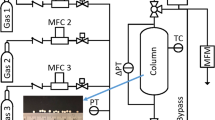
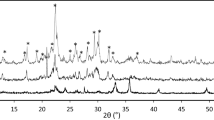
Abstract
Reliable adsorption equilibrium data and theoretical models for their accurate representation are crucial to the design of any adsorption based separation. The adsorption equilibria of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrogen are particularly important to the development of industrial pressure swing adsorption processes intended to separate CO2 and N2 from a variety of conventional as well as unconventional natural gas sources. The adsorption equilibrium capacities of gas mixtures needed for process design and simulation are often predicted from pure component adsorption data using various models including the ideal adsorbed solution theory (IAST). In this work, we present the adsorption equilibrium capacity data for a ternary gas mixture of CO2, CH4 and N2 as well as pure and binary gas mixtures of the same components on a commercial zeolite 13X, measured at temperatures of (273, 303 and 333 K) and pressures from (25 to 900 kPa) using a dynamic column breakthrough (DCB) apparatus. Although previous adsorption studies have reported the adsorption equilibria of pure and to a lesser degree binary gas mixtures on zeolite 13X, no experimental data are available in the literature for a ternary gas mixture of CO2, CH4 and N2 on zeolite 13X APG-III, a promising adsorbent for carbon capture and natural gas separation. The measured pure component adsorption capacities were regressed to a Toth isotherm model and the obtained Toth parameters were used to implement an IAST model for binary and ternary adsorption predictions. The IAST predictions of mixture gas adsorption represented the binary and ternary adsorption equilibria well with their corresponding maximum deviations being 0.055 and 0.3 mmol/g, respectively. This indicates the IAST can be applied successfully to these adsorption systems even though they involve molecules with different adsorption affinity and adsorbents with heterogeneous surfaces.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavenati, S., Grande, C.A., Rodrigues, A.E.: Adsorption equilibrium of methane, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen on zeolite 13X at high pressures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 49(4), 1095–1101 (2004)
Cavenati, S., Grande, C.A., Rodrigues, A.E.: Separation of mixtures by layered pressure swing adsorption for upgrade of natural gas. Chem. Eng. Sci. 61(12), 3893–3906 (2006)
Delgado, J.A., et al.: Adsorption equilibrium of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrogen onto Na- and H-mordenite at high pressures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 48(3), 223–228 (2006)
Delgado, J.A., et al.: Carbon dioxide/methane separation by adsorption on sepiolite. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 16(3), 235–243 (2007)
Hefti, M., et al.: Adsorption equilibrium of binary mixtures of carbon dioxide and nitrogen on zeolites ZSM-5 and 13X. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 215, 215–228 (2015)
Hofman, P.S., et al.: A dynamic column breakthrough apparatus for adsorption capacity measurements with quantitative uncertainties. Adsorption 18(3–4), 251–263 (2012)
Kidnay, A.J., Parrish, W.R., McCartney, D.G.: Fundamentals of Natural Gas Processing, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Bosa Roca (2011)
Kumar, K.V., et al.: A site energy distribution function from Toth isotherm for adsorption of gases on heterogeneous surfaces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13(13), 5753–5759 (2011)
McEwen, J., Hayman, J.-D., Yazaydin, A.O.: A comparative study of CO2, CH4 and N2 adsorption in ZIF-8, Zeolite-13X and BPL activated carbon. Chem. Phys. 412, 72–76 (2013)
Mofarahi, M., Shokroo, E.J.: Comparison of two pressure swing adsorption processes for air separation Using Zeolite 5A and Zeolite 13X. Petroleum Coal 55(3), 216–225 (2013)
Mulgundmath, V.P., et al.: Adsorption and separation of CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 by 13X zeolite. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 90(3), 730–738 (2012)
Myers, A.L., Monson, P.A.: Physical adsorption of gases: the case for absolute adsorption as the basis for thermodynamic analysis. Adsorption 20(4), 591–622 (2014)
Myers, A.L., Prausnitz, J.M.: Thermodynamics of mixed-gas adsorption. AIChE J. 11(1), 121–127 (1965)
NIST, REFPROP-Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties, Version 9.1. National Institute of Standards and Technology, USA (2013)
Rao, M.B., Sircar, S.: Thermodynamic consistency for binary gas adsorption equilibria. Langmuir 15(21), 7258–7267 (1999)
Rufford, T.E., et al.: The removal of CO2 and N2 from natural gas: a review of conventional and emerging process technologies. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 94–95(0), 123–154 (2012)
Rufford, T.E., et al.: Adsorption equilibria and kinetics of methane + nitrogen mixtures on the activated carbon Norit RB3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52(39), 14270–14281 (2013)
Saleman, T.L.H., et al.: Capacity and kinetic measurements of methane and nitrogen adsorption on H+-mordenite at 243–303 K and pressures to 900 kPa using a dynamic column breakthrough apparatus. Adsorption 19(6), 1165–1180 (2013)
Saleman, T.L.H., et al.: A robust dynamic column breakthrough technique for high-pressure measurements of adsorption equilibria and kinetics. Adsorption 23(5), 671–684 (2017)
Sudibandriyo, M., et al.: Adsorption of methane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and their binary mixtures on dry activated carbon at 318.2 K and pressures up to 13.6 MPa. Langmuir 19(13), 5323–5331 (2003)
Talu, O.: Net adsorption of gas/vapor mixtures in microporous solids. J Phys. Chem. C 117(25), 13059–13071 (2013)
Thomas, W.J., Crittenden, B.: Adsorption Technology & Design. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1998)
Valenzuela, D.P., Myers, A.L.: Adsorption Equilibrium Data Handbook. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1989)
Walton, K.S., Sholl, D.S.: Predicting multicomponent adsorption: 50 years of the ideal adsorbed solution theory. AIChE J. 61(9), 2757–2762 (2015)
Wang, L., et al., CO2 capture from flue gas by two successive VPSA units using 13XAPG. Adsorption 8, 445 (2012)
Wang, L., et al.: Experimental and modeling investigation on post-combustion carbon dioxide capture using zeolite 13X-APG by hybrid VTSA process. Chem. Eng. J. 197, 151–161 (2012)
Watson, G., et al.: Equilibrium adsorption measurements of pure nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and methane on a carbon molecular sieve at cryogenic temperatures and high pressures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 54(9), 2701–2707 (2009)
Watson, G.C., et al.: Volumetric adsorption measurements of N2, CO2, CH4, and a CO2 + CH4 mixture on a natural chabazite from (5 to 3000) kPa. J. Chem. Eng. Data 57(1), 93–101 (2011)
Xiao, G., et al.: CO2 capture at elevated temperatures by cyclic adsorption processes. RSC Adv. 2(12), 5291–5297 (2012)
Xiao, G., et al.: Adsorption equilibria and kinetics of CH4 and N2 on commercial zeolites and carbons. Adsorption 23(1), 131–147 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avijegon, G., Xiao, G., Li, G. et al. Binary and ternary adsorption equilibria for CO2/CH4/N2 mixtures on Zeolite 13X beads from 273 to 333 K and pressures to 900 kPa. Adsorption 24, 381–392 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-018-9952-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-018-9952-3