Abstract
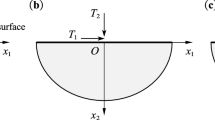
The reflection and refraction of a longitudinal wave at an interface between a perfectly conducting nonviscous liquid half-space and a perfectly conducting microstretch elastic solid half-space are studied. The appropriate solutions to the governing equations are obtained in both the half-spaces satisfying the required boundary conditions at the interface to obtain a system of five non-homogeneous equations in the amplitude ratios of various reflected and transmitted waves. The system is solved by a Fortran program of the Gauss elimination method for a particular example of an interface between water and aluminum-epoxy composite. Numerical values of the amplitude ratios are computed for a certain range of the incidence angle both in the presence and absence of an impressed transverse magnetic field. The effects of the presence of the transverse magnetic field on the amplitude ratios of various reflected and transmitted waves are shown graphically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eringen, A. C. Micropolar Elastic Solids with Stretch, Ari Kitabevi Matbassi, Istanbul, 1–18 (1971)
Eringen, A. C. Theory of microstretch elastic solids. International Journal of Engineering Science, 28(12), 1291–1301 (1990)
Eringen, A. C. Microcontinuum Field Theories, I, Foundations and Solids, Springer-Verlag, Inc., New York (1999)
Pabst, W. Micropolar materials. Ceramics, 49(3), 170–180 (2005)
Parfitt, V. R. and Eringen, A. C. Reflection of plane waves from the flat boundary of a micropolar elastic half-space. Journal of Acoustical Society of America, 45(5), 1258–1272 (1969)
Singh, B. Reflection of plane waves from free surface of a microstretch elastic solid. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Earth and Planetary Sciences, 111(1), 29–37 (2002)
Tomar, S. K. and Garg, M. Reflection and transmission of waves from a plane interface between two microstretch solid half-spaces. International Journal of Engineering Science, 43(1–2), 139–169 (2005)
Singh, D. and Tomar, S. K. Rayleigh lamb waves in a microstretch elastic plate cladded with liquid layers. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 302(1–2), 313–331 (2007)
Singh, B. Reflection and refraction of microstretch elastic waves at a liquid-solid interface in the presence of magnetic field. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Earth and Planetary Sciences, 72A(II), 95–108 (2002)
Kaliski, S. Attenuation of surface waves between perfectly conducting fluid and solid in a magnetic field normal to the contact surface. Proceedings of Vibrational Problems, 4, 375 (1963)
Kaliski, S. and Nowacki, W. International Union of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Brown University Press, Providence (1963)
Gauthier, R. D. Experimental investigation on micropolar media. Mechanics of Micropolar Media (eds. Brulin, O. and Hsieh, R. K. T.), World Scientific, Singapore (1982)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, B. Influence of magnetic field on wave propagation at liquid-microstretch solid interface. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 32, 595–602 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-011-1441-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-011-1441-6