Abstract
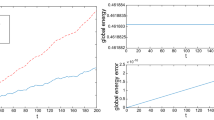
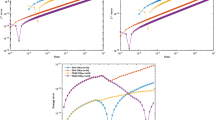
By applying the continuous finite element methods of ordinary differential equations, the linear element methods are proved having second-order pseudo-symplectic scheme and the quadratic element methods are proved having third-order pseudo-symplectic scheme respectively for general Hamiltonian systems, and they both keep energy conservative. The finite element methods are proved to be symplectic as well as energy conservative for linear Hamiltonian systems. The numerical results are in agreement with theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng Kang. Collected works of Feng Kang[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 1995, 1–185 (in Chinese).
Feng Kang, Qin Mengzhao. Symplectic geometry algorithm for Hamiltonian systems[M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Science and Technology Publishing House, 2003, 1–386 (in Chinese).
Sanz-Serna J M. Runge-kutta schemes for Hamiltonian systems.[J]. BIT, 1988, 28:877–883.
Aubry A, Chartier P. Pseudo-symplectic Runge-kutta methods[J]. BIT, 1997, 37:1–21.
Gonzalez O, Simo J C. On the stability of symplectic and energy-momentum algorithms for non-linear Hamiltonian systems with symmetry[J]. Comput Methods Appl Mech Engi, 1996, 134:197–222.
Kane C, Marsde J E, Ortiz M. Symplectic-energy-momentum preserving variational integrators[J]. J Math Phys, 1999, 40:3353–3371.
Bridges T J, Reich S. Multisymplectic intergrators: numerical schemes for Hamiltonian PDEs that conserve symplecticity[J]. Phys Lett A, 2001, 284:184–193.
Chen Chuanmiao, Huang Yunqing. High accuracy theory of finite element[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1995, 197–227.
Chen Chuanmiao. Finite element superconvergence construction theory[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 2001, 19–255 (in Chinese).
Yang Luyuan, Tang Qiong. Superconvergence in continuous finite elements for initial value problem of ordinary differntial equation[J]. Numerical Mathematics a Journal of Chinese Universities, 2004, 26(1):91–96 (in Chinese).
Li Yanxin, Ding Peizhu, Wu Chengxun, Jing M X. Symplectic algorithm of classical trajectories of A 2 B molecule system.[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 1995, 15(8):1181–1186 (in Chinese).
Ji Jiangwei, Liao Xinhao, Liu Lin. The conservation of the symplectic difference scheme and stability[J]. Comp Phys, 1997, 14(1):68–74 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by ZHONG Wan-xie
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 10471038)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Q., Chen, Cm. Continuous finite element methods for Hamiltonian systems. Appl Math Mech 28, 1071–1080 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-007-0809-y
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-007-0809-y