Abstract
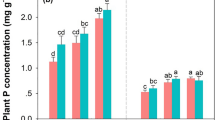
The conversion of native vegetation to tree plantation (afforestation) implies a drastic change in life forms and as a consequence, changes in the microenvironmental conditions, and the quantity and quality of organic matter entering the soil. This could affect soil microbial communities and the processes catalyzed by them. In Patagonia, afforestation with exotic, fast-growing tree species was a common practice but the consequences on the ecosystem remain poorly quantified. The objective was to study the effects of pine afforestation on litter decomposition, soil organic matter, soil microbial activity and associated biogeochemical functions in a semiarid area of NW Patagonia. We hypothesized that afforestation would decrease litter decomposition rate and soil biological activity including net N mineralization, due to changes of environmental conditions and organic matter quality. We measured in situ and potential soil net N mineralization, soil microbial biomass-C, soil enzyme activities (β-glucosidase, acid phosphatase and leucin-aminopeptidase) and litter decomposition rate. We also characterized soil pH, electrical conductivity, extractable P and total C and N. Pine plantations clearly affected decomposition rates of native grass vegetation, which was 10% lower under pine canopy cover, and decreased soil microbial biomass. Acid phosphatase activity and leucin-aminopeptidase activities were also marginally reduced. On the other hand, we did not find any significant effects of pines on soil chemical properties and N transformations after 13 years of plantation. Because effects depend strongly on time, the decrease of soil microbial biomass, acid phosphatase activity and grass decomposition rate (and the trend to lower enzyme activities related to P and N) under pine cover could be an evidence of possible changes on the long-term.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Martínez V, Acosta-Mercado D, Sotomayor-Ramírez D, Cruz-Rodríguez L (2008) Microbial communities and enzymatic activities under different management in semiarid soils. Appl Soil Ecol 38:249–260
AIC (2015) Base de datos de la Autoridad Interjurisdiccional de las Cuencas de los ríos Limay, Neuquén y Negro. http://www.aic.gov.ar
Araujo PI, Austin AT (2015) A shady business: pine afforestation alters the primary controls on litter decomposition along a precipitation gradient in Patagonia, Argentina. J Ecol 103:1408–1420
Austin AT, Vivanco L (2006) Plant litter decomposition in a semi-arid ecosystem controlled by photodegradation. Nature 442:555–558
Austin AT, Méndez MS, Ballaré CL (2016) Photodegradation alleviates the lignin bottleneck for carbon turnover in terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:4392–4397
Bahamonde HA, Peri PL, Martínez Pastur G, Lencinas MV (2009) Variaciones microclimáticas en bosques primarios y bajo uso silvopastoril de Nothofagus antárctica en dos Clases de Sitio en Patagonia Sur. In: Systems PotsNCoS (ed) INTA edn. Misiones, Argentina, pp 289–296
Bahamonde HA, Peri PL, Alvarez R, Barneix A, Moretto A, Martínez Pastur G (2012) Litter decomposition and nutrients dynamics in Nothofagus antarctica forests under silvopastoral use in Southern Patagonia. Agrofor Syst 84:345–360
Bahamonde HA, Peri PL, Alvarez R, Barneix A, Moretto A, Martínez Pastur G (2013) Silvopastoral use of Nothofagus antarctica in Southern Patagonian forests, influence over net nitrogen soil mineralization. Agrofor Syst 87:259–271
Bastida F, Barbera GG, García C, Hernández T (2008) Influence of orientation, vegetation and season on soil microbial and biochemical characteristics under semiarid conditions. Appl Soil Ecol 38:62–70
Berthrong ST, Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB (2009a) A global meta-analysis of soil exchangeable cations, pH, carbon, and nitrogen with afforestation. Ecol Appl 19:2228–2241
Berthrong ST, Schadt CW, Piñeiro G, Jackson RB (2009b) Afforestation alters the composition of functional genes in soil and biogeochemical processes in South american grasslands. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6240–6248
Berthrong ST, Piñeiro G, Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB (2012) Soil C and N changes with afforestation of grasslands across gradients of precipitation and plantation age. Ecol Appl 22:76–86
Bertiller MB, Mazzarino MJ, Carrera AL, Diehl P, Satti P, Gobbi M, Sain CL (2006) Leaf strategies and soil N across a regional humidity gradient in Patagonia. Oecologia 148:612–624
Broquen P, Girardin JL, Frugoni MC (1995) Evaluación de algunas propiedades de suelos derivados de cenizas volcánicas asociadas con forestaciones de coníferas exóticas (S.O. de la provincia de Neuquén-R. Argentina). Bosque 16:69–79
Broquen P, Falbo G, Candan F, Pellerini V, Girardin JL (2004) Penetration resistance of an humic vitrixerand and a vitrandic haploxeroll with different uses. Agro Sur 32:16–27
Buduba CG (2006) Modificaciones en el pH y contenido de materia orgánica en suelos del ecotono estepa/bosque andino patagónico por implantación de pino ponderosa. Faculty of Agronomy, University of Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires
Caballé G, Fernández ME, Gyenge J, Lantschner V, Rusch V, Letourneau F, Borrelli L (2016) Silvopastoral systems based on natural grassland and ponderosa pine in NW Patagonia (Argentina). In: Peri PL, Dube F, Varella A (eds) Silvopastoral systems in Southern South America (Argentina, Brazil and Chile). Springer, Brazil, pp 89–116
Carrera AL, Bertiller MB, Sain CL, Mazzarino MJ (2003) Relationship between plant nitrogen conservation strategies and the dynamics of soil nitrogen in the arid Patagonian Monte, Argentina. Plant Soil 255:595–604
Chauchard L, Frugoni MC, Nowak C (2016) Manejo de plantaciones forestales en Patagonia Andina: manual de buenas prácticas. Ministerio de Agroindustria
Chen CR, Condron LM, Xu ZH (2008) Impacts of grassland afforestation with coniferous trees on soil phosphorus dynamics and associated microbial processes: a review. For Ecol Manage 255:396–409
Cornwell WK, Cornelissen JHC, Amatangelo K, Dorrepaal E, Eviner VTE, Godoy O, Hobbie SE, Hoorens B, Kurokawa H, Pérez-Harguindeguy N, Quested HM, Santiago LS, Wardle DA, Wright IJ, Aerts R, Allison SD, van Bodegom P, Brovkin V, Chatain A, Callaghan TV, Díaz S, Garnier E, Gurvich DE, Kazakou E, Klein JA, Read J, Soudzilovskaia NA, Vaieretti MV, Westoby M (2008) Plant species traits are the predominant control on litter decomposition rates within biomes worldwide. Ecol Lett 11:1065–1171
Dube F, Thevathasan NV, Stolpe NB, Zagal E, Gordon AM, Espinosa M, Sáez K (2013) Selected carbon fluxes in Pinus ponderosa-based silvopastoral systems, exotic plantations and natural pastures on volcanic soils in the Chilean Patagonia. Agrofor Syst 87:525–542
Eclesia R, Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB, Biganzoli F, Piñeiro G (2012) Shifts in soil organic carbon for plantation and pasture establishment in native forests and grasslands of South America. Glob Change Biol 18:3237–3251
FAO (2010) Global Forest Resources Assessment 2010: main report. FAO
Gillson L, Hoffman M (2007) Rangeland ecology in a changing world. Science
Grünzweig JM, Gelfand I, Fried Y, Yakir D (2007) Biogeochemical factors contributing to enhanced carbon storage following afforestation of a semi-arid shrubland. Biogeosciences 4:891–904
Guo LB, Gifford RM (2002) Soil carbon stocks and land use change: a meta analysis. Glob Change Biol 8:345–360
Gyenge J, Fernández ME, Sarasola M, Schlichter T (2011) Stand density and drought interaction on water relations of Nothofagus antarctica: contribution of forest management to climate change adaptability. Trees 25:1111–1120
Hess LJT, Austin AT (2017) Pine afforestation alters rhizosphere effects and soil nutrient turnover across a precipitation gradient in Patagonia, Argentina. Plant and Soil
Jandl R, Lindner M, Vesterdal L, Bauwens B, Baritz R, Hagedorn F, Johnson DW, Minkkinen K, Byrne KA (2007) How strongly can forest management influence soil carbon sequestration? Geoderma 137:253–268
Jose S, Walter D, Mohan Kumar B (2017) Ecological considerations in sustainable silvopasture design and management. Agrofor Syst
Karki U, Goodman MS (2015) Microclimatic differences between mature loblolly-pine silvopasture and open-pasture. Agrofor Syst 89:319–325
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen-inorganic forms. In: Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 2. American society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 643–698
Kuo S (1996) Phosphorus. In: Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabatabai MA, Johnston CT, Sumner ME (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 3 chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 869–919
Laclau P (2003) Biomass and carbon sequestration of ponderosa pine plantations and native cypress forests in northwest Patagonia. For Ecol Manage 180:317–333
Laganière J, Angers DA, Paré D (2010) Carbon accumulation in agricultural soils after afforestation: a meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 16:439–453
Li D, Niu S, Luo Y (2012) Global patterns of the dynamics of soil carbon and nitrogen stocks following afforestation: a meta-analysis. New Phytol 195:172–181
Li M, Zhou X, Zhang Q, Cheng X (2014) Consequences of afforestation for soil nitrogen dynamics in central China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 183:40–46
Macdonald CA, Thomas N, Robinson L, Tate KR, Ross DJ, Dando J, Singh BK (2009) Physiological, biochemical and molecular responses of the soil microbial community after afforestation of pastures with Pinus radiata. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1642–1651
Mazzarino MJ, Bertiller MB, Sain C, Satti P, Coronato F (1998) Soil nitrogen dynamics in northeastern Patagonia steppe under different precipitation regimes. Plant Soil 202:125–131
Miltner A, Bombach P, Schmidt-Brücken B, Kästner M (2012) SOM genesis: microbial biomass as a significant source. Biogeochemistry 111:41–55
Mosquera-Losada MR, McAdam J, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A (2005) Silvopastoralism declaration. In: Mosquera-Losada MR, McAdam J, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A (eds) Silvopastoralism and sustainable land management. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, p 418
Ndiaye EL, Sandeno JM, McGrath D, Dick RP (2000) Integrative biological indicators for detecting change in soil quality. Am J Altern Agric 15:26–36
Nosetto MD, Jobbágy EG, Paruelo JM (2006) Carbon sequestration in semi-arid rangelands: comparison of Pinus ponderosa plantations and grazing exclusion in NW Patagonia. J Arid Environ 67:142–156
Nunes JS, Araujo ASF, Nunes LAPL, Lima LM, Carneiro RFV, Salviano AAC, Tsai SM (2012) Impact of land degradation on soil microbial biomass and activity in Northeast Brazil. Pedosphere 22:88–95
Panettieri M, Knicker H, Murillo JM, Madejón E, Hatcher PG (2014) Soil organic matter degradation in an agricultural chronosequence under different tillage regimes evaluated by organic matter pools, enzymatic activities and CPMAS 13C NMR. Soil Biol Biochem 78:170–181
Parfitt RL, Ross DJ (2011) Long-term effects of afforestation withPinus radiata on soil carbon, nitrogen, and pH: a case study. Soil Res 49:494–503
Paul KI, Polglase PJ, Richards GP (2003) Sensitivity analysis of predicted change in soil carbon following afforestation. Ecol Model 164:137–152
Peichl N, Leava NA, Kiely G (2012) Above- and belowground ecosystem biomass, carbon and nitrogen allocation in recently afforested grassland and adjacent intensively managed grassland. Plant Soil 350:281–296
Peri PL, Bahamonde H, Christiansen R (2015) Soil respiration in Patagonian semiarid grasslands under contrasting environmental and use conditions. J Arid Environ 119:1–8
Plassard C, Dell B (2010) Phosphorus nutrition of mycorrhizal trees. Tree Physiol 30:1129–1139
Prescott CE, Blevins LL, Staley CL (2000) Effects of clear-cutting on decomposition rates of litter and forest floor in forests of British Columbia. Can J For Res 30:1751–1757
Rilling MC, Maestre FT, Lamit LJ (2003) Microsite difference in fungal hyphal length, glomalin, and soil aggregate stability in semiarid Mediterranean steppes. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1257–1260
Rutigliano FA, Ascoli RD, Virzo de Santo A (2004) Soil microbial metabolism and nutrient status in a Mediterranean area as affected by plant cover. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1719–1729
Seneviratne G (2000) Litter quality and nitrogen release in tropical agriculture: a synthesis. Biol Fertil Soils 31:60–64
StatSoft (1984–2003) Statistica release 6.1. StatSoft, Inc., Tulsa
Swift MJ, Heal OW, Anderson JM (1979) Decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. University of California Press, Berkeley
Udawatta RP, Kremer RJ, Garrett HE, Anderson SH (2009) Soil enzyme activities and physical properties in a watershed managed under agroforestry and row-crop systems. Agr Ecosyst Environ 131:98–104
Vallejo VE, Roldan F, Dick RP (2010) Soil enzymatic activities and microbial biomass in an integrated agroforestry chronosequence compared to monoculture and a native forest of Colombia. Biol Fertil Soils 46:577–587
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Zeller V, Bahn M, Aichner M, Tappeiner U (2000) Impact of land-use change on nitrogen mineralization in subalpine grasslands in the Southern Alps. Biol Fertil Soils 31:441–448
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Proyecto de Manejo Sustentable de Recursos Naturales Componentes II: “Plantaciones forestales Sustentables” BIRF No 7520, Programa Silvopastoril Módulos Experimentales con Fines Demostrativos. We thank the Estancia Los Peucos for study site facilitation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez-Polo, M., Bahamonde, H.A., Peri, P.L. et al. Soil microbial processes in a pine silvopastoral system in NW Patagonia. Agroforest Syst 93, 255–266 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-018-0210-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-018-0210-1