Abstract
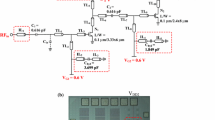
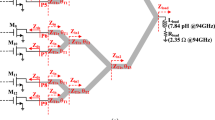
A low-power and wideband low-noise amplifier (LNA) for 77 GHz automobile radar and 94 GHz image radar systems using 90 nm CMOS technology is reported. Half-wavelength (λ/2)-spiral-inductor-based positive feedback technique is used at the common-source input stage for gain (S21) enhancement. Moreover, T-match technique is utilized to achieve simultaneously wideband input and output impedance matching, and wideband S21 and noise figure (NF). The LNA consumes 6.3 mW and achieves S11 and S22 better than − 10 dB for frequencies of 76.9–94.1 GHz and 77.2–96.7 GHz, respectively. That is, the corresponding input and output matching bandwidth are 17.2 GHz and 19.5 GHz, respectively. Additionally, high and flat S21 of 13.5 ± 1.5 dB is achieved for frequencies of 77–99.5 GHz, which means the corresponding 3-dB bandwidth is 22.5 GHz. Furthermore, the LNA achieves NF of 6.3–8.1 dB for frequencies of 75–100 GHz and excellent FOM (figure-of-merit) of 5.97 GHz/mW, one of the best results ever reported for a CMOS LNA with similar operation frequency.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, Y. S., Chen, C. C., & Lee, C. Y. (2016). 7.2 mW CMOS low-noise amplifier with 17.3 dB gain and 7.7 dB NF for 76–77 GHz long-range and 717 ~ 81 GHz short-range automotive radars. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 87(1), 1–9.
Lee, C. J., Lee, H. J., Lee, J. G., Jang, T. H., & Park, C. S. (2015). A W-band CMOS low power wideband low noise amplifier with 22 dB gain and 3 dB bandwidth of 20 GHz. In Asia-Pacific microwave conference (APMC) (vol. 2, pp. 1–3).
Mustapha, A., & Shabra, A. (2017). A 60–90 GHz stagger-tuned low-noise amplifier with 1.2 dBm OP1 dB in 65 nm CMOS. In IEEE international conference on electronics, circuits and systems (ICECS) (pp. 26–29).
Feng, G., Boon, C. C., Meng, F., Yi, X., & Li, C. (2016). An 88.5–110 GHz CMOS low-noise amplifier for millimeter-wave imaging applications. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 26(2), 134–136.
Yu, Y., Liu, H., Wu, Y., & Kang, K. (2017). A 54.4–90 GHz low-noise amplifier in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 52(11), 2892–2904.
Vigilante, M., & Reynaert, P. (2016). A 68.1-to-96.4 GHz variable-gain low-noise amplifier in 28 nm CMOS. In IEEE international solid-state circuits conference (ISSCC) (pp. 360–361).
Lee, S. J., Baek, T. J., Han, M., Choi, S. G., Ko, D. S., & Rhee, J. K. (2012). 94 GHz MMIC single-balanced mixer for FMCW radar sensor application. In Proceedings of the global symposium on millimeter waves (pp. 351–354).
Kim, J., Kornegay, K. T., Alvarado, J., Jr., Lee, C. H., & Laskar, J. (2009). W-band double-balanced down-conversion mixer with Marchand baluns in silicon-germanium technology. Electronics Letters, 45(16), 841–843.
Lin, Y. S., & Nguyen, V. K. (2017). 94 GHz CMOS power amplifiers using miniature dual Y-shaped combiner with RL load. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 64(6), 1285–1298.
Lin, Y. S., Chen, C. Z., Yang, H. Y., Chen, C. C., Lee, J. H., Huang, G. W., et al. (2010). Analysis and design of a CMOS UWB LNA with dual-RLC-branch wideband input matching network. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58(2), 287–296.
Liscidini, A., Brandolini, M., Sanzogni, D., & Castello, R. (2006). A 0.13 μm CMOS front-end, for DCS1800/UMTS/802.11b-g with multiband positive feedback low-noise amplifier. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41(4), 981–989.
Chang, J. F., & Lin, Y. S. (2011). A 0.99 mW 3–10 GHz CG CMOS UWB LNA using T-match input network and self-body-bias technique. IET Electronics Letters, 47(11), 658–659.
Lin, Y. S., Chang, J. F., Liang, H. B., Wang, T., & Lu, S. S. (2007). High-performance transmission-line inductors for 30–60 GHz RFIC applications. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 54(9), 2512–2519.
Edwards, M. L., & Sinsky, J. H. (1992). A new criterion for linear 2-port stability using a single geometrically derived parameter. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 40(12), 2303–2311.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of the R.O.C. under contracts MOST105-2221-E-260-025-MY3 and MOST106-2221-E-260-025-MY2. The authors are very grateful for the support from National Chip Implementation Center (CIC), Taiwan, for chip fabrication, and National Nano-Device Laboratory (NDL), Taiwan, for high-frequency measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YS., Lan, KS. W-band low-noise amplifier using λ/2-spiral-inductor-based positive feedback technique in 90 nm CMOS. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 99, 679–691 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01411-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01411-3