Abstract
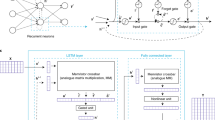
Long-short term memory (LSTM) is a cognitive architecture that aims to mimic the sequence temporal memory processes in human brain. The state and time-dependent based processing of events is essential to enable contextual processing in several applications such as natural language processing, speech recognition and machine translations. There are many different variants of LSTM and almost all of them are software based. The hardware implementation of LSTM remains as an open problem. In this work, we propose a hardware implementation of LSTM system using memristors. Memristor has proved to mimic behavior of a biological synapse and has promising properties such as smaller size and absence of current leakage among others, making it a suitable element for designing LSTM functions. Sigmoid and hyperbolic tangent functions hardware realization can be performed by using a CMOS-memristor threshold logic circuit. These ideas can be extended for a practical application of implementing sequence learning in real-time sensory processing data.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benediktsson, J. A., Swain, P. H., & Ersoy, O. K. (1990). Neural network approaches versus statistical methods in classification of multisource remote sensing data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 28(4), 540–552.
Specht, D. F. (1990). Probabilistic neural networks. Neural Networks, 3(1), 109–118.
Hopfield, D. A. (1982). Diagonal recurrent neural networks for dynamics control. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 79, 2554–2561.
Jordan, M. I. (1997). Serial order: A parallel distributed processing approach. Advances in Psychology, 121, 471–495.
Lipton, Z. C., Berkowitz, J., Elkan, C. (2015). A critical review of recurrent neural networks for sequence learning. //arXiv preprint arXiv:1506.00019.
Hochreiter, S., & Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 9(8), 1735–1780.
Chua, L. (1971). Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 18(5), 507–519.
Strukov, D. B., et al. (2008). The missing memristor found. Nature, 453(7191), 80–83.
Williams, R. S. (2008). How we found the missing memristor. IEEE Spectrum, 45, 12.
Kim, K. H., et al. (2011). A functional hybrid memristor crossbar-array/CMOS system for data storage and neuromorphic applications. Nano Letters, 12(1), 389–395.
Hasan, R., Taha, T. M., & Yakopcic, C. (2017). On-chip training of memristor crossbar based multi-layer neural networks. Microelectronics Journal, 66, 31–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smagulova, K., Krestinskaya, O. & James, A.P. A memristor-based long short term memory circuit. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 95, 467–472 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1180-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1180-y