizing heat source/sink and variable magnetic field: multiple solutions. Journal of Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 58, 155–164 (2016)
Cao, L., Si, X., and Zheng, L. Convection of Maxwell fluid over stretching porous surface with heat source/sink in presence of nanoparticles: Lie group analysis. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 37(4), 433–442 (2016) DOI 10.1007/s10483-016-2052-9
Merkin, J. H. On dual solutions occurring in mixed convection in a porous medium. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 20, 171–179 (1986)
Weidman, P. D., Kubitschek, D. G., and Davis, A. M. J. The effect of transpiration on selfsimilar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. International Journal of Engineering Science, 44, 730–737 (2006)
Harris, S. D., Ingham, D. B., and Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary-layer flow near the stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium: Brinkman model with slip. Transport in Porous Media, 77, 267–285 (2009)
Bachok, N., Ishak, A., and Pop, I. Stagnation-point flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid. Nanoscale Research Letters, 6, 1–10 (2011)
Bachok, N., Ishak, A., and Pop, I. Boundary layer stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 55, 8122–8128 (2012)
Zaimi, K., Ishak, A., and Pop, I. Flow past a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid using two-phase model. PLoS One, 9, e111743 (2014)
Zaimi, K., Ishak, A., and Pop, I. Boundary layer flow and heat transfer over a nonlinearly permeable stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid. Scientific Reports, 4, 4404 (1–8) (2014)
Zaimi, K., Ishak, A., and Pop, I. Stagnation-point flow toward a stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid containing both nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Journal of Heat Transfer, 136, 041705 (2014)
Eringen A. C. Simple microfluids. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2, 205–217 (1964)
Eringen, A. C. Theory of thermomicrofluids. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 38, 480–496 (1972)
Gorla, R. S. R. and Kumari, M. Mixed convection flow of a non-Newtonian nanofluid over a non-linearly stretching sheet. Journal of Nanofluids, 1, 186–195 (2012)
Hussain, S. T., Nadeem, S., and Haq, R. U. Model-based analysis of micropolar nanofluid flow over a stretching surface. The European Physical Journal Plus, 129, 1–10 (2014)
Bourantas, G. C. and Loukopoulos, V. C. Modeling the natural convective flow of micropolar nanofluids. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 68, 35–41 (2014)
Nadeem, S., Rehman, A., Vajravelu, K., Lee, J., and Lee, C. Axisymmetric stagnation flow of a micropolar nanofluid in a moving cylinder. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2012, 378259 (2012)
Rehman, A. and Nadeem, S. Mixed convection heat transfer in micropolar nanofluid over a vertical slender cylinder. Chinese Physics Letters, 29, 124701 (2012)
Yacob, N. A. and Ishak, A. Micropolar fluid flow over a shrinking sheet. Meccanica, 47, 293–299 (2012)
Kuznetsov, A. V. and Nield, D. A. Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate: a revised model. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 77, 126–129 (2014)
Khan, W. A., Uddin, M. J., and Ismail, A. I. M. Effect of multiple slips and dissipation on boundary layer flow of nanofluid over a porous flat plate in porous media. Journal of Porous Media, 18, 1–14 (2015)
Uddin, M. J., Bg, O. A., and Ismail, A. I. M. Radiative convective nanofluid flow past a stretching/ shrinking sheet with slip effects. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 29, 513–523 (2015)
Uddin, M. J., Kabir, M. N., and Alginahi, Y. M., Lie group analysis and numerical solution of magnetohydrodynamic free convective slip flow of micropolar fluid over a moving plate with heat transfer. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 70, 846–856 (2015)
Karniadakis, G. E. M., Beskok, A., and Gad-el-Hak, M. Micro flows: fundamentals and simulation. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 55, B76 (2002)
Ahmadi, G. Self-similar solution of incompressible micropolar boundary layer flow over a semiinfinite plate. International Journal of Engineering Science, 14, 639–646 (1976)
Bluman, G. and Anco, S. Symmetry and Integration Methods for Differential Equations, Vol. 154, Springer Science & Business Media, New York (2008)
Dhanai, R., Rana, P., and Kumar, L. Multiple solutions in MHD flow and heat transfer of Sisko fluid containing nanoparticles migration with a convective boundary condition: critical points. The European Physical Journal Plus, 131, 142 (1–14) (2016)
Dhanai, R., Rana, P., and Kumar, L. MHD mixed convection nanofluid flow and heat transfer over an inclined cylinder due to velocity and thermal slip effects: Buongiorno’s model. Powder Technology, 288, 140–150 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by Universiti Sains Malaysia (No.1001/PMATHS/811252)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, P., Uddin, M.J., Gupta, Y. et al. Two-component modeling for non-Newtonian nanofluid slip flow and heat transfer over sheet: Lie group approach. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 37, 1325–1340 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-016-2140-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-016-2140-9