Abstract
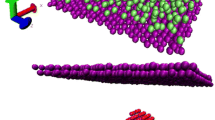
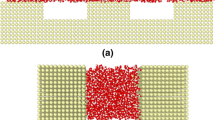
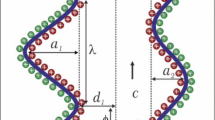
The atomic behavior of liquid-solid mixed-phase nanofluid flows inside nanochannels is investigated by a molecular dynamics simulation (MDS). The results of visual observation and statistic analysis show that when the nanoparticles reach near each other, the strong interatomic force will make them attach together. This aggregation continues until all nanoparticles make a continuous cluster. The effect of altering the external force magnitude causes changes in the agglomeration rate and system enthalpy. The density and velocity profiles are shown for two systems, i.e., argon (Ar)-copper (Cu) nanofluid and simple Ar fluid between two Cu walls. The results show that using nanoparticles changes the base fluid particles ordering along the nanochannel and increases the velocity. Moreover, using nanoparticles in simple fluids can increase the slip length and push the near-wall fluid particles into the main flow in the middle of the nanochannel.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F ij :
-
intermolecular force on molecule i by molecule j, N
- F ext :
-
external applied force, N
- M :
-
molecule mass, kg
- P :
-
pressure, Pa
- r c :
-
cutoff distance, nm
- r ij :
-
position between molecules i and j, nm
- t :
-
time, s
- T :
-
temperature, K
- V :
-
volume of system, (nm)3
- V i :
-
velocity of molecule i, m/s
- ɛ :
-
energy parameter in Lennard-Jones (LJ) potential, J
- σ :
-
molecular length scale, nm
- τ :
-
characteristic time, s
- ρ :
-
density, kg/m3
- φ :
-
interaction potential, J
References
Saidur, R., Leong, K. Y., and Mohammad, H. A. A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15, 1646–1668 (2011)
Wang, X. Q. and Mujumdar, A. S. Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids: a review. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 46, 1–19 (2007)
Allen, M. P. and Tildesley, D. J. Computer Simulations of Liquids, Clarendon, Oxford (1987)
Sarkar, S. and Selvam, R. P. Molecular dynamics simulation of effective thermal conductivity and study of enhanced thermal transport mechanism in nanofluids. Journal of Applied Physics, 102, 074302 (2007)
Sankar, N., Mathew, N., and Sobhan, C. B. Molecular dynamics modeling of thermal conductivity enhancement in metal nanoparticle suspensions. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 35, 867–872 (2008)
Li, L., Zhang, Y., Ma, H., and Yang, M. Molecular dynamics simulation of effect of liquid layering around the nanoparticle on the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 12, 811–821 (2010)
Xue, L., Keblinski, P., Phillpot, S. R., Choi, S. U., and Eastman, J. A. Effect of liquid layering at the liquid-solid interface on thermal transport. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 47, 4277–4284 (2004)
Kang, H., Zhang, Y., Yang, M., and Li, L. Nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulation of coupling between nanoprticles and base-fluid in a nanofluid. Physics Letters A, 376, 521–524 (2012)
Mohebbi, A. Prediction of specific heat and thermal conductivity of nanofluids by a combined equilibrium and non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 175, 51–58 (2012)
Kondarajau, S., Jin, E. K., and Lee, J. S. Direct numerical simulation of thermal conductivity of nanofluids: the effect of temperature two-way coupling and coagulation of particles. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 53, 862–869 (2010)
Vladkov, M. and Barrat, J. L. Modeling thermal conductivity and collective effects in a simple nanofluid. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 5, 187–193 (2008)
Sofos, F., Karakasidis, T. E., and Liakopoulos, A. Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics investigation of parameters affecting planar nanochannel flows. Contemporary Engineering Sciences, 2, 283–298 (2009)
Sofos, F., Karakasidis, T. E., and Liakopoulos, A. Transport properties of liquid argon in krypton nanochannels: anisotropy and non-homogeneity introduced by the solid walls. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 52, 735–743 (2009)
Sofos, F., Karakasidis, T. E., and Liakopoulos, A. Parameters affecting slip length at the nanoscale. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 10, 648–650 (2013)
Priezjev, N. V. Rate-dependent slip boundary conditions for simple fluids. Physical Review E, 75, 051605 (2007)
Li, L., Zhang, Y., Ma, H., and Yang, M. An investigation of molecular layering at the liquid-solid interface in nanofluids by molecular dynamics simulation. Physics Letters A, 372, 4541–4544 (2008)
Evans, W., Fish, J., and Keblinski, P. Role of Brownian motion hydrodynamics on nanofluid thermal conductivity. Applied Physics Letters, 88, 093116 (2006)
Merabia, S., Shenogin, S., Joly, L., Keblinski, P., and Barrat, J. L. Heat transfer from nanoparticles: a corresponding state analysis. Applied Physical Sciences, 106, 15113–15118 (2009)
Lv, J., Cui, W., Bai, M., and Li, X. Molecular dynamics simulation on flow behavior of nanofluids between flat plates under shear flow condition. Microfluid Nanofluid, 10, 475–480 (2011)
Lv, J., Cui, W., Bai, M., and Li, X. The molecular dynamic simulation on impact and friction characters of nanofluids with many nanoparticles system. Nanoscale Research Letters, 6, 200 (2011)
Cui, W., Bai, M., Lv, J., and Li, X. On the microscopic flow characteristics of nanofluids by molecular dynamics simulation on Couette flow. The Open Fuels and Energy Science Journal, 5, 21–27 (2012)
Cui, W., Bai, M., Lv, J., Zhang, L., Li, G., and Xu, M. On the flow characteristics of nanofluids by experimental approach and molecular dynamics simulation. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 39, 148–157 (2012)
Ziarani, A. S. and Mohamad, A. A. A molecular dynamics study of perturbed Poiseuille flow in a nanochannel. Microfluid Nanofluid, 2, 12–20 (2005)
Li, Y. X., Xu, J. L., and Li, D. Q. Molecular dynamics simulation of nanoscale liquid flows. Microfluid Nanofluid, 9, 1011–1013 (2010)
Soong, C. Y., Yen, T. H., and Tzeng, P. Y. Molecular dynamics simulation of nanochannel flows with effects of wall lattice-fluid interactions. Physical Review E, 76, 036303 (2007)
Aminfar, H., Jafarizadeh, M. A., and Razmara, N. Nanoparticles aggregation in nanofluid flow through nanochannels: insights from molecular dynamic study. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 25, 1450066 (2014)
Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. Journal of Computational Physics, 117, 1–19 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aminfar, H., Razmara, N. & Mohammadpourfard, M. On flow characteristics of liquid-solid mixed-phase nanofluid inside nanochannels. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 35, 1541–1554 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-014-1889-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-014-1889-6