Abstract
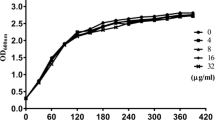
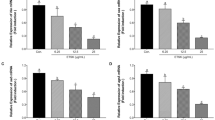
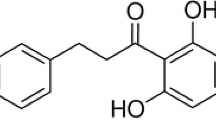
Staphylococcus aureus is a significant human pathogen that causes a wide range of diseases. Alpha-hemolysin (Hla), a pore-forming cytotoxin that is produced by most S. aureus strains, can cause tissue injury and plays a critical role in the virulence of this pathogen. In the present study, we discovered that diosmetin, a natural flavonoid that occurs primarily in citrus fruits and exhibits little anti-S. aureus activity, could diminish the production of Hla in culture supernatants in a concentration-dependent manner. The analysis of cytotoxicity in the co-culture system of S. aureus and A549 epithelial cells showed that such inhibition confers significant protection against S. aureus-mediated injury. Our results suggested that diosmetin has the potential to be a new anti-virulence drug for S. aureus infection, particularly for the targeting of Hla.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayer AS, Ramos MD, Menzies BE, Yeaman MR, Shen AJ, Cheung AL (1997) Hyperproduction of alpha-toxin by Staphylococcus aureus results in paradoxically reduced virulence in experimental endocarditis: a host defense role for platelet microbicidal proteins. Infect Immun 65:4652–4660
Berube BJ, Bubeck Wardenburg J (2013) Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin: nearly a century of intrigue. Toxins (Basel) 5:1140–1166
Brandt C, Makarewicz O, Fischer T, Stein C, Pfeifer Y, Werner G, Pletz MW (2014) The bigger picture: the history of antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance displayed by scientometric data. Int J Antimicrob Agents 44:424–430
Bubeck Wardenburg J, Patel RJ, Schneewind O (2007) Surface proteins and exotoxins are required for the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Infect Immun 75:1040–1044
Cegelski L, Marshall GR, Eldridge GR, Hultgren SJ (2008) The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:17–27
Chan BC, Ip M, Gong H et al (2013) Synergistic effects of diosmetin with erythromycin against ABC transporter over-expressed methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) RN4220/pUL5054 and inhibition of MRSA pyruvate kinase. Phytomedicine 20:611–614
Clatworthy AE, Pierson E, Hung DT (2007) Targeting virulence: a new paradigm for antimicrobial therapy. Nat Chem Biol 3:541–548
Defoirdt T (2013) Antivirulence therapy for animal production: filling an arsenal with novel weapons for sustainable disease control. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003603
Defoirdt T, Boon N, Bossier P (2010) Can bacteria evolve resistance to quorum sensing disruption? PLoS Pathog 6:e1000989
Dinges MM, Orwin PM, Schlievert PM (2000) Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Rev 13:16–34
Donnenberg MS (2000) Pathogenic strategies of enteric bacteria. Nature 406:768–774
Hanson MR, Chung CL (2009) Antibiotic selection for MRSA: case presentations and review of the literature. J Drugs Dermatol 8:281–286
Hirst RA, Yesilkaya H, Clitheroe E et al (2002) Sensitivities of human monocytes and epithelial cells to pneumolysin are different. Infect Immun 70:1017–1022
Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J et al (2007) Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA 298:1763–1771
Liang X, Yan M, Ji Y (2009) The H35A mutated alpha-toxin interferes with cytotoxicity of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun 77:977–983
Lowy FD (1998) Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 339:520–532
Nambiar S, Laessig K, Toerner J, Farley J, Cox E (2014) Antibacterial drug development: challenges, recent developments, and future considerations. Clin Pharmacol Ther 96:147–149
Ohlsen K, Ziebuhr W, Koller KP, Hell W, Wichelhaus TA, Hacker J (1998) Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on alpha-toxin (hla) gene expression of methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42:2817–2823
Parker D, Prince A (2012) Immunopathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus pulmonary infection. Semin Immunopathol 34:281–297
Patel K, Gadewar M, Tahilyani V, Patel DK (2013) A review on pharmacological and analytical aspects of diosmetin: a concise report. Chin J Integr Med 19:792–800
Powers JH (2004) Antimicrobial drug development–the past, the present, and the future. Clin Microbiol Infect 10(Suppl 4):23–31
Powers ME, Kim HK, Wang Y, Bubeck Wardenburg J (2012) ADAM10 mediates vascular injury induced by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin. J Infect Dis 206:352–356
Rossolini GM, Arena F, Pecile P, Pollini S (2014) Update on the antibiotic resistance crisis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 18C:56–60
Wang J, Qiu J, Dong J et al (2011) Chrysin protects mice from Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. J Appl Microbiol 111:1551–1558
Wang SY, Sun ZL, Liu T, Gibbons S, Zhang WJ, Qing M (2014) Flavonoids from Sophora moorcroftiana and their synergistic antibacterial effects on MRSA. Phytother Res 28:1071–1076
Wang J, Qiu J, Tan W et al (2015a) Fisetin inhibits Listeria monocytogenes virulence by interfering with the oligomerization of Listeriolysin O. J Infect Dis 211:1376–1387
Wang J, Zhou X, Liu S et al (2015b) Morin hydrate attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence by inhibiting the self-assembly of alpha-hemolysin. J Appl Microbiol 118:753–763
Xiong YQ, Willard J, Yeaman MR, Cheung AL, Bayer AS (2006) Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin gene (hla) expression by agr, sarA, and sae in vitro and in experimental infective endocarditis. J Infect Dis 194:1267–1275
Zhang Y, Wang JF, Dong J et al (2013) Inhibition of alpha-toxin production by subinhibitory concentrations of naringenin controls Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Fitoterapia 86:92–99
Acknowledgments
We thank Timothy J. Foster (Department of Microbiology, Moyne Institute of Preventive Medicine, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland) for kindly providing strain 8325-4. This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant 2013CB127205), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant 31130053) and the National 863 program (grant 2012AA020303).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Statement
The defibrinated rabbit blood was commercially obtained from Zheng Zhou Jiu Long Biological Products Co Ltd and no animals were directly used in the experiments above.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Shui Liu, Xuan Zhou and Wenhua Li have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Zhou, X., Li, W. et al. Diosmetin inhibits the expression of alpha-hemolysin in Staphylococcus aureus . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108, 383–389 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0491-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0491-6