Abstract
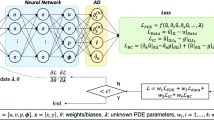
A heuristic technique is developed for a nonlinear magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) Jeffery-Hamel problem with the help of the feed-forward artificial neural network (ANN) optimized with the genetic algorithm (GA) and the sequential quadratic programming (SQP) method. The two-dimensional (2D) MHD Jeffery-Hamel problem is transformed into a higher order boundary value problem (BVP) of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). The mathematical model of the transformed BVP is formulated with the ANN in an unsupervised manner. The training of the weights of the ANN is carried out with the evolutionary calculation based on the GA hybridized with the SQP method for the rapid local convergence. The proposed scheme is evaluated on the variants of the Jeffery-Hamel flow by varying the Reynold number, the Hartmann number, and the angles of the walls. A large number of simulations are performed with an extensive analysis to validate the accuracy, convergence, and effectiveness of the scheme. The comparison of the standard numerical solution and the analytic solution establishes the correctness of the proposed designed methodologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeffery, G. B. The two-dimensional steady motion of a viscous fluid. Philosophical Magazine, 6, 455–465 (1915)
Hamel, G. Spiralfrmige bewgungen zher flssigkeiten. Philosophical Magazine, 25, 34–60 (1916)
Reza, M. S. Channel Entrance Flow, Ph.D. dissertation, The University of Western Ontario, Ontario (1997)
Hamadiche, M., Scott, J., and Jeandel, D. Temporal stability of Jeffery-Hamel flow. Philosophical Magazine, 268, 71–88 (1994)
Makinde, O. D. and Mhone, P. Y. Hermite-Padé approximation approach to MHD Jeffery-Hamel flows. Philosophical Magazine, 181, 966–972 (2006)
Schlichting, H. Boundary-Layer Theory, McGraw-Hill Press, New York (2000)
McAlpine, A. and Drazin, P. G. On the spatio-temporal development of small perturbations of Jeffery-Hamel flows. Fluid Dynamics Research, 22, 123–138 (1998)
Axford, W. I. The magnetohydrodynamic Jeffrey-Hamel problem for a weakly conducting fluid. Quarterly Journal of Mechanics and Applied Mathematics, 14, 335–351 (1961)
Esmaili, Q., Ramiar, A., Alizadeh, E., and Ganji, D. D. Anapproximation of the analytical solution of the Jeffery-Hamel flow by decomposition method. Physics Letters A, 372, 3434 (2008)
Makinde, O. D. Effect of arbitrary magnetic Reynolds number on MHD flows in convergentdivergent channels. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat and Fluid Flow, 18, 697–707 (2008)
He, J. H. A coupling method of a homotopy technique and a perturbation technique for non-linear problems. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 35, 37–43 (2000)
Reza, H., Sadegh, P., and Saeed, D. MHD flow of an incompressible viscous fluid through convergent or divergent channels in presence of a high magnetic field. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2012, 157067 (2012)
Domairry, G., Mohsenzadeh, A., and Famouri, M. The application of homotopy analysis method to solve nonlinear differential equation governing Jeffery-Hamel flow. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 14, 85–95 (2008)
He, J. H. Variational iteration method: a kind of non-linear analytical technique: some examples. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 34, 699–708 (1999)
He, J. H. A coupling method of a homotopy technique and a perturbation technique for non-linear problems. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 35, 37–43 (2000)
Sheikholeslami, M., Ganji, D. D., Ashorynejad, H. R., and Rokni, H. B. Analytical investigation of Jeffery-Hamel flow with high magnetic field and nanoparticle by Adomian decomposition method. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 33(1), 25–36 (2012) DOI 10.1007/s10483012-1531-7
Bararnia, H., Ganji, Z. Z., Ganji, D. D., and Moghimi, S. M. Numerical and analytical approaches to MHD Jeffery-Hamel flow in a porous channel. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat and Fluid Flow, 22, 491–502 (2012)
Abbasbandy, S. and Shivanian, E. Exact analytical solution of the MHD Jeffery-Hamel flow problem. Meccanica, 47, 1379–1389 (2012)
Motsa, S. S., Sibanda, P., Awad, F. G., and Shateyi, S. A new spectral-homotopy analysis method for the MHD Jeffery-Hamel problem. Computers and Fluids, 39, 1219–1225 (2010)
Khan, J. A., Raja, M. A. Z., and Qureshi, I. M. Stochastic computational approach for complex nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Chinese Physics Letter, 28, 020206 (2011)
Zongben, X., Mingwei, D., and Deyu, M. Fast and efficient strategies for model selection of support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, IEEE Transactions, 39, 1292–1307 (2009)
Meada, A. J. and Fernandez, A. A. The numerical solution of linear ordinary differential equation by feed forward neural network. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 19, 1–25 (1994)
Khan, J. A., Raja, M. A. Z., and Qureshi, I. M. Novel approach for van der Pol oscillator on the continuous time domain. Chinese Physics Letters, 28, 110205 (2011)
Khan, J. A., Raja, M. A. Z., and Qureshi, I. M. Numerical treatment of nonlinear Emden-Fowler equation using Stochastic technique. Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, 63, 185–207 (2011)
Raja, M. A. Z. Solution of the one-dimensional Bratu equation arising in the fuel ignition model using ANN optimised with PSO and SQP. Connection Science, 26, 195–214 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z. and Ahmad, S. I. Numerical treatment for solving one-dimensional Bratu problem using neural networks. Neural Computing and Applications, 24, 549–561 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z., Ahmad, S. I., and Raza, S. Neural network optimized with evolutionary computing technique for solving the 2-dimensional Bratu problem. Neural Computing and Applications, 23, 2199–2210 (2013)
Raja, M. A. Z., Samar, R., and Rashidi, M. M. Application of three unsupervised neural network models to singular nonlinear BVP of transformed 2D Bratu equation. Neural Computing and Applications, 25, 1585–1601 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z., Ahmad, S. I., and Raza, S. Solution of the 2-dimensional Bratu problem using neural network, swarm intelligence and sequential quadratic programming. Neural Computing and Applications, 25, 1723–1739 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z., Sabir, Z., Mahmood, N., Eman, S. A., and Khan, A. I. Design of Stochastic solvers based on variants of genetic algorithms for solving nonlinear equations. Neural Computing and Applications, 26, 1–23 (2015)
Raja, M. A. Z. and Samar, R. Numerical treatment for nonlinear MHD Jeffery-Hamel problem using neural networks optimized with interior point algorithm. Neurocomputing, 124, 178–193 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z. and Samar, R. Numerical treatment of nonlinear MHD Jeffery-Hamel problems using stochastic algorithms. Computers and Fluids, 91, 28–46 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z., Khan, J. A., and Haroon, T. Stochastic numerical treatment for thin film flow of third grade fluid using unsupervised neural networks. Journal of Chemical Institute of Taiwan, 48, 26–39 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z. Stochastic numerical techniques for solving Troesch’s Problem. Information Sciences, 279, 860–873 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z. Unsupervised neural networks for solving Troesch’s problem. Chinese Physics B, 23, 018903 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z. Numerical treatment for boundaryvalue problems of Pantograph functional differential equation using computational intelligence algorithms. Applied Soft Computing, 24, 806–821 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z., Khan, J. A., Behloul, D., Tahira, H., Siddiqui, A. M., and Samar, R. Exactly satisfying initial conditions neural network models for mumerical treatment of first Painlevé equation. Applied Soft Computing, 26, 244–256 (2015)
Raja, M. A. Z., Khan, J. A., Ahmad, S. I., and Qureshi, I. M. A new stochastic technique for Painlevé equation-I using neural network optimized with swarm intelligence. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2012, 1–10 (2012)
Raja, M. A. Z., Khan, J. A., and Qureshi, I. M. Swarm intelligent optimized neural networks for solving fractional differential equations. International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control, 7, 6301–6318 (2011)
Raja, M. A. Z., Khan, J. A., and Qureshi, I. M. Heuristic computational approach using swarm intelligence in solving fractional differential equations. Computers and Fluids, 91, 28–46 (2014)
Raja, M. A. Z., Khan, J. A., and Qureshi, I. M. A new Stochastic approach for solution of Riccati differential equation of fractional order. Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence, 60, 229–250 (2010)
Raja, M. A. Z., Khan, J. A., and Qureshi, I.M. Solution of fractional order system of Bagley-Torvik equation using Evolutionary computational intelligence. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2011, 675075 (2011)
Rajai, M. A. Z., Manzar, M. A., and Samar, R. An efficient computational intelligence approach for solving fractional order Riccati equations using ANN and SQP. Applied Mathematical Modeling, 39, 3075–3093 (2015)
Joneidi, A. A., Domairry, G., and Babaelahi, M. Three analytical methods applied to JefferyHamel flow. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 15, 3423–3434 (2010)
Moghimia, S. M., Ganji, D. D., Bararnia, H., Hosseini, M., and Jalaal, M. homotopy perturbation method for nonlinear MHD Jeffery-Hamel problem. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 61, 2213–2216 (2011)
Ganji, Z. Z., Ganji, D. D., and Esmaeilpour, M. Study on nonlinear Jeffery-Hamel flow by He’s semi-analytical methods and comparison with numerical results. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 58, 2107–2116 (2009)
Moghimi, S. M., Domairry, G., Soheil, S., Ghasemi, E., and Bararnia, H. Application of homotopy analysis method to solve MHD Jeffery-Hamel flows in non-parallel walls. Advances in Engineering Software, 42, 108–113 (2011)
Esmaeilpour, M. and Ganji, D. D. Solution of the Jeffery-Hamel flow problem by optimal homotopy asymptotic method. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 59, 3405–3411 (2010)
Beidokhti, R. S. and Malek, A. Solving initial-boundary value problems for systems of partial differential equations using neural networks and optimization techniques. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 346, 898–913 (2009)
Parisia, D. R., Mariani, M. C., and Laborde, M. A. Solving differential equations with unsupervised neural networks. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 42, 715–721 (2003)
Nocedal, J. and Wright, S. J. Numerical Optimization. Springer Series in Operations Research, Springer Verlag, Berlin (1999)
Fletcher, R. Practical Methods of Optimization, John Wiley and Sons, New York (1987)
Schittkowski, K. NLQPL: a FORTRAN-subroutine solving constrained nonlinear programming problems. Annals of Operations Research, 5, 485–500 (1985)
Zhu, Z. B., Jian, J. B., and Cong, Z. An SQP algorithm for mathematical programs with nonlinear complementarity constraints. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 30(5), 659–668 (2009) DOI 10.1007/s10483-009-0512-x
Qian, Q. J. and Sun, D. J. Numerical method for optimum motion of undulatory swimming plate in fluid flow. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 32(3), 339–348 (2011) DOI 10.1007/s10483-011-1419-x
Holland, H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology, Control, and Artificial Intelligence, University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor (1975)
Wang, G. M., Wang, X. J., Wan, Z. P., and Jia, S. H. An adaptive genetic algorithm for solving bilevel linear programming problem. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 28(12), 1605–1612 (2007) DOI 10.1007/s10483-007-1207-1
Mousavi, S. S., Hooman, K., and Mousavi, S. J. Genetic algorithm optimization for finned channel performance. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 28(12), 1597–1604 (2007) DOI 10.1007/s10483-007-1206-z
Wang, L., Wang, T. G., and Luo, Y. Improved non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA)-II in multi-objective optimization studies of wind turbine blades. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 32(6), 739–748 (2011) DOI 10.1007/s10483-011-1453-x
Bai, Y. L., Ma, X. Y., and Meng, X. Lift enhancement of airfoil and tip flow control for wind turbine. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 32(7), 825–836 (2011) DOI 10.1007/s10483-011-1462-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raja, M.A.Z., Samar, R., Haroon, T. et al. Unsupervised neural network model optimized with evolutionary computations for solving variants of nonlinear MHD Jeffery-Hamel problem. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 36, 1611–1638 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-2000-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-2000-6
Keywords
- Jeffery-Hamel problem
- neural network
- genetic algorithm (GA)
- nonlinear ordinary differential equation (ODE)
- hybrid technique
- sequential quadratic programming