Abstract
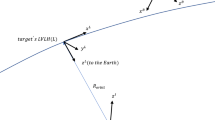
A charged spacecraft is subject to the Lorentz force when it orbits a central body with a magnetic field. The induced Lorentz force provides a new mean of propellantless electromagnetic propulsion for orbital control. Modeling the Earth magnetic field as a tilted dipole that co-rotates with the Earth, this paper develops a nonlinear dynamical model that describes the relative motion of the Lorentz spacecraft about an arbitrary reference orbit. Based on the proposed dynamical model, feasibility of Lorentz-propelled rendezvous with no restrictions on the initial states is investigated. The rendezvous problem is then formulated as an optimal control problem, and solved with the Gauss pseudospectral method (GPM). Numerical simulations substantiate the validity of proposed model and method, and results show that the propellantless rendezvous is achieved at both fixed and free final time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peck, M. A. Prospects and challenges for Lorentz-augmented orbits. AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, San Francisco, California, 2005–5995 (2005)
Pollock, G. E., Gangestad, J. W., and Longuski, J. M. Inclination change in low-Earth-orbit via the geomagnetic Lorentz force. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 33(5), 1387–1395 (2010)
Pollock, G. E., Gangestad, J. W., and Longuski, J. M. Analytical solutions for the relative motion of spacecraft subject to Lorentz-force perturbations. Acta Astronautica, 68(1–2), 204–217 (2011)
Yamakawa, H., Bando, M., Yano, K., and Tsujii, S. Spacecraft relative dynamics under the influence of geomagnetic Lorentz force. AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, Toronto, Ontario Canada, 2010–8128 (2010)
Huang, X., Yan, Y., Zhou, Y., and Yi, T. Improved analytical solutions for relative motion of Lorentz spacecraft with application to relative navigation in low Earth orbit. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 228(11), 2138–2154 (2014)
Huang, X., Yan, Y., and Zhou, Y. Dynamics and control of spacecraft hovering using the geomagnetic Lorentz force. Advances in Space Research, 53(3), 518–531 (2014)
Huang, X., Yan, Y., Zhou, Y., and Zhang, H. Sliding mode control for Lorentz-augmented spacecraft hovering around elliptic orbits. Acta Astronautica, 103(10–11), 257–268 (2014)
Peck, M. A., Streetman, B., Saaj, C. M., and Lappas, V. Spacecraft formation flying using Lorentz force. Journal of the British Interplanetary Society, 60(7), 263–267 (2007)
Peng, C., and Gao, Y. Lorentz-force-perturbed orbits with application to J 2-invariant formation. Acta Astronautica, 77(8–9), 12–28 (2011)
Tsujii, S., Bando, M., and Yamakawa, H. Spacecraft formation flying dynamics and control using the geomagnetic Lorentz force. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 36(1), 136–148 (2013)
Wu, B., Wang, D., Poh, E. K., and Xu, G. Nonlinear optimization of low-thrust trajectory for satellite formation: Legendre pseudospectral method. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 32(4), 1371–1381 (2009)
Huntington, G. T. and Rao, A. V. Optimal reconfiguration of spacecraft formations using the Gauss pseudospectral method. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 31(3), 689–698 (2008)
Vaddi, S. S., Vadali., S. R., and Alfriend., K. T. Formation flying: accommodating nonlinearity and eccentricity perturbations. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 26(2), 214–223 (2003)
Benson, D. A., Huntington, G. T., Thorvaldsen, T. P., and Rao, A. V. Direct trajectory optimization and costate estimation via an orthogonal collocation method. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 29(6), 1435–1440 (2006)
Fahroo, F. and Ross, I. M. Costate estimation by a Legendre pseudospectral method. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 24(2), 270–277 (2001)
Fahroo, F. and Ross, I. M. Direct trajectory optimization by a Chebyshev pseudospectral method. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 25(1), 160–166 (2002)
Williams, P. Jacobi pseudospectral method for solving optimal control problems. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 27(2), 293–297 (2004)
Garg, D., Patterson, M. A., Francolin, C., Darby, C. L., Huntington, G. T., Hager, W. W., and Rao., A. V. Direct trajectory optimization and costate estiamtion of finite-horizon and infinitehorizon optimal control problems using a Radau pseudospectral method. Computational Optimization and Applications, 49(2), 335–358 (2011)
Darby, C. L., Hager, W. W., and Rao, A. V. Direct trajectory optimization using a variable loworder adaptive pseudospectral method. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 48(3), 433–445 (2011)
Huntington, G. T., Benson, D., and Rao, A. V. A comparison of accuracy and computational efficiency of three pseudospectral method. AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference and Exhibit, Hilton Head, South Carolina, 2007–6405 (2007)
Garg, D., Patterson, M., Hager, W. W., Rao, A. V., Benson, D. A., and Huntington, G. T. A unified framework for the numerical solution of optimal control problems using pseudospectral methods. Automatica, 46(11), 1843–1851 (2010)
Rao, A. V., Benson, D. A., Darby, C., Patterson, M. A., Francolin, C., Sanders, I., and Huntington, G. T. Algorithm 902: GPOPS, a Matlab software for solving multiple-phase optimal control problems using the Gauss pseudospectral method. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 37(2), 1–39 (2010)
Gill, P. E., Murray, W., and Saunders, M. A. SNOPT: an SQP algorithm for large-scale constrained optimization. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 12(4), 979–1006 (2002)
Huang, X., Yan, Y., and Zhou, Y. Optimal control of Lorentz spacecraft rendezvous on circular equatorial orbit (in Chinese). Proceedings of the 32nd Chinese Control Conference, Xi’an, 26–28 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the Fund of Innovation by Graduate School of National University of Defense Technology (No. B140106)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Yan, Y., Zhou, Y. et al. Pseudospectral method for optimal propellantless rendezvous using geomagnetic Lorentz force. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 36, 609–618 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-1936-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-1936-7