Abstract
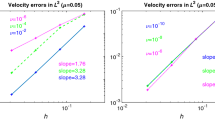
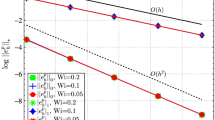
This paper extends the results of Matthies, Skrzypacz, and Tubiska for the Oseen problem to the Navier-Stokes problem. For the stationary incompressible Navier-Stokes equations, a local projection stabilized finite element scheme is proposed. The scheme overcomes convection domination and improves the restrictive inf-sup condition. It not only is a two-level approach but also is adaptive for pairs of spaces defined on the same mesh. Using the approximation and projection spaces defined on the same mesh, the scheme leads to much more compact stencils than other two-level approaches. On the same mesh, besides the class of local projection stabilization by enriching the approximation spaces, two new classes of local projection stabilization of the approximation spaces are derived, which do not need to be enriched by bubble functions. Based on a special interpolation, the stability and optimal prior error estimates are shown. Numerical results agree with some benchmark solutions and theoretical analysis very well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Franca, L. P. and Frey, S. L. Stabilized finite element methods: II. the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 99(2–3), 209–233 (1992)
Tobiska, L. and Verfürth, R. Analysis of a streamline diffusion finite element method for the Stokes and Navier-Stokes equation. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 33(1), 107–127 (1996)
Li, J., He, Y. N., and Chen, Z. X. Performance of several stabilized finite element methods for the Stokes equations based on the lowest equal-order pairs. Computing 86(1), 37–51 (2009) DOI 10.1007/s00607-009-0064-5
He, Y. N. and Li, J. A stabilized finite element method based on local polynomial pressure projection for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Applied Numerical Mathematics 58(10), 1503–1514 (2008)
Li, J., He, Y. N., and Xu, H. A multi-level stabilized finite element method for the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 196(4–6), 2852–2862 (2007)
Li, J., He, Y. N., and Chen, Z. X. A new stabilized FEM for the transient Navier-Stokes equations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 197, 22–35 (2007)
Qin, Y. M., Feng, M. F., and Zhou, T. X. A new full discrete stabilized viscosity method for transient Navier-Stokes equations. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) 30(7), 839–852 (2009) DOI 10.1007/s10483-009-0704-z
Luo, Y. and Feng, M. F. Discontinous element pressure gradient stabilizations for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations based on local projections. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) 29(2), 171–183 (2008) DOI 10.1007/s10483-008-0205-z
Luo, K., Feng, M. F., and Wang, C. An accurate locking-free quadrilateral plate element (in Chinese). Journal of Sichuan University (Engeering Science Edition) 38(1), 44–48 (2006)
Becker, R. and Braack, M. A finite element pressure gradient stabilization for the Stokes equations based on local projections. Calcolo 38(4), 173–199 (2001)
Becker, R. and Braack, M. A two-level stabilization scheme for the Navier-Stokes equations. Numerical Mathematics and Advanced Applications (eds. Feistauer, M., Dolejší, V., Knobloch, P., and Najzar, K.), Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 123–130 (2003)
Braack, M. and Burman, E. Local projection stabilization for the Oseen problem and its interpretation as a variational multiscale method. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 43(6), 2544–2566 (2006)
Matthies, G., Skrzypacz, P., and Tobiska, L. A unified convergence analysis for local projection stabilizations applied to the Oseen problem. Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis 41(4), 713–742 (2007)
Codina, R. and Blasco, J. Analysis of a pressure-stabilized finite element approximation of the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Numerische Mathematik 87, 59–81 (2000)
Codina, R. and Blasco, J. A finite element formulation for the Stokes problem allowing equal velocity-ressure interpolation. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 143, 373–391 (1997)
Codina, R. and Blasco, J. Stabilized finite element method for the transient Navier-Stokes equations based on a pressure gradient projection. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 182, 277–300 (2000)
Codina, R., Vázquez, M., and Zienkiewicz, O. C. A general algorithm for compressible and incompressible follow-Part III, the semiimplicit form. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 27, 13–32 (1998)
Chacõn, T. A term by term stabilization algorithm for the finite element solution of incompressible flow problems. Numerische Mathematik 79, 283–319 (1998)
Franca, L. P. and Frey, S. L. Stabilized finite element methods: II. the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 99, 209–233 (1992)
Tobiska, L. and Lube, G. A modified streamline-diffusion method for solving the stationary Navier-Stokes equations. Numerische Mathematik 59, 13–29 (1991)
Tobiska, L. and Verfürth, R. Analysis of a streamline diffusion finite element method for the Stokes and Navier-Stokes equations. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 33, 107–127 (1996)
Girault, V. and Raviart, P. Finite Element Methods for the Navier-Stokes Equations, Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg (1986)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Xing-ming GUO
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 10872085), the Sichuan Science and Technology Project (No. 05GG006-006-2), and the Youth Science Foundation of Neijiang Normal University (No. 09NJZ-6)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Ym., Feng, Mf., Luo, K. et al. Local projection stabilized finite element method for Navier-Stokes equations. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 31, 651–664 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-010-0513-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-010-0513-z