Abstract
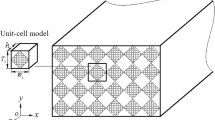
In many engineering applications, 3D braided composites are designed for primary loading-bearing structures, and they are frequently subjected to multi-axial loading conditions during service. In this paper, a unit-cell based finite element model is developed for assessment of mechanical behavior of 3D braided composites under different biaxial tension loadings. To predict the damage initiation and evolution of braiding yarns and matrix in the unit-cell, we thus propose an anisotropic damage model based on Murakami damage theory in conjunction with Hashin failure criteria and maximum stress criteria. To attain exact stress ratio, force loading mode of periodic boundary conditions which never been attempted before is first executed to the unit-cell model to apply the biaxial tension loadings. The biaxial mechanical behaviors, such as the stress distribution, tensile modulus and tensile strength are analyzed and discussed. The damage development of 3D braided composites under typical biaxial tension loadings is simulated and the damage mechanisms are revealed in the simulation process. The present study generally provides a new reference to the meso-scale finite element analysis (FEA) of multi-axial mechanical behavior of other textile composites.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai, D.A., Zhou, G.M., Wang, X.P., Li, C., Deng, J.: Experimental investigation on mechanical properties of unidirectional and woven fabric glass/epoxy composites under off-axis tensile loading. Polym. Test. 58, 142–152 (2017)
Quaresimin, M., Susmel, L., Talreja, R.: Fatigue behaviour and life assessment of composite laminates under multiaxial loadings. Int. J. Fatigue. 32(1), 2–16 (2010)
Makris, A., Ramault, C., Van Hemelrijck, D., Zarouchas, D., Lamkanfi, E., Van Paepegem, W.: An investigation of the mechanical behavior of carbon epoxy cross ply cruciform specimens under biaxial loading. Polym. Compos. 31(9), 1554–1561 (2010)
Chen, Z., Fang, G.D., Xie, J.B., Liang, J.: Experiment investigation on biaxial tensile strength of 3D in-plane braided C/C composites. J. Solid. Rocket. Technol. 38(2), 267–272 (2015)
Li, L.Y., Meng, H.S., Wang, G.Y., Zhang, T., Xu, C.H., Ke, H.J.: Mechanical behaviors of the composites reinforced by non-crimp unidirectional carbon fiber fabrics under biaxial compression loading. J. Harb. Inst. Technol. 47(10), 20–24 (2015)
Cichosz, J., Wehrkamp-Richter, T., Koerber, H., Hinterholzl, R., Camanho, P.P.: Failure and damage characterization of biaxial braided composites under multiaxial stress states. Compos. Part A. 90, 748–759 (2016)
Rashedi, A., Sridhar, I., Tseng, K.J.: Fracture characterization of glass fiber composite laminate under experimental biaxial loading. Compos. Struct. 138, 17–29 (2016)
Cai, D.A., Tang, J., Zhou, G.M., Wang, X.P., Li, C., Silberschmidt, V.V.: Failure analysis of plain woven glass/epoxy laminates: comparison of off-axis and biaxial tension loadings. Polym. Test. 60, 307–320 (2017)
Correa, E., Barroso, A., Perez, M.D., Paris, F.: Design for a cruciform coupon used for tensile biaxial transverse tests on composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 145, 138–148 (2017)
Wehrkamp-Richter, T., Hinterholzl, R., Pinho, S.T.: Damage and failure of triaxial braided composites under multi-axial stress states. Compos. Sci. Technol. 150, 32–44 (2017)
Zhou, Y., Lu, Z.X., Yang, Z.Y.: Progressive damage analysis and strength prediction of 2D plain weave composites. Compos. Part B. 47, 220–229 (2013)
Lu, Z.X., Zhou, Y., Yang, Z.Y., Liu, Q.: Multi-scale finite element analysis of 2.5D woven fabric composites under on-axis and off-axis tension. Comput. Mater. Sci. 79, 485–494 (2013)
Zhang, D.T., Sun, Y., Wang, X.M., Chen, L.: Meso-scale finite element analyses of three-dimensional five-directional braided composites subjected to uniaxial and biaxial loading. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 34(24), 1989–2005 (2015)
Wang, B.L., Fang, G.D., Liang, J., Wang, Z.Q.: Failure locus of 3D four-directional braided composites under biaxial loading. Appl. Compos. Mater. 19(3–4), 529–544 (2012)
Fang, G.D., Liang, J., Wang, B.L.: Progressive damage and nonlinear analysis of 3D four-directional braided composites under unidirectional tension. Compos. Struct. 89, 126–133 (2009)
Lu, Z.X., Xia, B., Yang, Z.Y.: Investigation on the tensile properties of three dimensional full five directional braided composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 77, 445–455 (2013)
Zhang, C., Li, N., Wang, W.Z., Binienda, W.W., Fang, H.B.: Progressive damage simulation of triaxially braided composite using a 3D meso-scale finite element model. Compos. Struct. 125, 104–116 (2015)
Kang, H.R., Shan, Z.D., Zang, Y., Liu, F.: Progressive damage analysis and strength properties of fiber-bar composites reinforced by three-dimensional weaving under uniaxial tension. Compos. Struct. 141, 264–281 (2016)
Zhang, C., Curiel-Sosa, J.L., Bui, T.Q.: A novel interface constitutive model for prediction of stiffness and strength in 3D braided composites. Compos. Struct. 163, 32–43 (2017)
Wang, R.Q., Zhang, L., Hu, D.Y., et al.: Progressive damage simulation in 3D four-directional braided composites considering the jamming-action-induced yarn deformation. Compos. Struct. 178, 330–340 (2017)
Zhang, C., Mao, C.J., Zhou, Y.X.: Meso-scale damage simulation of 3D braided composites under quasi-static axial tension. Appl. Compos. Mater. 24(5), 1179–1199 (2017)
Hashin, Z.: Failure criteria for unidirectional fiber composite. J. Appl. Mech. 47, 329–334 (1980)
Lapczyk, I., Hurtado, J.A.: Progressive damage modeling in fiber reinforced materials. Compos. Part A. 38(11), 2333–2341 (2007)
Murakami, S.: Mechanical modeling of material damage. ASME. J. Appl. Mech. 55, 280–286 (1988)
Zako, M., Uetsuji, Y., Kurashiki, T.: Finite element analysis of damaged woven fabric composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 63(3–4), 507–516 (2003)
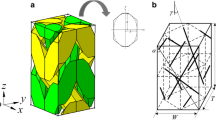
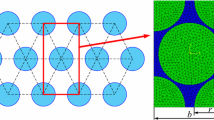
Chen, L., Tao, X.M., Choy, C.L.: On the microstructure of three-dimensional braided preforms. Compos. Sci. Technol. 59(3), 391–404 (1999)
Xu, K., Xu, X.: On the microstructure model of four-step 3D rectangular braided composites. Acta. Mater. Compos. Sin. 23(5), 154–160 (2006)
Xia, Z.H., Zhang, Y.F., Ellyin, F.: A unified periodical boundary conditions for representative volume elements of composites and applications. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40(8), 1907–1921 (2003)
Li, S.G.: Boundary conditions for unit cells from periodic microstructures and their implications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 68(9), 1962–1974 (2008)
Zhang, C., Curiel-Sosa, J.L., Bui, T.Q.: Comparison of periodic mesh and free mesh on the mechanical properties prediction of 3D braided composites. Compos. Struct. 159, 667–676 (2017)
Chamis, C.C.: Mechanics of composites materials: past, present and future. J. Compos. Technol. Res. 11(1), 3–14 (1989)
Wang, X.F., Wang, X.W., Zhou, G.M., Zhou, C.W.: Multi-scale analyses of 3D woven composite based on periodicity boundary conditions. J. Compos. Mater. 41, 1773–1788 (2007)
Xu, K., Xu, X.: Finite element analysis of mechanical properties of 3D five-directional braided composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 487(1–2), 499–509 (2008)
Zhang, C., Xu, X.W.: Finite element analysis of 3D braided composites based on three unit-cells models. Compos. Struct. 98, 130–142 (2013)
Zhang, D.T., Chen, L., Wang, Y.J., et al.: Stress field distribution of warp-reinforced 2.5D woven composites using an idealized meso-scale voxel-based model. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 6814–6836 (2017)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (17KJB130004), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20150479, BK20160786), Jiangsu Government Scholarship for Overseas Studies and Jiangsu University Study-abroad Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Curiel-Sosa, J.L. & Bui, T.Q. Meso-Scale Finite Element Analysis of Mechanical Behavior of 3D Braided Composites Subjected to Biaxial Tension Loadings. Appl Compos Mater 26, 139–157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-018-9686-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-018-9686-0