Abstract
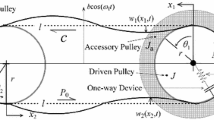
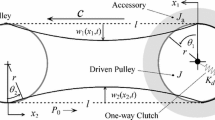
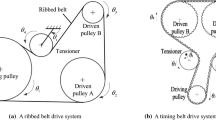
The modal method is applied to analyze coupled vibration of belt drive systems. A belt drive system is a hybrid system consisting of continuous belts modeled as strings as well as discrete pulleys and a tensioner arm. The characteristic equation of the system is derived from the governing equation. Numerical results demenstrate the effects of the transport speed and the initial tension on natural frequencies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen L Q, Zu J W. Advance in analysis of vibrations of serpentine belt drive systems[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2001, 23(4):8–12 (in Chinese).
Chen L Q. Analysis and control of transverse vibrations of axially moving strings[J]. ASME Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2005, 58(2):91–116.
Ulsoy A G, Whitesell J E, Hooven M D. Design of belt-tensioner systems for dynamic stability[J]. ASME Journal of Vibration, Acoustics, Stress, and Reliability in Design, 1985, 107(2):282–290.
Beikmann R S, Perkins N C, Ulsoy A G. Free vibration of serpentine belt drive systems[J]. ASME Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 1996, 118(3):406–413.
Beikmann R S, Perkins N C, Ulsoy A G. Nonlinear coupled response of serpentine belt drive systems[J]. ASME Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 1996, 118(4):567–574.
Zhang L, Zu J W. Modal analysis of serpentine belt drive systems[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1999, 222(2):259–279.
Zhang L, Zu J W. One-to-one auto-parametric resonance in serpentine belt drive systems[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2000, 232(4):783–806.
Zhang L Zu J W, Hou Z. Complex modal analysis of non-self-adjoint hybrid serpentine belt drive systems[J]. ASME Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2001, 123(2):150–156.
Parker R G. Efficient eigensolution, dynamic response, and eigensensitivity of serpentine belt drives[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004, 270(1):15–38.
Leamy M J, Wasfy T M. Transient and steady-state dynamic finite element modeling of beltdrives[J]. ASME Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2002, 124(6):575–581.
Leamy M J. On a perturbation method for the analysis of unsteady belt-drive operation[J]. ASME Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2005, 72(4):570–580.
Tonoli A, Amati N, Zenerino E. Dynamic modeling of belt drive systems: effects of the shear deformations[J]. ASME Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2006, 128(4):555–567.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributed by CHEN Li-qun
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 10672092 and 10725209), the Scientific Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. 07ZZ07), and Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (No. Y0103)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xj., Chen, Lq. Modal analysis of coupled vibration of belt drive systems. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 29, 9–13 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-008-0102-x
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-008-0102-x