Abstract
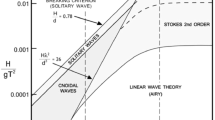
A two-dimensional (2D) numerical model is developed for the wave simulation and propagation in a wave flume. The fluid flow is assumed to be viscous and incompressible, and the Navier-Stokes and continuity equations are used as the governing equations. The standard k-ɛ model is used to model the turbulent flow. The Navier-Stokes equations are discretized using the staggered grid finite difference method and solved by the simplified marker and cell (SMAC) method. Waves are generated and propagated using a piston type wave maker. An open boundary condition is used at the end of the numerical flume. Some standard tests, such as the lid-driven cavity, the constant unidirectional velocity field, the shearing flow, and the dam-break on the dry bed, are performed to valid the model. To demonstrate the capability and accuracy of the present method, the results of generated waves are compared with available wave theories. Finally, the clustering technique (CT) is used for the mesh generation, and the best condition is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Contento, G. Numerical wave tank computations of nonlinear motions of two-dimensional arbitrarily shaped free floating bodies. Ocean Engineering, 27, 531–556 (2000)
Grilli, S. T., Vogelmenn, S., and Watts, P. Development of a 3D numerical wave tank for modeling tsunami generation by underwater landslides. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 26, 301–313 (2002)
Fochesato, C., Grilli, S., and Dias, F. Numerical modeling of extreme rogue waves generated by directional energy focusing. Wave Motion, 44, 395–416 (2007)
Ducrozet, G., Bonnefoy, F., Le Touzé, D., and Ferrant, P. A modified high-order spectral method for wavemaker modeling in a numerical wave tank. European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids, 34, 19–34 (2012)
Park, J. C., Kim, M. H., Miyata, H., and Chun, H. H. Fully nonlinear numerical wave tank (NWT) simulations and wave run-up prediction around 3D structures. Ocean Engineering, 30, 1969–1996 (2003)
Li, Y. and Lin, M. Regular and irregular wave impacts on floating body. Ocean Engineering, 42, 93–101 (2012)
Rudman, M. Volume-tracking methods for interfacial flow calculations. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 24, 671–691 (1997)
Troch, P. and de Rouck, J. An active wave generating-absorbing boundary condition for VOF type numerical model. Coastal Engineering, 38, 223–247 (1999)
Choi, J. W. and Yoon, S. B. Numerical simulation using momentum source wave-maker applied RANS equation model. Coastal Engineering, 56, 1043–1060 (2009)
Zhao, X. Z., Hu, C. H., and Sun, Z. C. Numerical simulation of extreme wave generation using VOF method. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 22, 466–477 (2010)
Schäffer, H. A. and Steenberg, C. M. Second-order wavemaker theory for multidirectional waves. Ocean Engineering, 30, 1203–1231 (2003)
Teng, B. and Ning, D. Z. A simplified model for extreme-wave kinematics in deep sea. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 8, 27–32 (2009)
Wei, G., Le, J. C., and Dai, S. Q. Surface effects of internal wave generated by a moving source in a two-layer fluid of finite depth. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 24(9), 1025–1040 (2003) DOI 10.1007/BF02437635
Lara, J. L., Garcia, N., and Losada, I. J. RANS modelling applied to random wave interaction with submerged permeable structure. Coastal Engineering, 113, 396–417 (2006)
Lin, P. and Karunarathna, S. A. S. Numerical study of solitary wave interaction with porous breakwaters. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal and Ocean Engineering, 133(5), 352–363 (2007)
Shin, S., Bae, S. Y., Kim, I. C., Kim, Y. J., and Yoo, H. K. Simulation of free surface flows using the flux-difference splitting scheme on the hybrid Cartesian/immersed boundary method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 68, 360–376 (2012)
Rafei, R. Numerical Solution of Incompressible 3 D Turbulent Flow in a Spiral Channel, M. Sc. dissertation, Amirkabir University of Technology (2004)
Li, C. W. and Zang, Y. F. Simulation of free surface recirculating flows in semi-enclosed water bodies by a k-w model. Applied Mathematical Modeling, 22, 153–164 (1998)
Gao, H., Gu, H. Y., and Guo, L. J. Numerical study of stratified oil-water two-phase turbulent flow in a horizontal tube. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 46, 749–754 (2003)
Ren, B. and Wang, Y. Numerical simulation of random wave slamming on structures in the splash zone. Ocean Engineering, 31, 547–560 (2004)
Shen, Y. M., Ng, C. O., and Zheng, Y. H. Simulation of wave propagation over a submerged bar using the VOF method with a two-equation k-ɛ turbulence modeling. Ocean Engineering, 31, 87–95 (2004)
Mirbagheri, S. M. H., Dadashzadeh, M., Serajzadeh, S., Taheri, A. K., and Davami, P. Modeling the effect of mould wall roughness on the melt flow simulation in casting process. Applied Mathematical Modeling, 28, 933–956 (2004)
Geuyffier, D., Li, J., Nadim, A., Scardovelli, R., and Zaleski, S. Volume-of-fluid interface tracking with smoothed surface stress methods for three-dimensional flows. Journal of Computational Physics, 152, 423–456 (1999)
Harvie, D. J. E. and Fletcher, D. F. A new volume of fluid advection algorithm: the defined donating region scheme. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 35, 151–172 (2001)
Ketabdari, M. J., Nobari, M. R. H., and Moradi-Larmaei, M. Simulation of waves group propagation and breaking in coastal zone using a Navier-Stokes solver with an improved VOF free surface treatment. Applied Ocean Research, 30, 130–143 (2008)
Hur, D. S. and Mizutani, M. Numerical estimation of the wave forces acting on a three-dimensional body on submerged breakwater. Coastal Engineering, 47, 329–345 (2003)
Duff, E. S. Fluid Flow Aspects of Solidification Modeling, Simulation of Low Pressure Die Casting, Ph. D. dissertation, University of Queenland (1999)
Ghia, U., Ghia, K. N., and Shin, C. T. High-Re solutions for incompressible flow using the Navier-Stokes equations and a multigrid method. Journal of Computational Physics, 48, 387–411 (1982)
Scardovelli, R. and Zaleski, S. Interface reconstruction with least-square fit and split Eulerian-Lagrangian advection. International Journal of Numerical Methods in Fluids, 41, 251–274 (2003)
Martin, J. C. and Moyce, W. J. An experimental study of the collapse of liquid columns on a rigid horizontal plane. Philosophical Transaction of the Royal Society of London, 244, 312–324 (1982)
Boussinesq, M. J. Théorie de l’intumescence liquide, appelée onde solitaire ou de translation, se propageant dans un canal rectangulaire. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Scinces, 72, 755–759 (1871)
Rayleigh, L. On waves. Philosophical Magazine, 1, 257–279 (1876)
Clamond, D. and Germain, J. P. Interaction between a Stokes wave packet and a solitary wave. European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids, 18, 67–91 (1999)
Temperville, A. Contribution à l’étude des Ondes de Gravité en Eau Peu Profonde, Thèse d’Etat, Université Joseph Fourier (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saghi, H., Ketabdari, M.J. & Booshi, S. Generation of linear and nonlinear waves in numerical wave tank using clustering technique-volume of fluid method. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 33, 1179–1190 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-012-1614-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-012-1614-9
Key words
- numerical wave tank
- free surface simulation
- Navier-Stokes equation
- staggered grid
- clustering technique (CT)
- wave generation