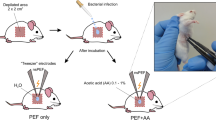
Abstract
Irreversible electroporation of cell membrane with pulsed electric fields is an emerging physical method for disinfection that aims to reduce the doses and volumes of used antibiotics for wound healing. Here we report on the design of the IGBT-based pulsed electric field generator that enabled eradication of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 on the gel. Using a concentric electric configuration we determined that the lower threshold of the electric field required to kill P. aeruginosa PAO1 was 89.28 ± 12.89 V mm−1, when 200 square pulses of 300 µs duration are delivered at 3 Hz. These parameters disinfected 38.14 ± 0.79 mm2 area around the single needle electrode. This study provides a step towards the design of equipment required for multidrug-resistant bacteria disinfection in patients with pulsed electric fields.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram, F., J. P. P. M. Smelt, R. Bos, and P. C. Wouters. Modelling and optimization of inactivation of Lactobacillus plantarum by pulsed electric field treatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.01869.x.
Alneami, A. Q., E. G. Khalil, R. A. Mohsien, and A. F. Albeldawi. Effect of electrical current stimulation on Pseudomonas Aeruginosa growth. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1003:012112, 2018.
Arena, C. B., M. B. Sano, J. H. Rossmeisl, J. L. Caldwell, P. A. Garcia, M. Rylander, and R. V. Davalos. High-frequency irreversible electroporation (H-FIRE) for non-thermal ablation without muscle contraction. Biomed. Eng. 10:102, 2011.
Bae, S., A. Kwasinski, M. M. Flynn, and R. E. Hebner. High-power pulse generator with flexible output pattern. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25:1675–1684, 2010.
Blumrosen, G., A. Abazari, A. Golberg, M. L. Yarmush, and M. Toner. Single-step electrical field strength screening to determine electroporation induced transmembrane transport parameters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2041–2049:2016, 1858.
Bowler, P. G., B. I. Duerden, and D. G. Armstrong. Wound microbiology and associated approaches to wound management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 14(2):244–269, 2001.
Cemazar, M., G. Sersa, W. Frey, D. Miklavcic, and J. Teissié. Recommendations and requirements for reporting on applications of electric pulse delivery for electroporation of biological samples. Bioelectrochemistry 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2018.03.005.
Church, D., S. Elsayed, O. Reid, B. Winston, and R. Lindsay. Burn wound infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 19:403–434, 2006.
Corovic, S., A. Zupanic, and D. Miklavcic. Numerical modeling and optimization of electric field distribution in subcutaneous tumor treated with electrochemotherapy using needle electrodes. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1109/tps.2008.2000996.
Dancer, S. J. The role of environmental cleaning in the control of hospital-acquired infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 73:378–385, 2009.
Davalos, R. V., L. M. Mir, and B. Rubinsky. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33:223–231, 2005.
Del Pozo, J. L., M. S. Rouse, J. N. Mandrekar, J. M. Steckelberg, and R. Patel. The electricidal effect: reduction of Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas biofilms by prolonged exposure to low-intensity electrical current. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00680-08.
Fernand, F., L. Rubinsky, A. Golberg, and B. Rubinsky. Variable electric fields for high throughput electroporation protocol design in curvilinear coordinates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109:2168–2171, 2012.
Giladi, M., Y. Porat, A. Blatt, E. Shmueli, Y. Wasserman, E. D. Kirson, and Y. Palti. Microbial growth inhibition by alternating electric fields in mice with Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2010. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.01841-09.
Golberg, A., G. F. Broelsch, D. Vecchio, S. Khan, M. R. Hamblin, W. G. Austen, R. L. Sheridan, and M. L. Yarmush. Eradication of multidrug-resistant A. baumannii in burn wounds by antiseptic pulsed electric field. Technology 2:153–160, 2014.
Golberg, A., G. F. Broelsch, D. Vecchio, S. Khan, M. R. M. R. Hamblin, W. G. Austen, R. L. Sheridan, and M. L. Yarmush. Pulsed electric fields for burn wound disinfection in a murine model. J. Burn Care Res. 36(1):7–13, 2014.
Golberg, A., J. Fischer, and B. Rubinsky. The use of irreversible electroporation in food preservation. Berlin: Springer, 2010.
Golberg, A., S. Khan, V. Belov, K. P. Quinn, H. Albadawi, G. Felix Broelsch, M. T. Watkins, I. Georgakoudi, M. Papisov, M. C. Mihm, W. G. Austen, and M. L. Yarmush. Skin rejuvenation with non-invasive pulsed electric fields. Sci. Rep. 5:10187, 2015.
Golberg, A., M. Villiger, G. Felix Broelsch, K. P. Quinn, H. Albadawi, S. Khan, M. T. Watkins, I. Georgakoudi, W. G. Austen, M. Bei, B. E. Bouma, M. C. Mihm, and M. L. Yarmush. Skin regeneration with all accessory organs following ablation with irreversible electroporation. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 1:100, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2374.
Golberg, A., M. Villiger, S. Khan, K. P. Quinn, W. C. Y. Lo, B. E. Bouma, M. C. Mihm, W. G. Austen, and M. L. Yarmush. Preventing scars after injury with partial irreversible electroporation. J. Invest. Dermatol. 136(11):2297–2304, 2016.
Gusbeth, C., W. Frey, H. Volkmann, T. Schwartz, and H. Bluhm. Pulsed electric field treatment for bacteria reduction and its impact on hospital wastewater. Chemosphere 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.066.
Hashimoto, M. C. E., R. A. Prates, I. T. Kato, S. C. Núñez, L. C. Courrol, and M. S. Ribeiro. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced infection. An in vivo study. Photochem. Photobiol. 88:590–595, 2012.
Ho, S. Y., G. S. Mittal, J. D. Cross, and M. W. Griffiths. Inactivation of Pseudomonas fluorescens by high voltage electric pulses. J. Food Sci. 60:1337–1340, 1995.
Hofmann, G. A. Instrumentation and electrodes for in vivo electroporation. In: Electrochemotherapy, Electrogenetherapy, and Transdermal Drug Delivery, edited by R. Heller, and R. Gilbert. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press, 2000, pp. 37–61. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-080-2:37.
Kaplan, J. B., C. Ragunath, K. Velliyagounder, D. H. Fine, and N. Ramasubbu. Enzymatic detachment of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:2633–2636, 2004.
Korem, M., N. S. Goldberg, A. Cahan, M. J. Cohen, I. Nissenbaum, and A. E. Moses. Clinically applicable irreversible electroporation for eradication of micro-organisms. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 67:15–21, 2018.
Kotnik, T., P. Kramar, G. Pucihar, D. Miklavčič, and M. Tarek. Cell membrane electroporation—part 1: the phenomenon. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 28:14–23, 2012.
Krieg, A. M., A. K. Yi, S. Matson, T. J. Waldschmidt, G. A. Bishop, R. Teasdale, G. A. Koretzky, and D. M. Klinman. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation. Nature 1995. https://doi.org/10.1038/374546a0.
Krishnaveni, S., R. Subhashini, and V. Rajini. Inactivation of bacteria suspended in water by using high frequency unipolar pulse voltage. J. Food Process Eng. 40:e12574, 2017.
Maor, E., A. Ivorra, and B. Rubinsky. Non thermal irreversible electroporation: novel technology for vascular smooth muscle cells ablation. PLoS ONE 2009. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004757.
Marty, M., G. Sersa, J. R. Garbay, J. Gehl, C. G. Collins, M. Snoj, V. Billard, P. F. Geertsen, J. O. Larkin, D. Miklavcic, I. Pavlovic, S. M. Paulin-Kosir, M. Cemazar, N. Morsli, D. M. Soden, Z. Rudolf, C. Robert, G. C. O’Sullivan, and L. M. Mir. Electrochemotherapy—an easy, highly effective and safe treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases: Results of ESOPE (European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy) Study. Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 4:3–13, 2006.
Neher, M. D., S. Weckbach, M. A. Flierl, M. S. Huber-Lang, and P. F. Stahel. Molecular mechanisms of inflammation and tissue injury after major trauma-is complement the “bad guy”? J. Biomed. Sci. 18:90, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-18-90.
Neumann, E., and S. Kakorin. Membrane electroporation: chemical thermodynamics and flux kinetics revisited and refined. Eur. Biophys. J. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-018-1305-3.
Nolff, M. C., S. Reese, M. Fehr, R. Dening, and A. Meyer-Lindenberg. Assessment of wound bio-burden and prevalence of multi-drug resistant bacteria during open wound management. J. Small Anim. Pract. 57:255–259, 2016.
Nomura, M., Y. Nakata, T. Inoue, A. Uzawa, S. Itamura, K. Nerome, M. Akashi, and G. Suzuki. In vivo induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for a single epitope introduced into an unrelated molecule. J. Immunol. Methods 193:41–49, 1996.
Novickij, V., A. Grainys, J. Novickij, S. Tolvaisiene, and S. Markovskaja. Compact electro-permeabilization system for controlled treatment of biological cells and cell medium conductivity change measurement. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2014. https://doi.org/10.2478/msr-2014-0038.
Nuccitelli, R., U. Pliquett, X. Chen, W. Ford, R. James Swanson, S. J. Beebe, J. F. Kolb, and K. H. Schoenbach. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields cause melanomas to self-destruct. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.02.181.
Okino, M., and H. Mohri. Effects of a high-voltage electrical impulse and an anticancer drug on in vivo growing tumors. Jpn. J. Cancer Res 72:1319–1321, 1987.
Pakhomova, O. N., B. W. Gregory, V. A. Khorokhorina, A. M. Bowman, S. Xiao, and A. G. Pakhomov. Electroporation-induced electrosensitization. PLoS ONE 2011. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017100.
Perez-Roa, R. E., D. T. Tompkins, M. Paulose, C. A. Grimes, M. A. Anderson, and D. R. Noguera. Effects of localised, low-voltage pulsed electric fields on the development and inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Biofouling 2006. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010601053541.
Pirac, E., M. Reberšek, and D. Miklavčič. Dosimetry in electroporation-based technologies and treatments. In: Dosimetry in Bioelectromagnetic, edited by M. S. Markov. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017, pp. 233–268.
Puc, M., S. Čorović, K. Flisar, M. Petkovšek, J. Nastran, and D. Miklavčič. Techniques of signal generation required for electropermeabilization. Survey of electropermeabilization devices. Bioelectrochemistry 2004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2004.04.001.
Pucihar, G., J. Krmelj, M. Reberšek, T. B. Napotnik, and D. Miklavčič. Equivalent pulse parameters for electroporation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58:3279–3288, 2011.
Pucihar, G., L. M. Mir, and D. Miklavčič. The effect of pulse repetition frequency on the uptake into electropermeabilized cells in vitro with possible applications in electrochemotherapy. Bioelectrochemistry 2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1567-5394(02)00116-0.
Raso, J., I. Alvarez, S. Condón, and F. J. Sala. Predicting inactivation of Salmonella senftenberg by pulsed electric fields. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2000. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1466-8564(99)00005-3.
Raso, J., W. Frey, G. Ferrari, G. Pataro, D. Knorr, J. Teissie, and D. Miklavčič. Recommendations guidelines on the key information to be reported in studies of application of PEF technology in food and biotechnological processes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2016.08.003.
Reberšek, M., and D. Miklavčič. Concepts of electroporation pulse generation and overview of electric pulse generators for cell and tissue electroporation. Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis, pp. 343–360, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1201/ebk1439819067-21.
Reberšek, M., D. Miklavčič, C. Bertacchini, and M. Sack. Cell membrane electroporation—part 3: the equipment. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 30:8–18, 2014.
Robins, E. V. Immunosuppression of the burned patient. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 1:767–774, 1989.
Rubinsky, L., B. Patrick, P. Mikus, and B. Rubinsky. Germicide wound pad with active, in situ, electrolytically produced hypochlorous acid. Biomed. Microdevices 18:1–10, 2016.
Sack, M., M. Hochberg, and G. Mueller. Synchronized switching and active clamping of IGBT switches in a simple marx generator. In PCIM Europe 2016; International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nuremberg, Germany, 2016.
Sack, M., J. Ruf, M. Hochberg, D. Herzog, and G. Mueller. A device for combined thermal and pulsed electric field treatment of food. In 2017 International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment (OPTIM) & 2017 Intl Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines and Power Electronics (ACEMP), Brasov, Romania, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/optim.2017.7974943.
Sano, M. B., C. B. Arena, K. R. Bittleman, M. R. Dewitt, H. J. Cho, C. S. Szot, D. Saur, J. M. Cissell, J. Robertson, Y. W. Lee, and R. V. Davalos. Bursts of bipolar microsecond pulses inhibit tumor growth. Sci. Rep. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14999.
Sano, M. B., C. C. Fesmire, M. R. Dewitt, and L. Xing. Burst and continuous high frequency irreversible electroporation protocols evaluated in a 3D tumor model. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/aacb62.
Spugnini, E. P., G. Arancia, A. Porrello, M. Colone, G. Formisano, A. Stringaro, G. Citro, and A. Molinari. Ultrastructural modifications of cell membranes induced by “electroporation” on melanoma xenografts. Microsc. Res. Tech. 70:1041–1050, 2007.
Stankevič, V., V. Novickij, S. Balevičius, N. Žurauskiene, A. Baškys, A. Dervinis, and V. Bleizgys. Electroporation system generating wide range square-wave pulses for biological applications. In 2013 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/biocas.2013.6679633.
Thomson, K. R., W. Cheung, S. J. Ellis, D. Federman, H. Kavnoudias, D. Loader-Oliver, S. Roberts, P. Evans, C. Ball, and A. Haydon. Investigation of the safety of irreversible electroporation in humans. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 22:611–621, 2011.
Toepfl, S., V. Heinz, and D. Knorr. High intensity pulsed electric fields applied for food preservation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2006.07.011.
Turner, K. H., J. Everett, U. Trivedi, K. P. Rumbaugh, and M. Whiteley. Requirements for Pseudomonas aeruginosa acute burn and chronic surgical wound infection. PLoS Genet. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004518.
Van Mellaert, L., M. Shahrooei, D. Hofmans, and J. Van Eldere. Immunoprophylaxis and immunotherapy of Staphylococcus epidermidis infections: challenges and prospects. Expert Rev. Vaccines 11(3):319–334, 2012.
Vernhes, M. C., P. A. Cabanes, and J. Teissie. Chinese hamster ovary cells sensitivity to localized electrical stresses. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1999. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0302-4598(98)00239-6.
Vernier, P. T., Y. Sun, M. J. Ziegler, and M. A. Gundersen. Nanoelectropulse-driven membrane perturbation and permeabilization. BMC Cell Biol. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1109/bmn.2006.330927.
Weaver, J. C., and Y. A. Chizmadzhev. Theory of electroporation: a review. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 41:135–160, 1996.
Wimmer, T., G. Srimathveeravalli, M. Silk, S. Monette, N. Gutta, M. Maybody, J. P. Erinjery, J. A. Coleman, S. B. Solomon, and C. T. Sofocleous. Feasibility of a modified biopsy needle for irreversible electroporation ablation and periprocedural tissue sampling. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533034615608739.
Wouters, P. C., N. Dutreux, J. P. Smelt, and H. L. Lelieveld. Effects of pulsed electric fields on inactivation kinetics of Listeria innocua. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65:5364–5371, 1999.
Yao, F., and E. Eriksson. Gene therapy in wound repair and regeneration. Wound Repair Regen. 8:443–451, 2000.
Yarmush, M. L., A. Golberg, G. Serša, T. Kotnik, and D. Miklavčič. Electroporation-based technologies for medicine: principles, applications, and challenges. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 16:295–320, 2014.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Bio-National USA-Israel Science Foundation (BSF) for the support of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Dan Elson oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubin, A.E., Levkov, K., Usta, O.B. et al. IGBT-Based Pulsed Electric Fields Generator for Disinfection: Design and In Vitro Studies on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ann Biomed Eng 47, 1314–1325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-019-02225-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-019-02225-0